The first symptoms of myasthenia gravis (MG) usually involve weakness of the ocular muscles, making it relevant that ophthalmologists have updated information on studies as regards its relationship with the consumption of drugs, such as statins.
Materials and methodsA bibliometric analysis was performed using the Scopus database and by a search strategy in the selection of documents containing descriptors related to statins in the «Title» («TI») field and the descriptors «ophthalm *’, «myast *’, «visual *’ in other fields of the document (period 1986–2015).
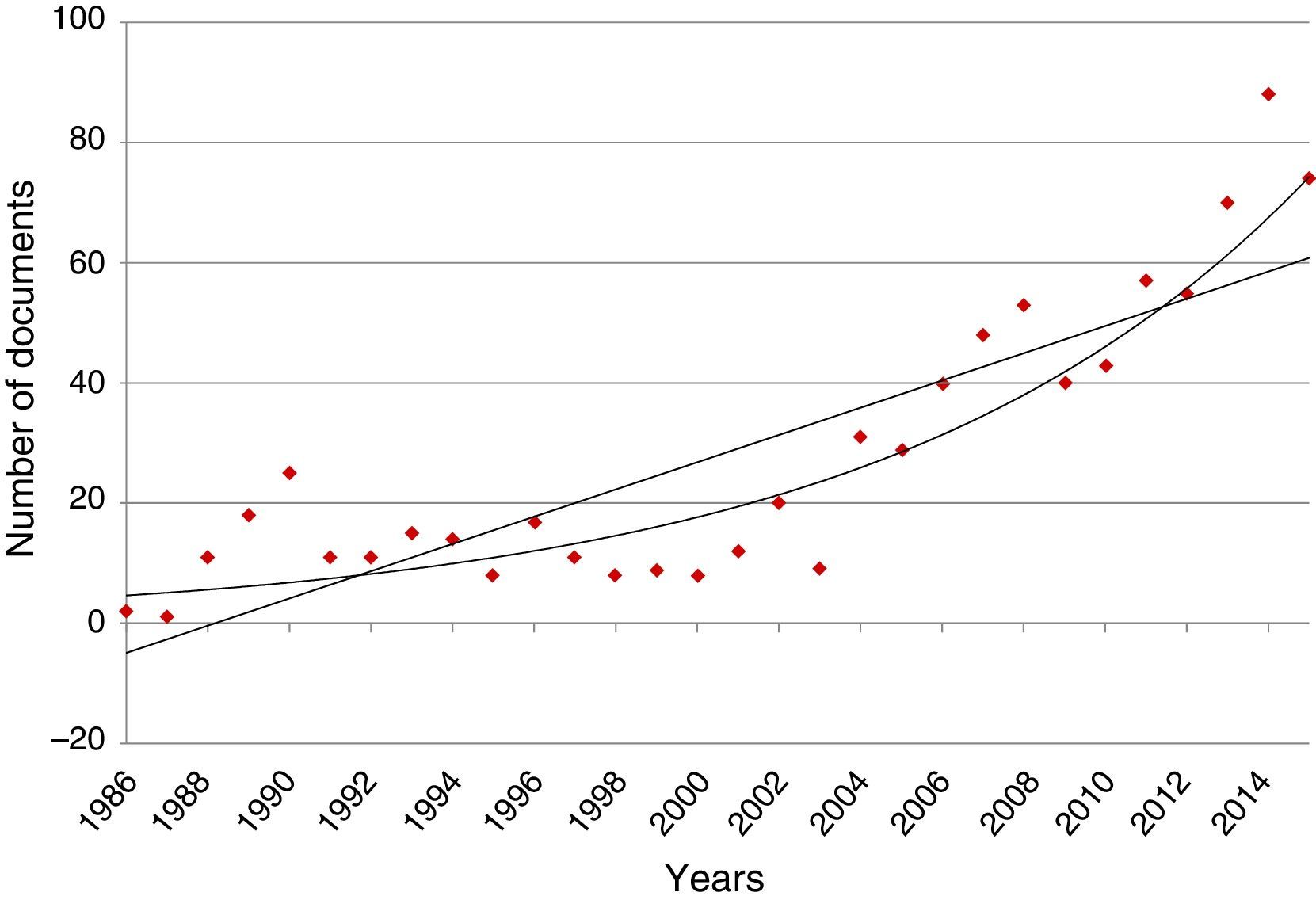
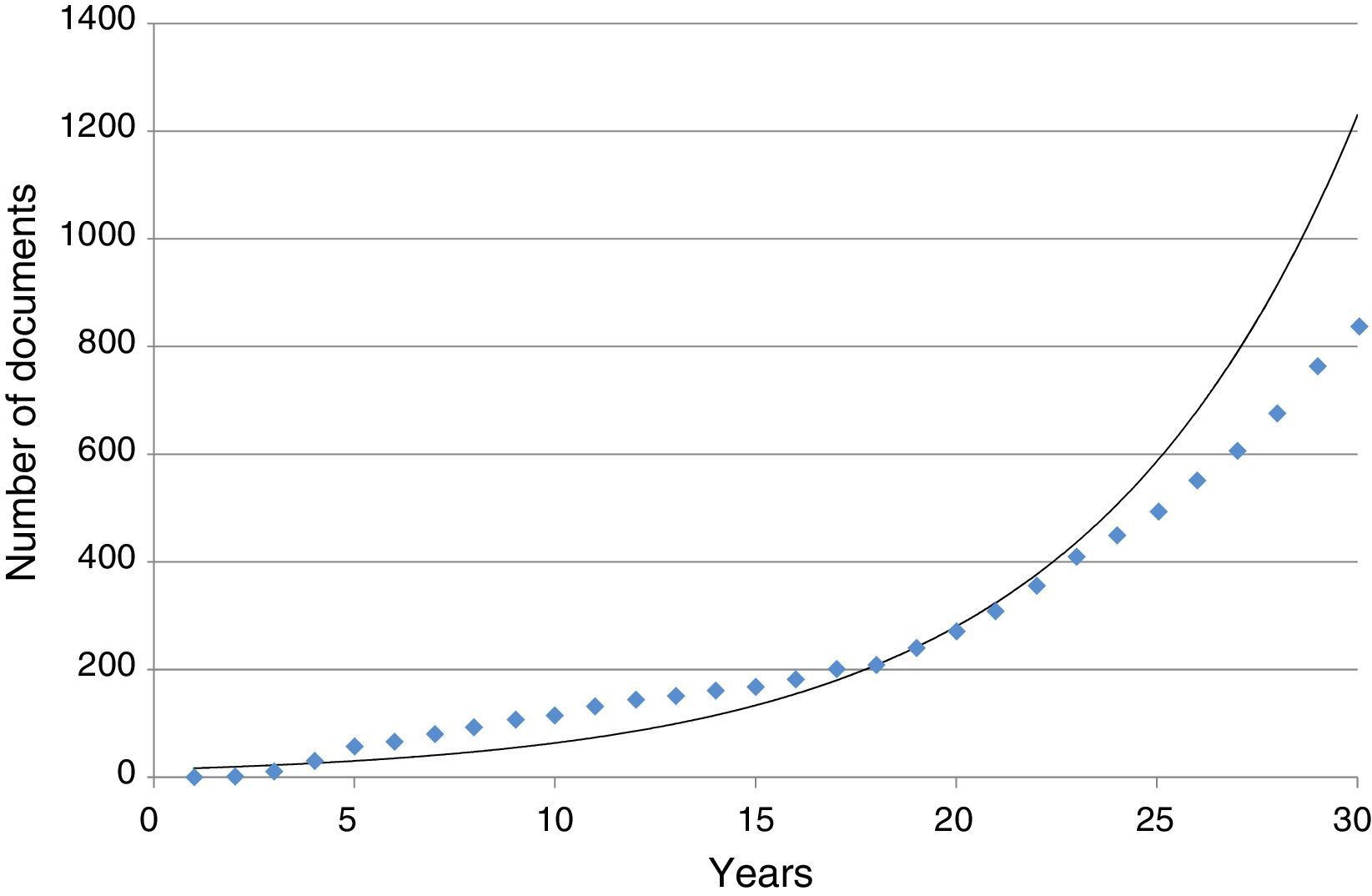
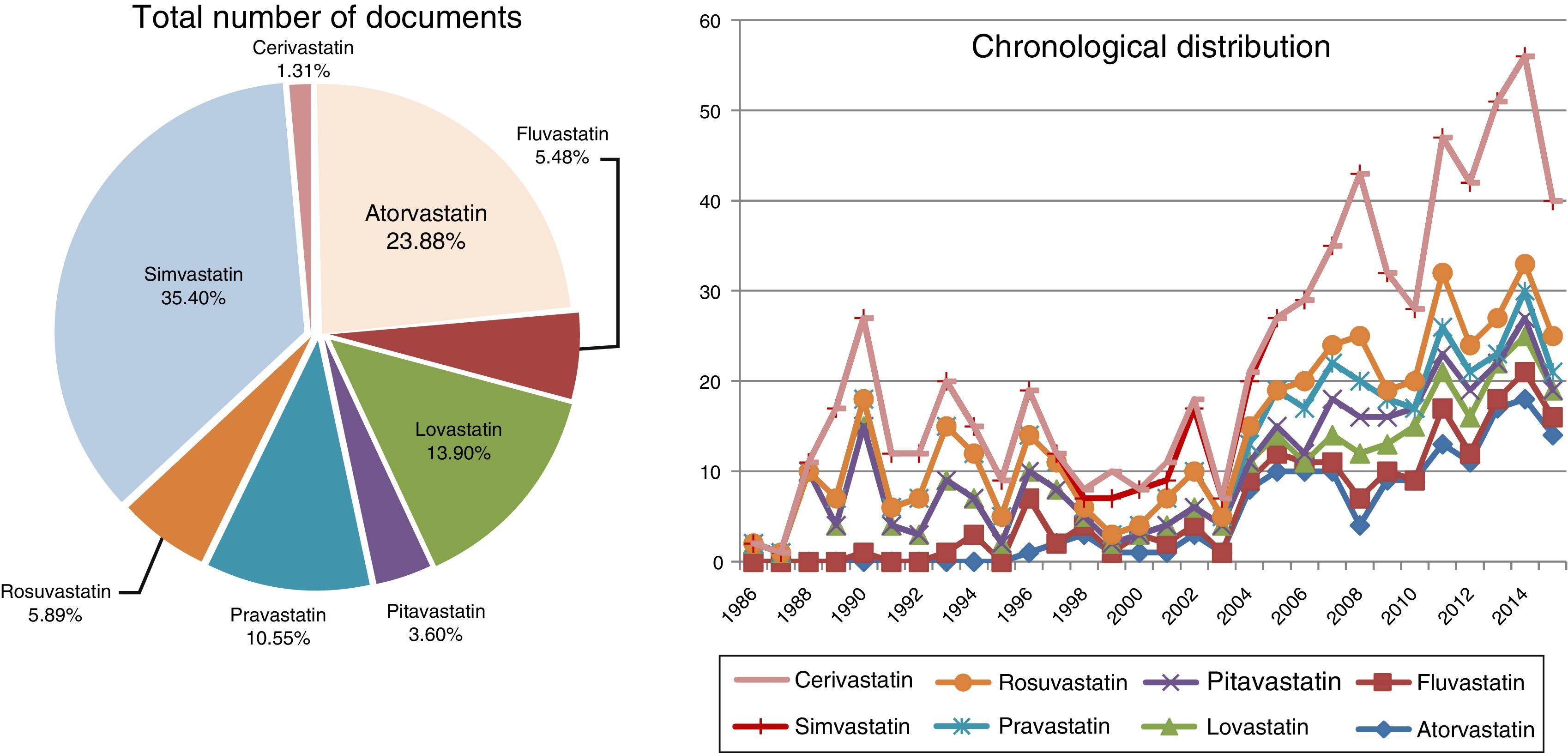
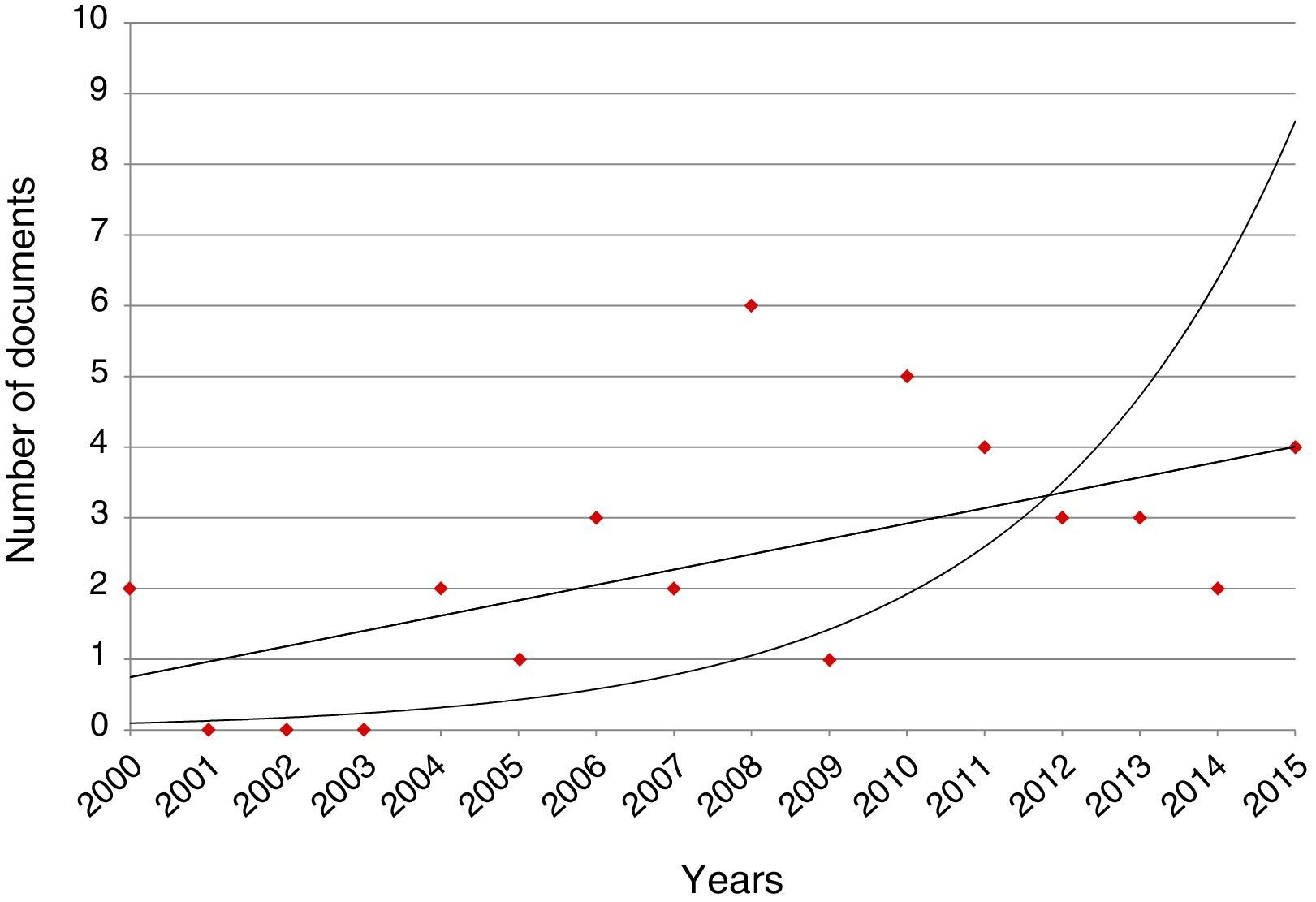
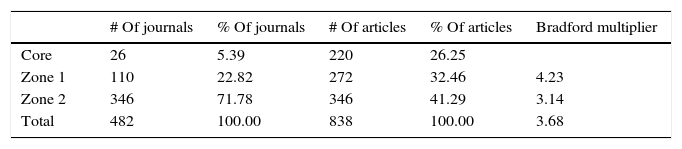
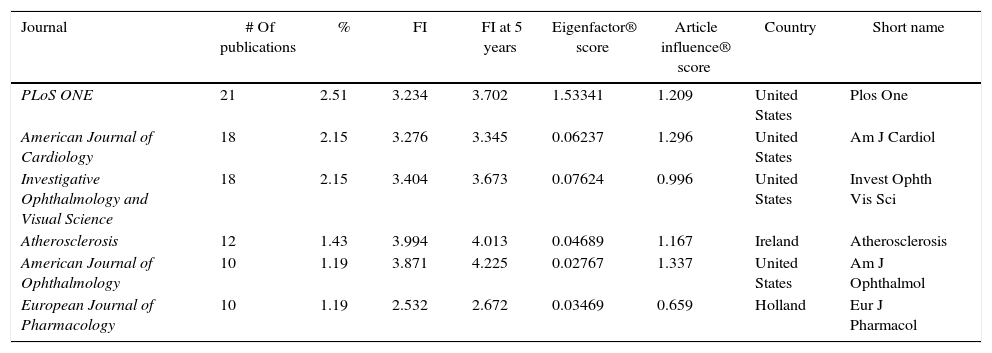
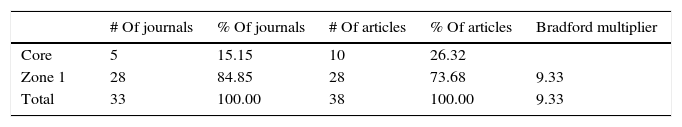
ResultsThe results showed that, while the number of scientific publications on ocular effects of statins has grown lineally (n=838; y=2.267x−4507.1; r=0.7221; time of duplication: 4.66 years, and rate of annual growth: 50.06%), the specific publications about MG have experienced an exponential growth (n=38; y=2E−262e0.3001x; r=0.3892; time of duplication: 2.95 years, and rate of annual growth: 46.25%) without reaching the saturation postulated in Price theory of the expansion of the scientific literature. The majority of publications relating to MG are reports of cases linked to a worsening of the MG symptoms, and simvastatin and atorvastatin are the agents mentioned in most of the publications.
ConclusionsThese results should enable ophthalmologists to expand their knowledge concerning the evolution of studies on statins and MG, pointing out the relevance of such causal relationships.
Los pacientes con miastenia gravis (MG) suelen empezar con afectación de la musculatura ocular. Es relevante que el oftalmólogo disponga de información actualizada del estado de la investigación respecto a la relación de esta enfermedad con el consumo de fármacos, como las estatinas.
Material y métodosSe realizó un análisis bibliométrico, utilizando la base de datos Scopus y aplicando una estrategia de búsqueda consistente en la selección de documentos que contuvieran los descriptores referidos a estatinas en el campo «Título» («TI») y los descriptores «ophthalm*», «myast*», «visual*» en cualquier otro campo del documento (de 1986 a 2015).
ResultadosLos resultados confirman que, mientras el número de publicaciones científicas sobre efectos oftalmológicos de las estatinas ha crecido linealmente (n=838; y=2,267x-4507,1; r=0,7221; tiempo de duplicación: 4,66 años y tasa de crecimiento anual: 50,06%), las publicaciones específicas sobre MG han experimentado un crecimiento exponencial (n=38; y=2E-262e0,3001x; r=0,3892; tiempo de duplicación: 2,95 años y tasa de crecimiento anual: 46,25%), sin que se haya alcanzado la saturación postulada en la teoría de Price de la expansión de la literatura científica. La mayor parte de las publicaciones relativas a la MG son reportes de casos vinculados a un empeoramiento de la sintomatología de la MG, y los agentes que más publicaciones aportan son simvastatina y atorvastatina.
ConclusionesEstos resultados permitirán al oftalmólogo ampliar su conocimiento respecto a la evolución de la investigación sobre estatinas y MG y reflejan un interés creciente por la relación entre el consumo de ambas, señal de la relevancia de dicha relación causal.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora