To compare intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements obtained using the Icare 200™ (IC200) rebound tonometer and the hand-held version of the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer (Perkins™ tonometer, GAT) in patients with primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) and in healthy subjects.
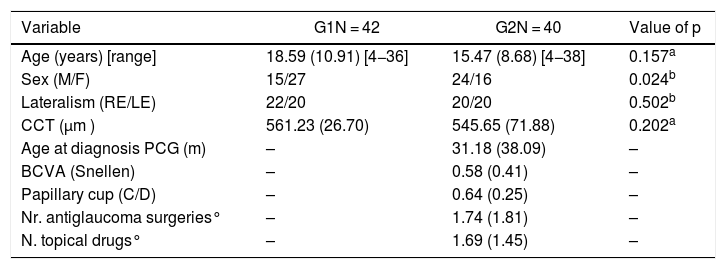
Material and methodsA total of 42 eyes of healthy subjects (G1) and 40 patients with PCG (G2) were analysed. The following clinical data were collected: gender, age, Cup/Disc ratio, central corneal thickness (CCT). IOP was determined in the examination room using the IC200 and GAT tonometers, in the same order.
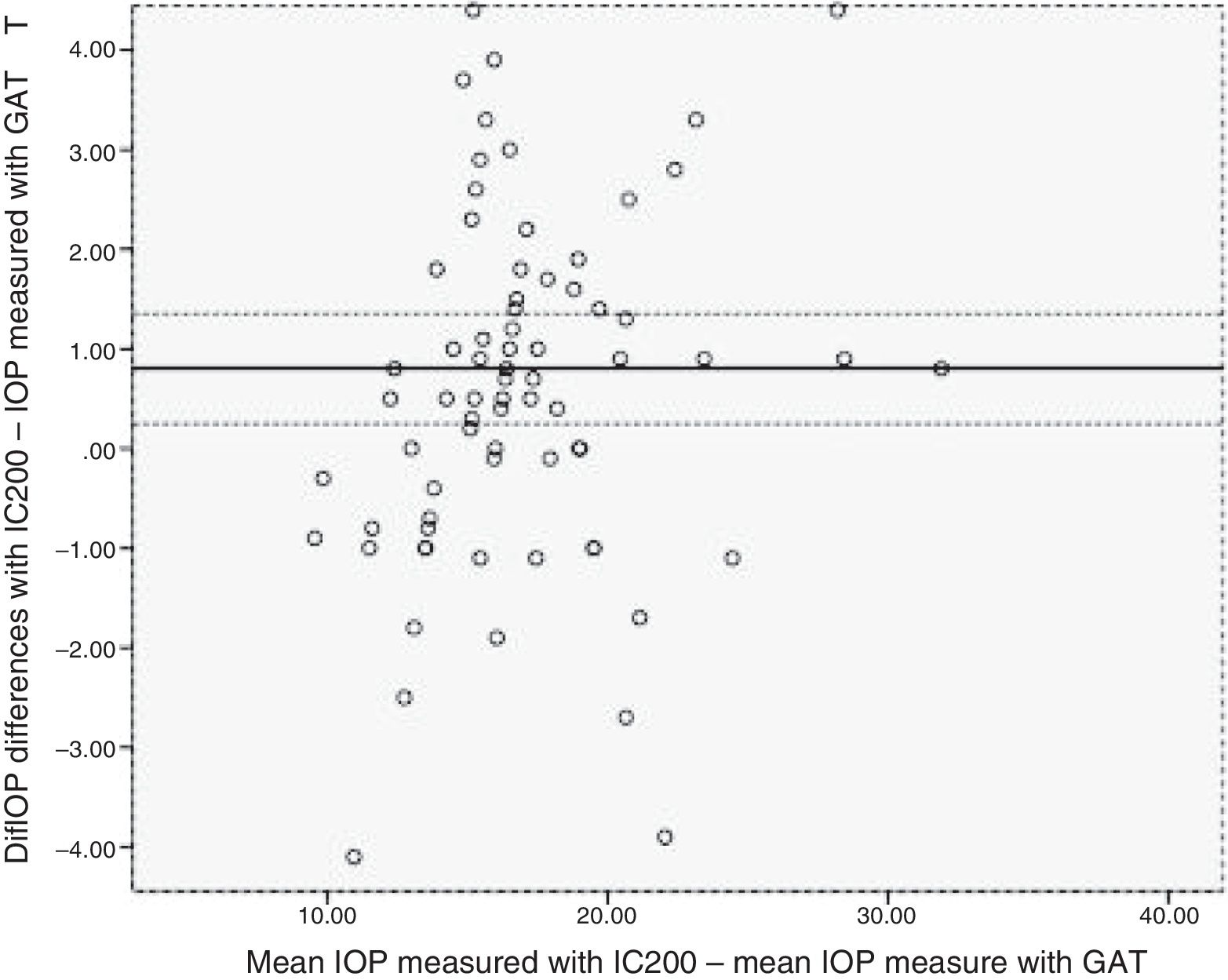
Agreement between both tonometers was determined using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman plot. A linear regression analysis was used to establish the IOP was affected by the studied variables.
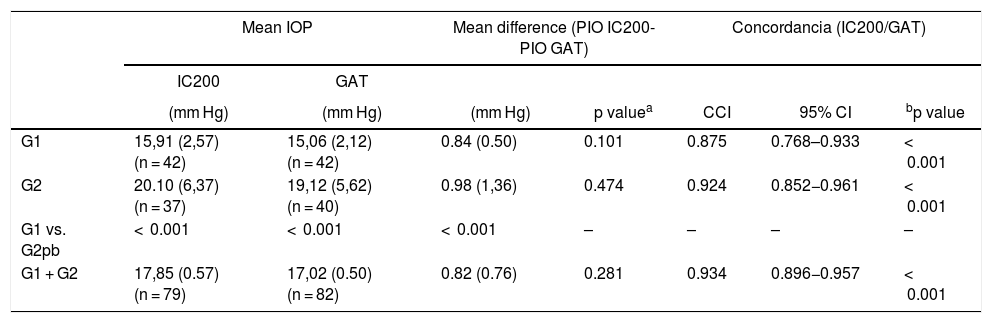
ResultsMean IOP between both tonometers (IC200 minus GAT) was: G1 = 15.91 (2.57) mmHg vs. 15.06 (2.12) mmHg (mean difference, MD = 0.84 (0.50) mmHg; P < .101) and G2=20.10 (6.37) vs.19.12 (5.62) (MD = 0.98 (1.36); P = 0.474).
Excellent agreement was found between IC200 and GAT in both groups (ICC = G1: 0.875 (95% CI; 0.768−0.933; P < .001); G2: 0.924 (95% CI; 0.852−0.961; P < .001), and there was a statistically significant correlation between the IOP difference measured with IC200 and GAT and CCT in G1 (B=0.021; 95% CI; 0.005–0.037; P = .008), but was not statistically significant in G2.
ConclusionsThere was excellent agreement between the IC200 and GAT tonometers, both in healthy subjects and PCG, with a trend to overestimate IOP when measured with IC200. There was no influence by CCT on IOP measurements in patients with PGC.
Comparar las medidas de presión intraocular (PIO) obtenidas con el tonómetro de rebote (TR) iCare 200 (IC200) con las obtenidas mediante la versión portátil del tonómetro de aplanación Goldmann, Perkins (GAT) en pacientes con Glaucoma Congénito Primario (GCP) y en sujetos sanos.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 42 sujetos sanos (G1) y 40 pacientes con GCP (G2). Se incluyó un ojo por paciente. Se recogieron las variables clínicas de interés: sexo, edad, grosor corneal central (GCC) y se midió la PIO mediante los tonómetros IC200 y GAT en el mismo orden, en consulta.
Se estudió la concordancia entre tonómetros mediante el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI) y el gráfico de Bland Altman. La influencia de las variables se analizó mediante test de regresión lineal.
ResultadosLas medias de PIO obtenidas mediante IC200 y GAT fueron: G1 = 15,91(2,57) vs 15,06(2,12) mmHg (diferencia de medias, DM = 0,84(0,50) mmHg; p = 0,101) y en el G2 = 20,10(6,37) vs.19,12(5,62) (DM = 0,98(1,36); p = 0,474).
Se observó excelente concordancia entre IC200/GAT en ambos los grupos (CCI = G1: 0,875 (IC95% 0,768-0,933; p < 0,001); G2: 0,924 (IC95% 0,852-0,961; p < 0,001), así como la influencia del GCC en la diferencia entre tonómetros en G1 (B = 0,021; IC95% 0,005–0,037; p = 0,008); sin significación estadística en G2.
ConclusiónSe ha encontrado una excelente concordancia entre ambos tonómetros, IC200 y GAT tanto en sujetos sanos como en pacientes con GCP, con una tendencia a sobreestimación de la PIO de IC200 sobre Perkins. No se ha demostrado la influencia del GCC en los pacientes con GCP.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora