To assess the vision-related quality of life and the depression and anxiety rates in patients with neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration (nAMD).
MethodsA cross-sectional study of patients with nAMD treated with intravitreal injections was performed. The patients completed two validated questionnaires: the Visual Functioning Questionnaire (VFQ-25, score from 0 to 100), and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) questionnaire. Age, gender and visual acuity (VA) in the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) scale was registered.
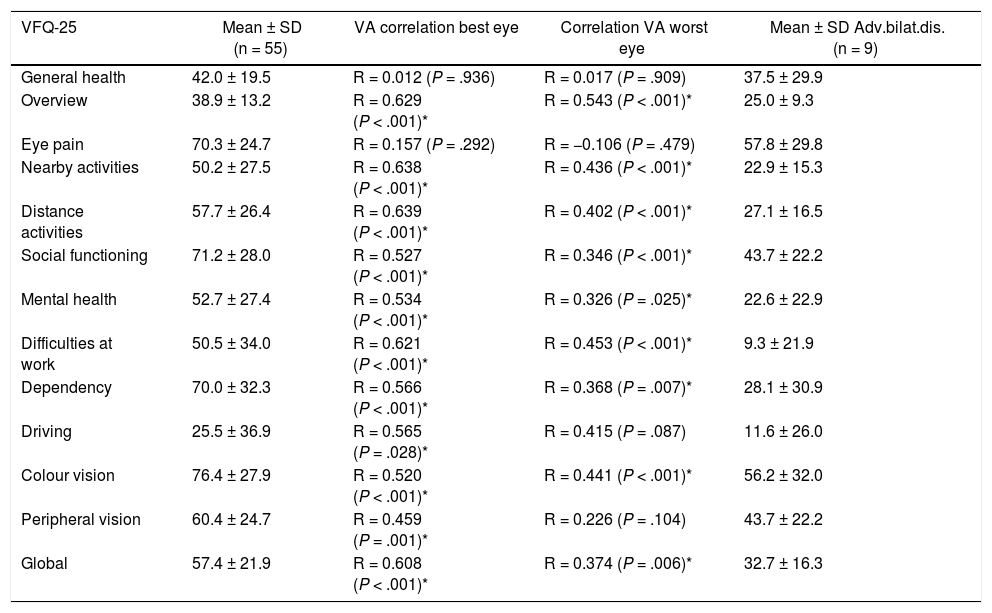
ResultsFifty-five patients with nAMD participated with a mean age of 80.9 ± 6.6 years-old (range 67–93) and a mean VA in the best eye of 73.5 ± 12.7 letters (range 44–95). The global VFQ-25 mean score was 57.4 ± 21.9 being 38.9 ± 13.2 for the general vision and 42.0 ± 19.5 for the general health. VA in the best eye was associated with the global score of the VFQ-25 scale (R = 0.608; P < .001), but no correlation was observed with general health (P = .936). In the HADS scale, 26.9% and 25.5% of patients had symptoms of depression and anxiety respectively. A negative correlation was found between the HADS and VFQ-25 scales for the general vision score (R = −0.438).
ConclusionThis study elucidates the impact of vision impairment and the visual functioning in nAMD, describing an important rate of depression and anxiety symptoms.
Evaluar la calidad de vida relacionada con la visión, así como la presencia de síntomas de depresión y ansiedad en los pacientes con degeneración macular asociada a la edad neovascular (DMAEn).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio transversal de pacientes con DMAEn en tratamiento con inyecciones intravítreas de antiangiogénicos. Los pacientes realizaron dos cuestionarios validados: el cuestionario de función visual (VFQ-25, cuya puntuación varía de 0 a 100) y la Escala Hospitalaria de ansiedad y depresión (HADS). Se registró la edad, el sexo y la agudeza visual (AV) en la escala Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 55 pacientes con DMAEn con una edad de 80,9 ± 6,6 años (rango 67 a 93) y una AV en el mejor ojo de 73,5 ± 12,7 letras (rango 44 a 95). La puntuación global media en el VFQ-25 fue de 57,4 ± 21,9, siendo 38,9 ± 13,2 para la visión general y 42,0 ± 19,5 para la salud general. La AV se correlacionó con la puntuación global de la escala VFQ-25 (R = 0,608; P < ,001), pero no con la salud general (P = ,936). Mediante la escala HADS se detectó un 27,2% y un 25,5% de pacientes con síntomas de depresión y ansiedad respectivamente. Se observó una correlación negativa entre las puntuaciones del HADS y VFQ-25 para el dominio de visión general (R = −0,438).
ConclusionesEste estudio muestra el impacto en la calidad de vida y función visual en los pacientes con DMAE neovascular, presentando en un porcentaje considerable de los casos síntomas de depresión y ansiedad.