Estimation of the error rate in the subjective determination of the optic nerve head edge and area.
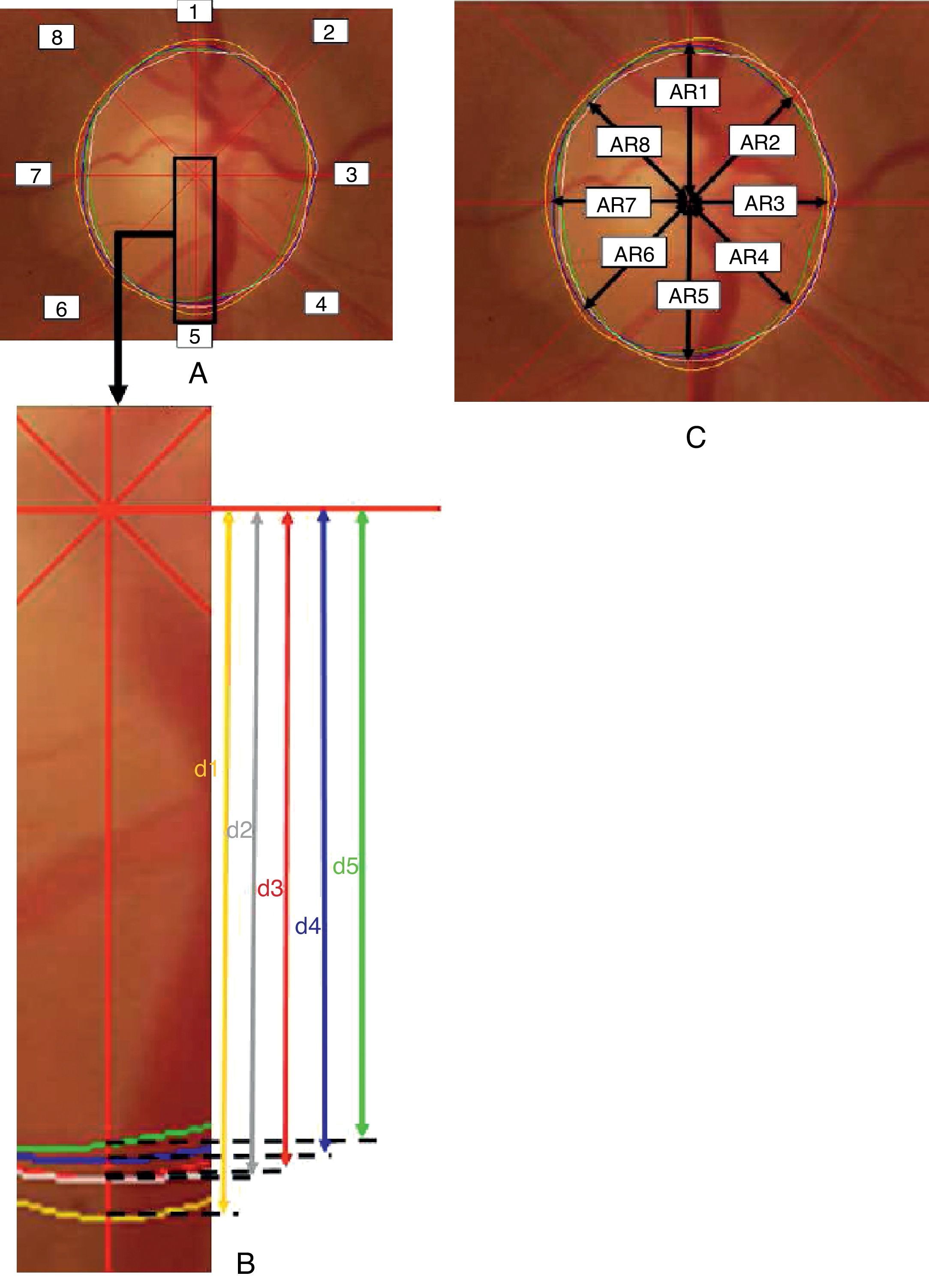
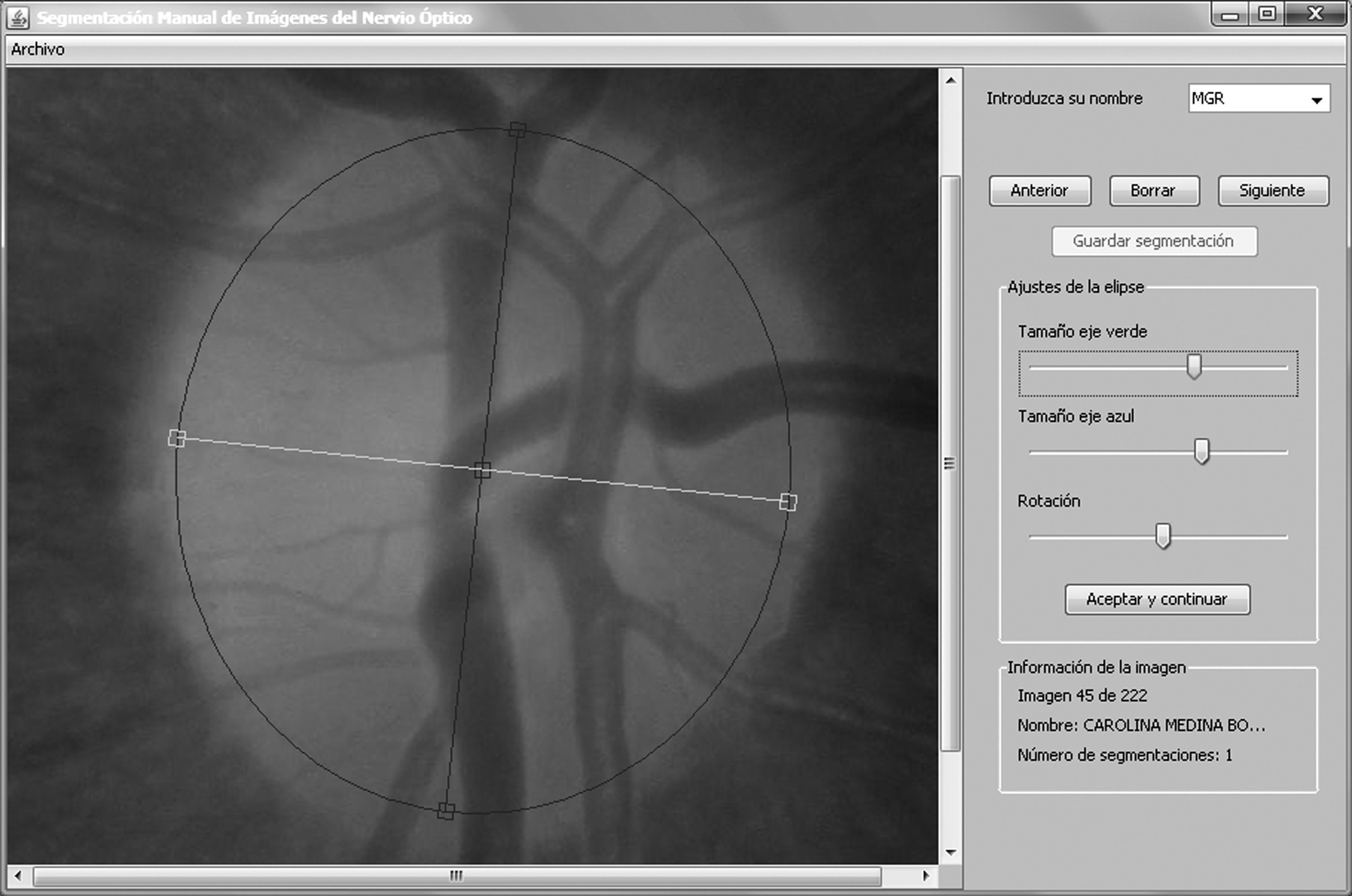
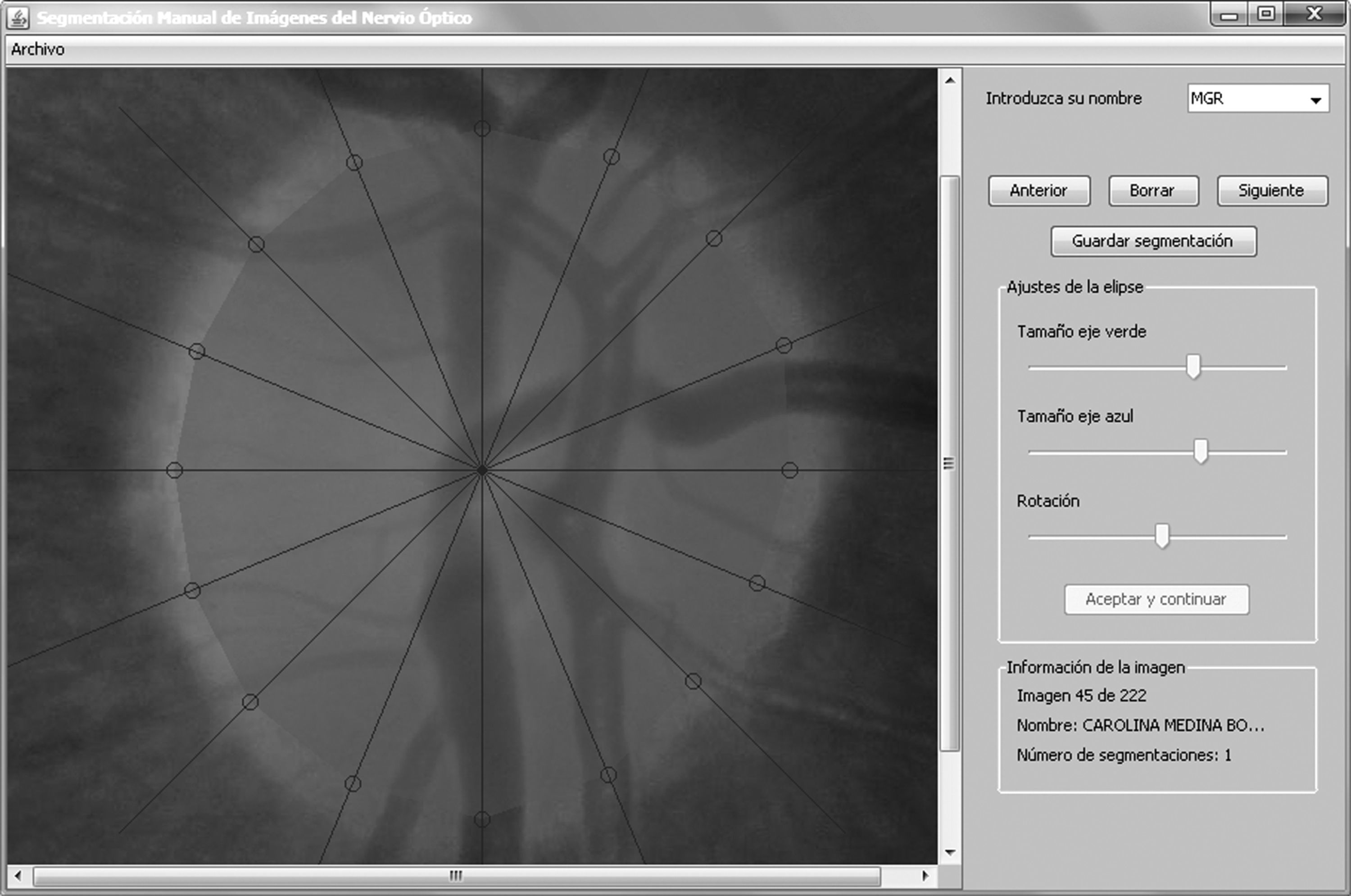
Method(1) 169 images of optic nerve disk were evaluated by five experts for the defining of the edges in 8 positions (every 45°). (2) The estimated areas of 26 cases were compared with the measurements of the Cirrus Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT-Cirrus).
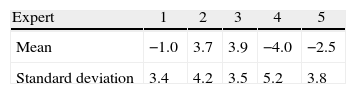
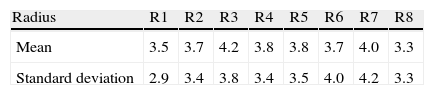
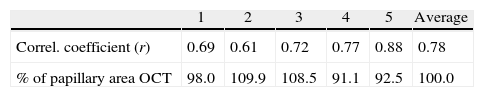
Results(1) The mean variation of the estimated radius was ±5.2%, with no significant differences between sectors. Specific differences were found between the 5 experts (p<0.001), each one compared with the others. (2) The disk area measured by the OCT-Cirros was 1.78mm2 (SD=0.27). The results corresponding to the experts who detected smaller areas were better correlated to the area detected by the OCT-Cirrus (r=0.77–0.88) than the results corresponding to larger areas (r=0.61–0.69) (p<0.05 in extreme cases).
ConclusionsThere are specific patterns in each expert for defining the disk edges and involve 20% variation in the estimation of the optic nerve area. The experts who detected smaller areass have a higher agreement with the objective method used. A web tool is proposed for self-assessment and training in this task.
Estimar el grado de error en la determinación subjetiva del límite papilar.
Método(1) Fueron evaluadas 169 imágenes papilares por cinco expertos para delimitar los bordes papilares en 8 posiciones (cada 45°). (2) Las áreas estimadas en 26 casos se compararon con las medidas mediante tomógrafo de coherencia óptica (OCT-Cirrus).
Resultados(1) La variación media del radio papilar estimado fue de ±5,2%, sin diferencias significativas entre sectores. Entre los cinco expertos existieron diferencias específicas (p<0,001) de cada uno respecto a los restantes. (2) El área papilar medida por OCT-Cirrus fue de 1,78mm2 (DE=0,27). Los resultados de los expertos que informaron de áreas menores estuvieron mejor correlacionados con el área de OCT-Cirrus (r=0,77–0,88) que los que informaron de áreas mayores (r=0,61–0,69) (p<0,05 en casos extremos).
ConclusionesExisten patrones específicos de cada experto para definir los límites papilares que pueden significar variaciones del 20% en la estimación de su área. Aquellos expertos que realizan delimitaciones menores tuvieron una mayor coincidencia con el método objetivo utilizado. Proponemos una herramienta web de autoevaluación y entrenamiento en esta tarea.