Abstracts of the 2023 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoNo
Introduction and ObjectivesAlcoholic hepatitis (AH) is acute liver inflammation associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Due to its high mortality rate, various predictive models have been studied. The ALBI model (serum albumin/bilirubin index) predicts patient mortality without the need for subjective data in patients with chronic liver disease, achieving significantly better performance than Child Pugh and MELD models.
Evaluate the prognostic utility of the ALBI model for determining the response to steroid treatment in patients diagnosed with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Patients / Materials and MethodsRetrospective cohort study from October 2019 to September 2023. We evaluated severity criteria, demographic characteristics, and endoscopic features. Maddrey, MELD, MELDNa, ABIC, Glasgow, and ALBI models were compared at the time of admission, and the Lille score was calculated 7 days after steroid treatment. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 26 software, with a p-value of <0.005 considered statistically significant.
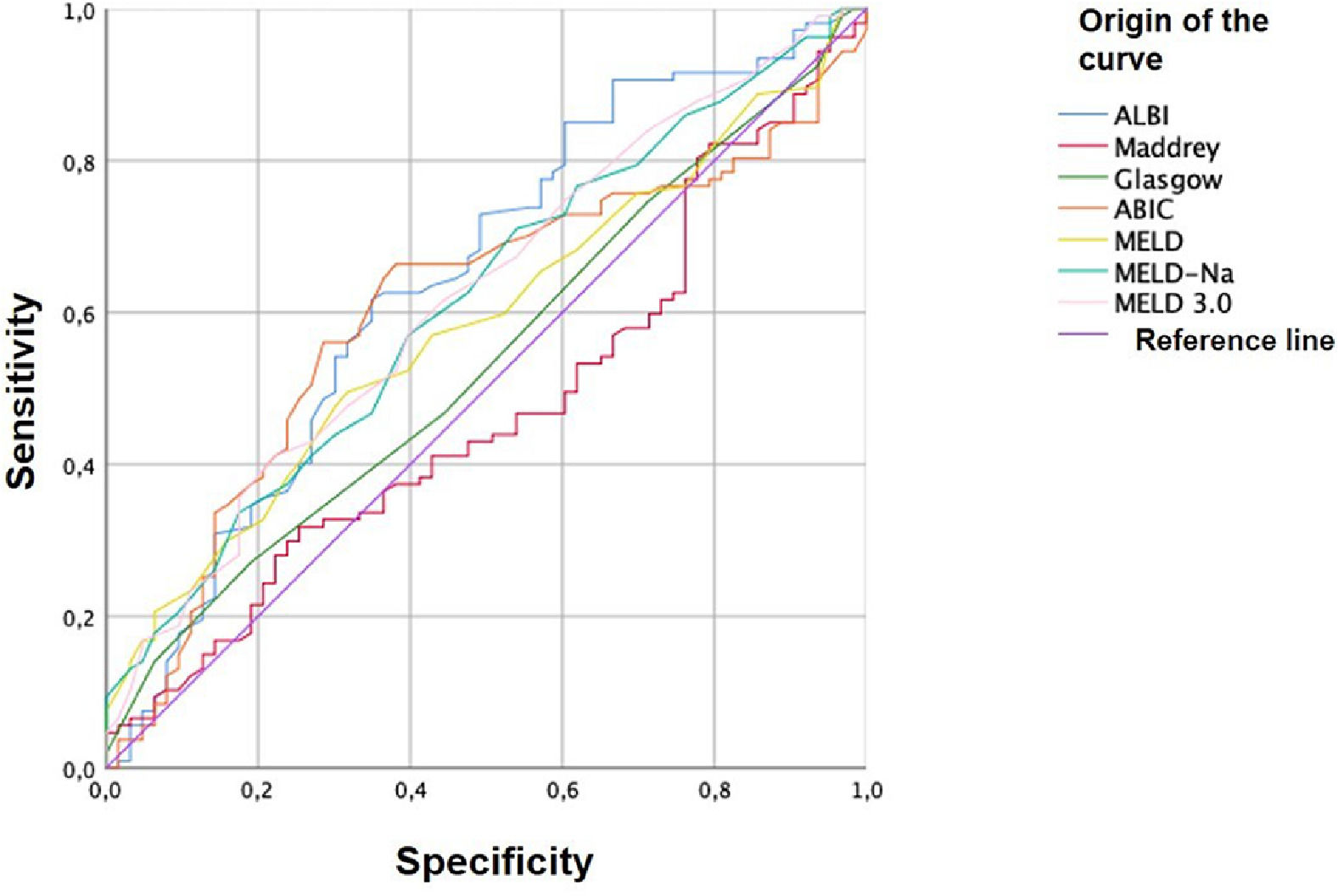
Results and DiscussionWe included 170 patients, 21 women (12.4%) and 149 men(87.6%), average age of 45 ± 13.5 years. Of these, 30.6% were classified as Child-Pugh B and 69.4% as Child-Pugh C. Concomitant infection was documented in 15.3%, with urinary tract infections being the most prevalent, and the most frequent endoscopic finding was portal hypertensive gastropathy in 98% of patients, of which 65.5% were mild and 34.4% were severe. The 90-day follow-up mortality rate was reported at 34.7%. Comparing the different scales, we found good diagnostic accuracy for ALBI(AUC:0.64[95%CI:0.57–0.73];p=0.002),MELD 3.0(AUC:0.62[95%CI:0.53–0.70];p=0.009),MELDNa(AUC:0.61[95%CI:0.52–0.69];p=0.01),and ABIC(AUC:0.60[95%CI:0.51–0.69];p=0.02).
ConclusionsThe ALBI model, due to its objective and straightforward nature, is increasingly employed in the evaluation of hepatic dysfunction. It provided prognostic assessment comparable to MELD, MELDNa, and MELD3.0 for predicting the response to steroid treatment in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.