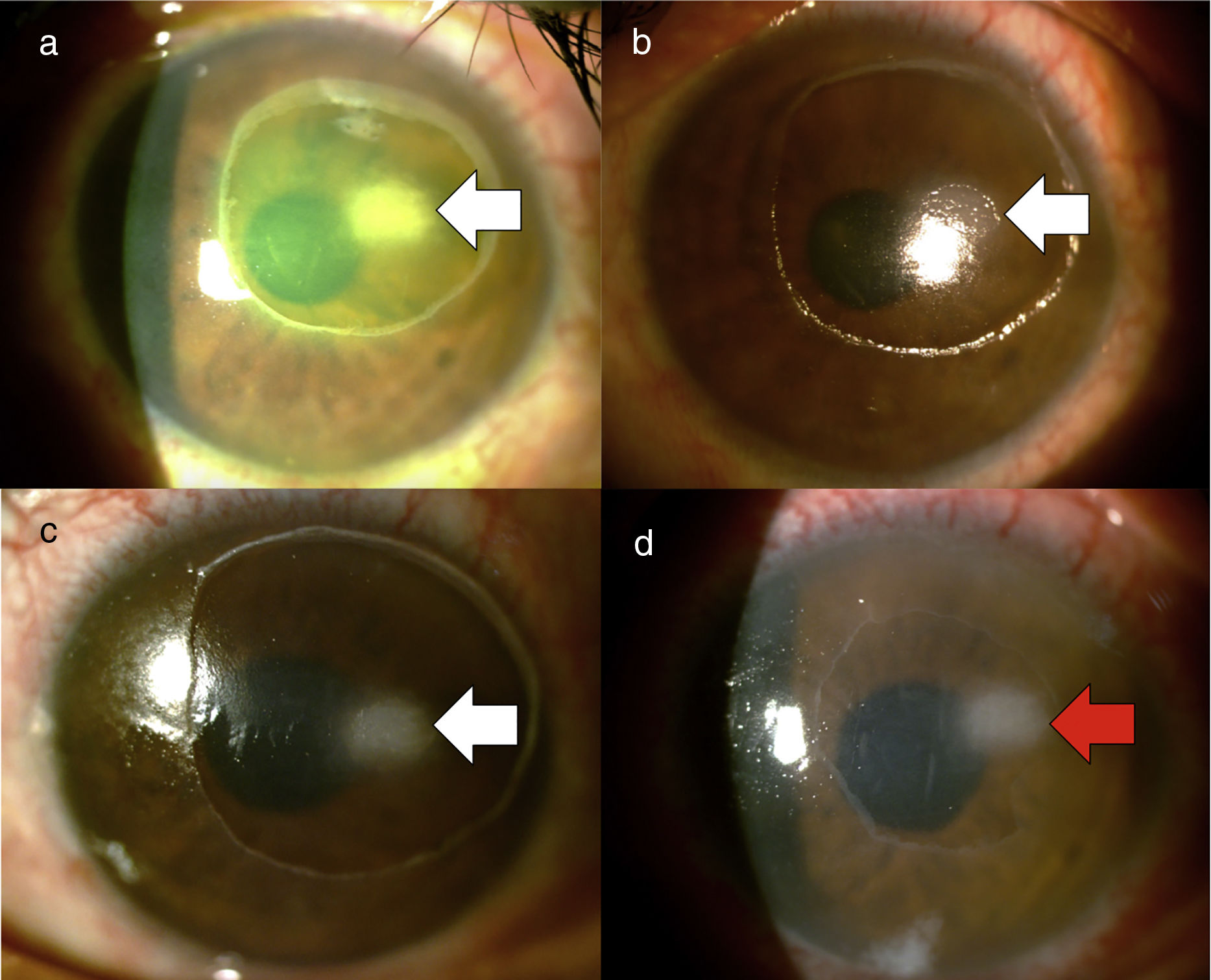
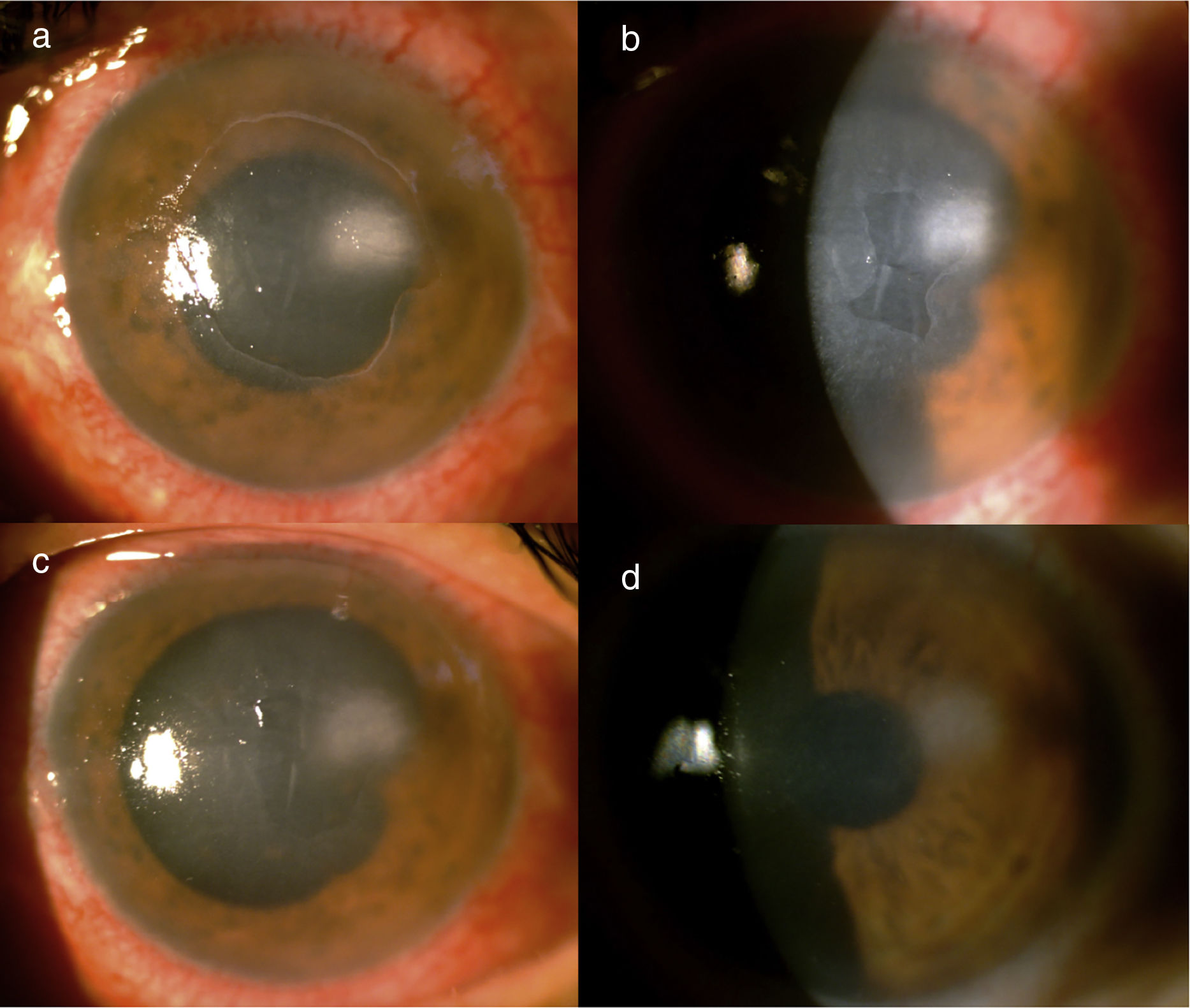
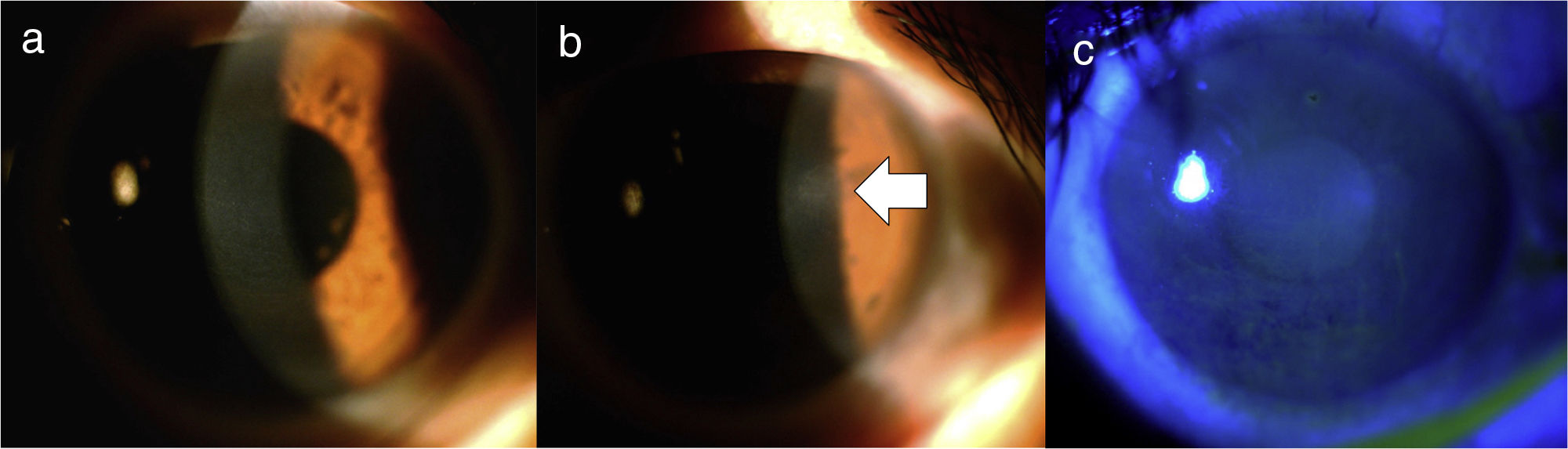
A patient with a history of surgical resection of an acoustic neuroma presented with involvement of both the left facial nerve and the left trigeminal nerve. She initially consulted for exposure keratitis, but two weeks later presented with an infectious keratitis. After taking the corneal sample, she presented with persistent epithelial defect, which did not respond to medical management. Topical insulin was indicated, and a decrease in the area of the lesion was seen in the following 5 days. A therapeutic contact lens was also placed at that time and finally, two weeks after the initiation of insulin, the epithelial defect completely closed.
DiscussionThis was a complex case due to the confluence of facial paralysis, neurotrophic keratitis, and infectious keratitis, which finally had a successful outcome. Topical insulin can be an effective adjuvant therapy in cases of neurotrophic ulcers that do not respond to standard therapy.
Una paciente con antecedente de resección quirúrgica de un neurinoma del acústico presentó compromiso tanto del nervio facial como del nervio trigémino izquierdos. Inicialmente consultó por queratitis de exposición, pero 2 semanas después presentó una queratitis infecciosa. Tras la toma de la muestra corneal cursó con un defecto epitelial persistente, que no respondió al manejo médico. Se indicó insulina tópica con lo que se evidenció disminución del área de la lesión en los siguientes 5 días. Se colocó además, en ese momento, una lente de contacto terapéutica y, finalmente, 2 semanas después de haberse iniciado la insulina, el defecto epitelial cerró por completo.
DiscusiónSe trata de un caso complejo por la confluencia de parálisis facial, queratitis neurotrófica y queratitis infecciosa, que finalmente tuvo un resultado exitoso. La insulina tópica puede ser una terapia coadyuvante efectiva en casos de úlceras neurotróficas que no respondan a la terapia convencional.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora