To study the results and safety of diagnostic vitrectomy in patients with unknown etiology panuveitis.
MethodsA retrospective descriptive observational study was carried out in which a total of 29 patients (37 eyes) were included, who underwent a vitreous biopsy due to acute intraocular inflammatory processes. In all, demographic and clinical data were collected. We studied the specific samples extraction methods and their diagnosic processing.
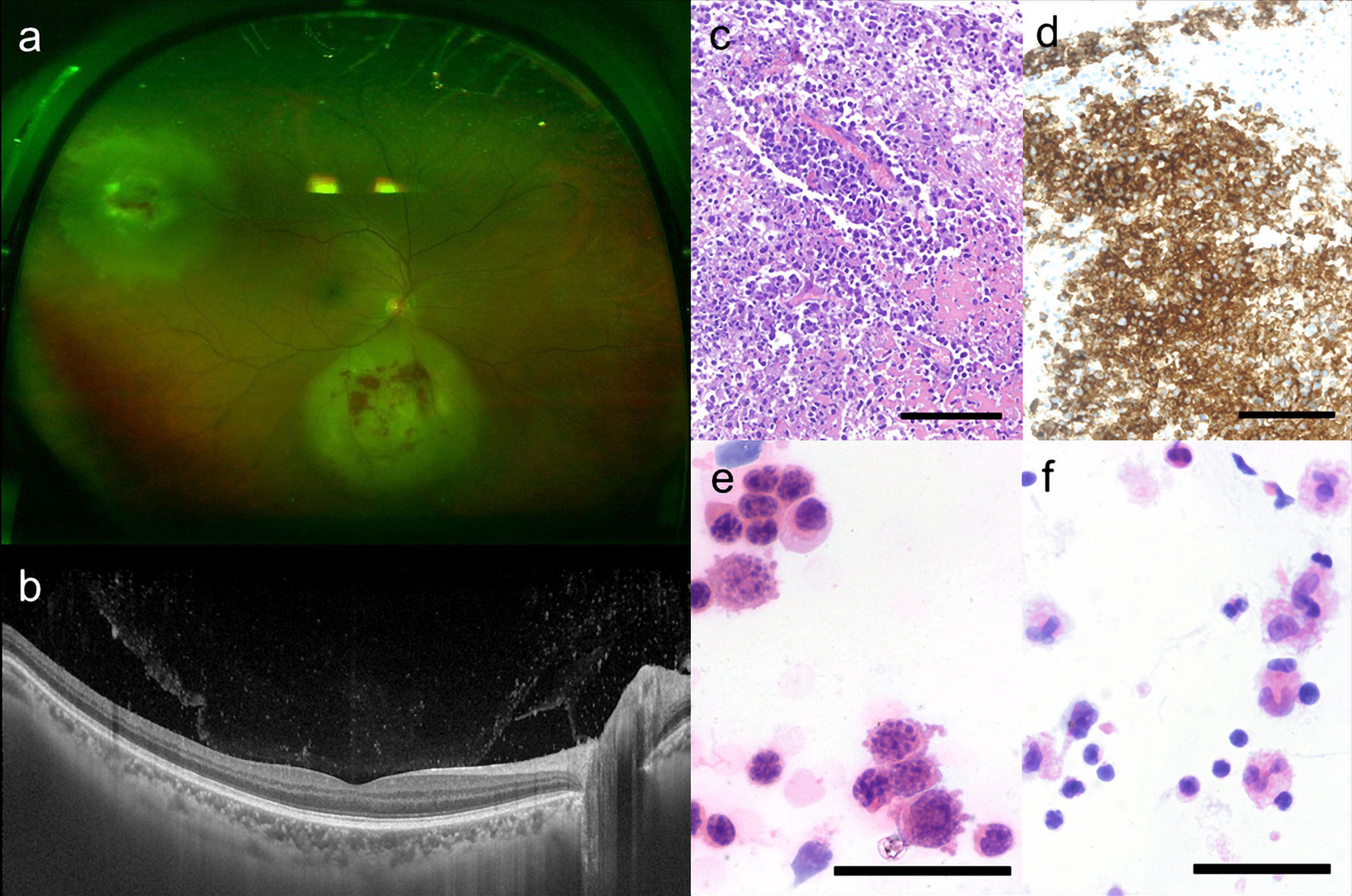
ResultsOf the 29 patients analyzed, 18 were men. Mean of age was 63.11 years old (Standard Deviation: 14.55). The most frequent initial symptom was visual acuity decrease, with mean initial visual acuity being 20/40, excluding 8 eyes that had vision lower than 20/200. 21 presented unilateral ocular involvement. Vitrectomy was performed in all of them obtaining a dry sample.
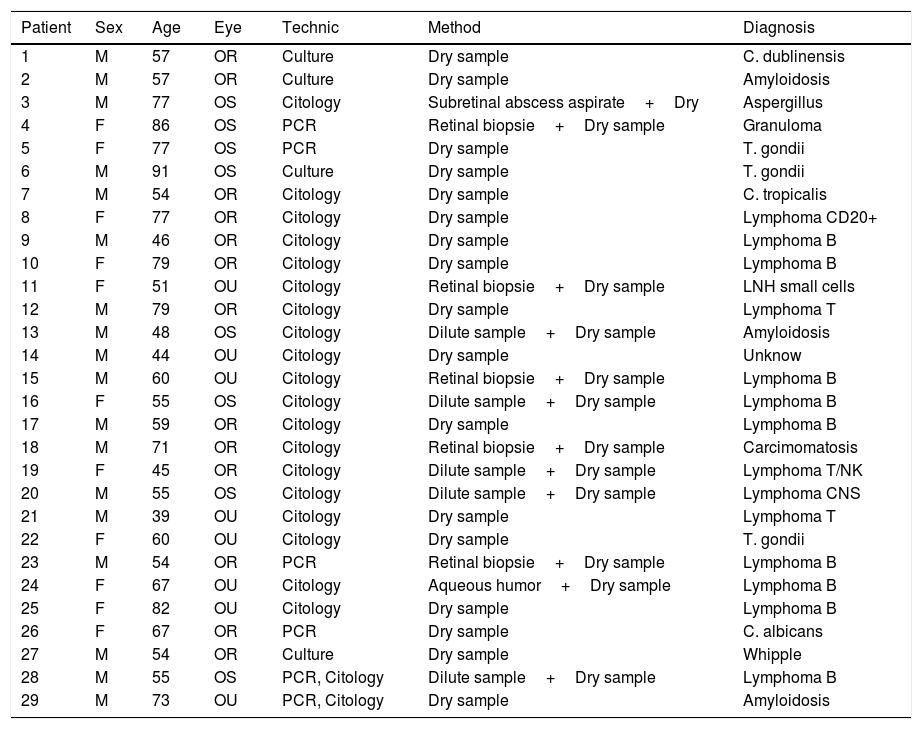
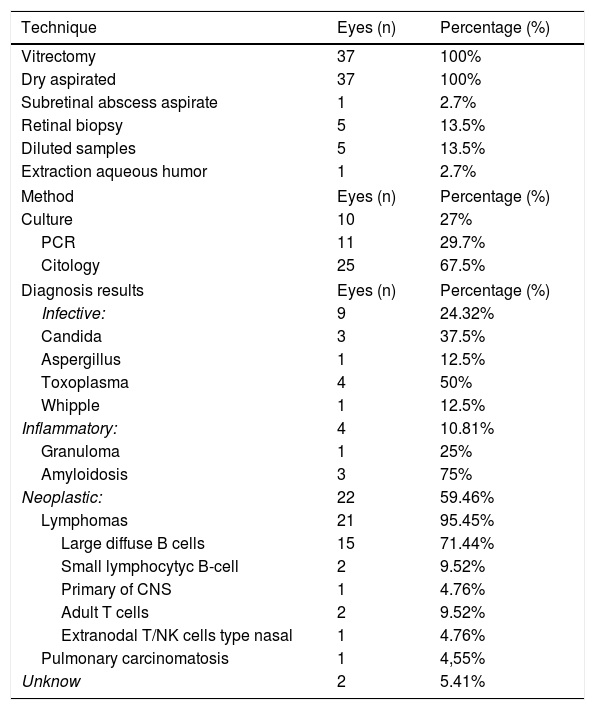
Vitrectomy was performed in all of the patients obtaining a dry sample. Moreover, the following techniques were done: 5 retinal biopsies, obtaining 5 Muestra diluidas, 1 subretinal abscess aspirate and 1 aqueous humor aspirate.
The most frequent processing technique that was used was cytology in 25 eyes, followed by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) in 11 eyes and culture in 10 eyes.
Diagnosis was achieved in 94.5% of patients. Main diagnosis found was lymphoma, followed by toxoplasmosis.
ConclusionsDiagnostic vitrectomy is very important in ophthalmic inflammation identification. Different techniques for obtaining and processing can be used.
Estudiar la eficacia y perfil de seguridad de la vitretomía diagnóstica en pacientes con uveítis no filiada.
MétodosEstudio observacional descriptivo retrospectivo de 29 pacientes (37 ojos) con panuveítis no filiada en los que se realizó vitrectomía diagnóstica. Las características clínicas y demográficas fueron recogidas. Se estudiaron los métodos de extracción de muestras y las técnicas de procesado aplicadas para el diagnóstico.
ResultadosDe los 29 pacientes analizados 18 (62%) eran hombres. La media de edad fue de 63,11 años (Desviación Standard: 14,55). El síntoma inicial más frecuente fue la disminuación de agudeza visual, la agudeza visual media fue de 20/40 excluyendo 8 ojos en los que resultó inferior a 20/200. Veintiún pacientes presentaban alteración unilateral. Se realizó extracción de muestra en seco a todos los pacientes. Además, las siguientes técnicas de toma de muestras fueron empleadas: 5 biopsisas retinianas, 5 muestras diluidas, 1 aspirado de abceso subretiniano, 1 aspirado de humor acuoso. Con respecto al procesado de las muestras la técnica más utilizada fue la citología en 25 ojos, seguida de la PCR (reacción en cadena de la polimerasa) en 11 ojos, el cultivo en 10 ojos. El diagnóstico etiológico fue encontrado en 94.5% de los casos, siendo el principal linfoma, seguido de toxoplasmosis.
ConclusiónLa vitrectomía diagnóstica es útil para la identificación de la inflamación oftalmológica. Pueden utilizarse diferentes técnicas de obtención de muestras y procesado de las mismas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora