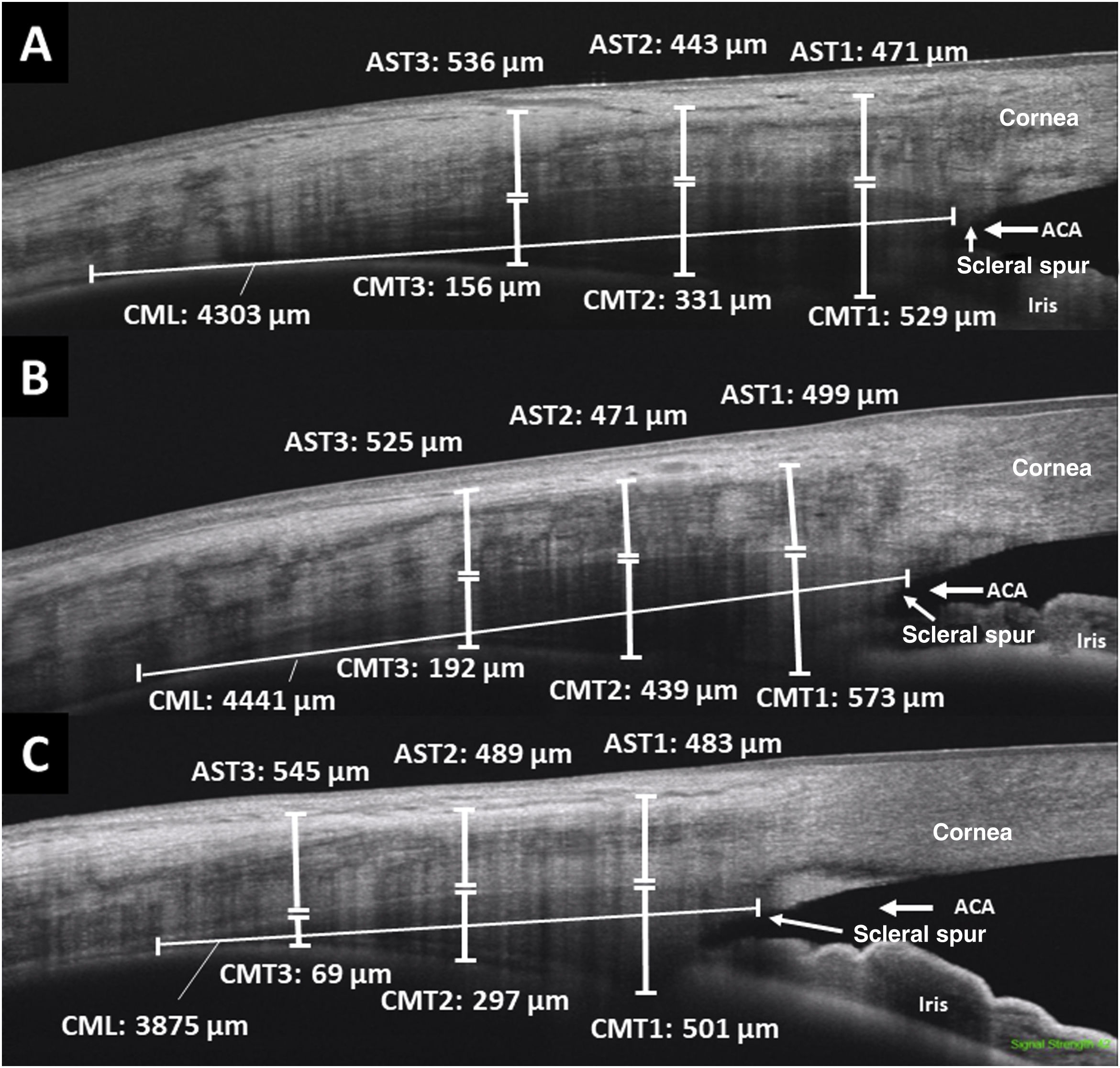
To assess ciliary muscle (CM) and anterior scleral thickness (AST) dimensions in vivo in high myopia using swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) and to compare with emmetropic and hyperopic subjects.
MethodsCross-sectional study that included 34 high myopic patients (≥ −6 diopters [D]), 90 emmetropes (−1 to +1 D) and 38 hyperopic patients (≥ +3.5 D). CM thickness (CMT) and AST were measured in the temporal and nasal quadrants at 1, 2, and 3 mm from the scleral spur using SS-OCT. In addition, the length of the CM (CML) was evaluated.
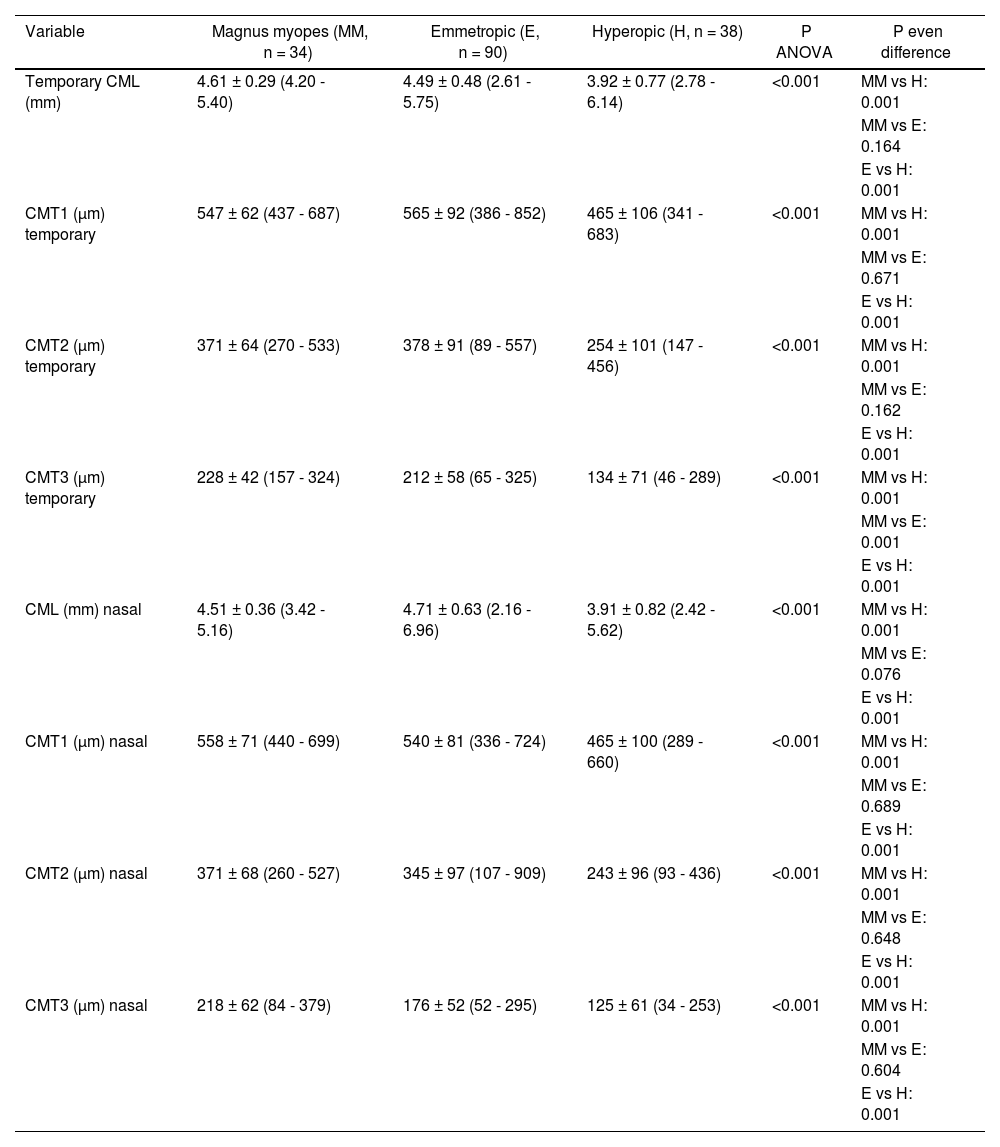
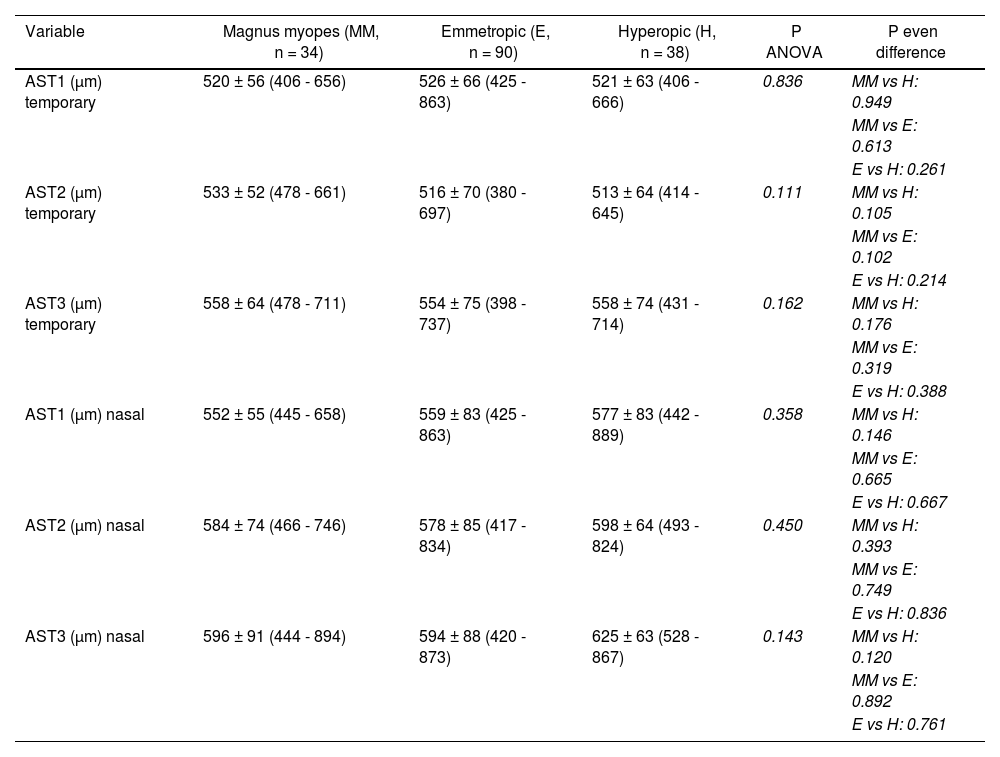
ResultsThe dimensions of the CML and the CMT at any of their measurement points were greater in high myopes and emmetropes than in hyperopes, both in the nasal and temporal quadrants (P < .001). However, there were no differences between high myopes and emmetropes for any of the parameters (P ≥ .076) except for the CMT at 3 mm in the temporal quadrant (P < .001). There were no differences in the AST between high myopes, emmetropes and hyperopes, in any of the measurement points or quadrants studied (P > .05).
ConclusionsThe SS-OCT allows to measure the CM in vivo, not observing differences in its dimensions between high myopes and emmetropes, but they were smaller in hyperopes. In the measurement of the anterior sclera, no differences were observed between the three groups analyzed according to refraction.
Evaluar las dimensiones del músculo ciliar (MC) y del grosor escleral anterior (AST) in vivo en miopes altos mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica de fuente de barrido (SS-OCT) y comparar con sujetos emétropes e hipermétropes.
MétodosEstudio transversal en el que se incluyeron 34 miopes altos (≥ −6 dioptrías [D]), 90 emétropes (−1 a +1 D) y 38 hipermétropes (≥ +3,5 D). Se midieron el grosor del MC (CMT) y el AST en los cuadrantes temporal y nasal a 1, 2 y 3 mm del espolón escleral utilizando la SS-OCT. Además, se evaluó la longitud del MC (CML).
ResultadosLas dimensiones tanto del CML como del CMT en cualquiera de sus puntos de medida fueron mayores en miopes altos y en emétropes que en hipermétropes, tanto en el cuadrante nasal como en el temporal (p < 0,001). Sin embargo, no existieron diferencias entre miopes magnos y emétropes para ninguno de los parámetros (p ≥ 0,076), salvo para el CMT a 3 mm en temporal (p < 0,001). No existieron diferencias en el AST entre miopes altos, emétropes e hipermétropes, en ninguno de los puntos de medida ni cuadrantes estudiados (p > 0,05).
ConclusionesLa SS-OCT permite medir el MC in vivo; no se observaron diferencias en sus dimensiones entre miopes altos y emétropes, pero sí que fueron menores en hipermétropes. En la medida de la esclera anterior no se observaron diferencias entre los tres grupos analizados según la refracción.