To determine the effect of posterior capsulotomy on macular thickness, intraocular pressure and endothelial cell loss in pseudophakic patients with posterior capsule opacification using the other eye of every patient as a control.
MethodsAn observational prospective study was conducted on 31 pseudophakic patients with posterior capsular opacification in one eye, using the other eye as a control. Patients did not suffer any other ocular pathology. All patients were treated by posterior capsular opacification with Nd:YAG capsulotomy, and followed up for a three-month period. The ocular examination included best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), intraocular pressure (IOP), macular optical coherence tomography (OCT), and endothelial cell assessment (including densitometry, cell size and coefficient of variation, hexagonal cell percentage and pachymetry), which were determined in both eyes before treatment, and one week, one month and 3 months after capsulotomy.
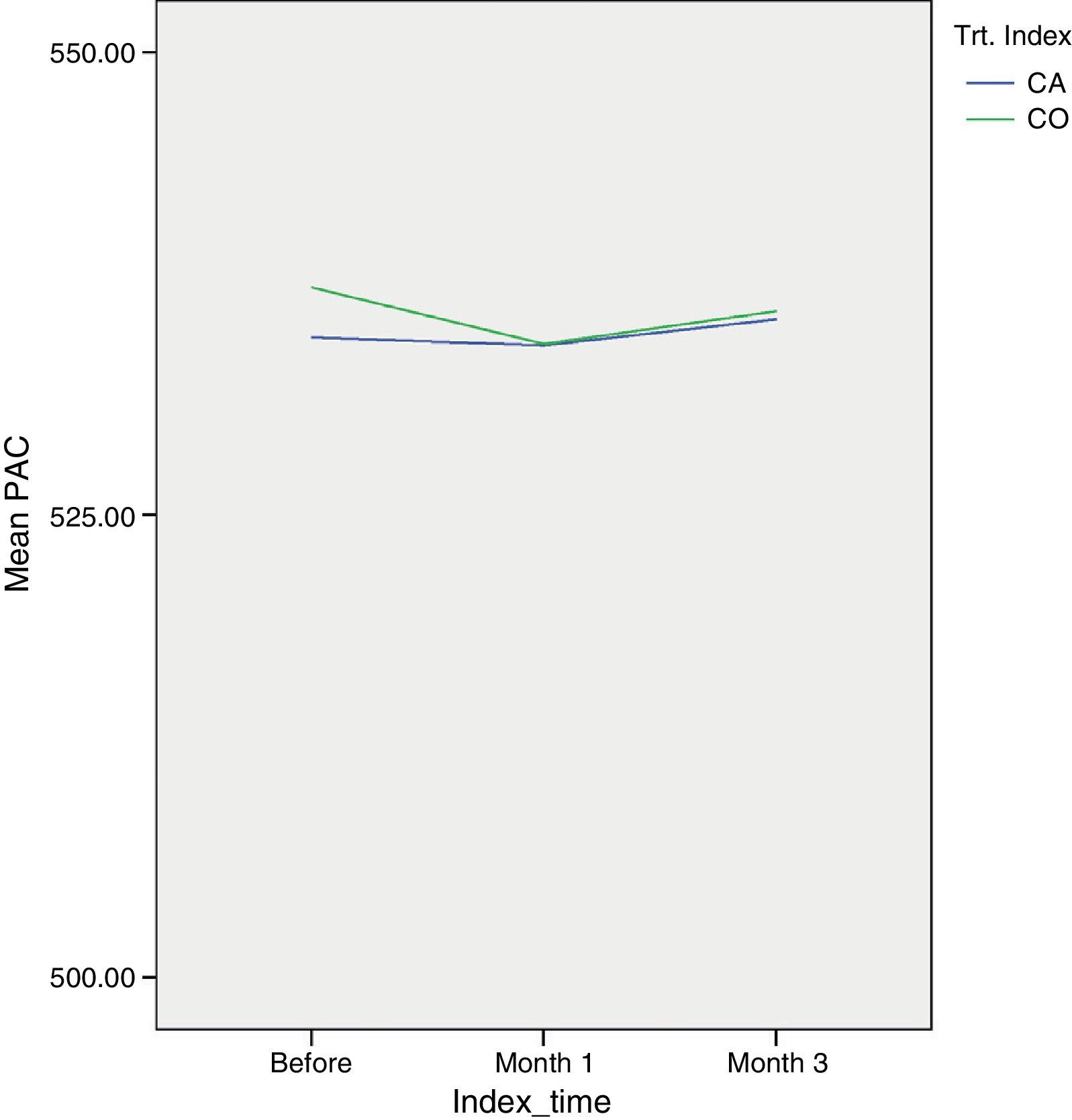
ResultsGeneralized estimating equations (GEE) were used to assess the capsulotomy effect adjusted by corresponding baseline measurements and time. No association was found between capsulotomy and IOP (p=0.597), macular thickness (p=0.085) or ECA densitometry (p=0.422), average size of cells (p=0.299), variation coefficient (p=0.495), hexagonal cell percent (p=0.093) and corneal pachymetry (p=0.423). A significant increase of 0.15 Snellen units in BCVA was found during the 3-month follow-up period (p<0.001).
ConclusionThis study shows that after Nd:YAG capsulotomy, BCVA improves significantly without any IOP, OCT or ECA changes during the three-month follow-up. Nd:YAG capsulotomy is a safe procedure in pseudophakic patients without any other ocular pathology.
Determinar el efecto de la capsulotomía posterior en el grosor macular, presión intraocular (PIO) y pérdida de células endoteliales en pacientes pseudofáquicos que presentaban opacidad de la cápsula posterior, utilizando el ojo adelfo de cada paciente como control.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo observacional en 31 pacientes pseudofáquicos con opacidad de la cápsula posterior en un ojo, utilizando el ojo adelfo como control durante un periodo de 3 meses. Se excluyó a los pacientes que presentaban otras enfermedades oculares o cirugías intraoculares aparte de la facoexéresis. A todos los pacientes se les realizó una capsulotomía posterior con láser Nd:YAG. El examen ocular, que se realizó previamente a la capsulotomía y en revisiones a la semana, al mes y a los 3 meses, incluía: agudeza visual mejor corregida (AVMC), PIO, tomografía de coherencia óptica macular (OCT) y recuento endotelial.
ResultadosSe utilizaron ecuaciones de estimación generalizadas para valorar el efecto de la capsulotomía ajustado en función de situación basal y tiempo de seguimiento. No se encontró asociación significativa entre la capsulotomía y la PIO (p=0,597), el grosor macular (p=0,085) o el recuento endotelial densitometría (p=0,422), tamaño celular medio (p=0,299), coeficiente de variación (p=0,495), porcentaje de células hexagonales (0,093) y paquimetría (p=0,423). Un incremento significativo de la AVMC se observó en la revisión a los 3 meses (p<0,001).
ConclusionesEste estudio indica que, tras la capsulotomía posterior, la AVMC mejora significativamente, sin observarse cambios significativos en PIO, grosor macular o recuento endotelial. La capsulotomía con Nd:YAG es un procedimiento seguro en pacientes que no presenten enfermedades oculares asociadas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora