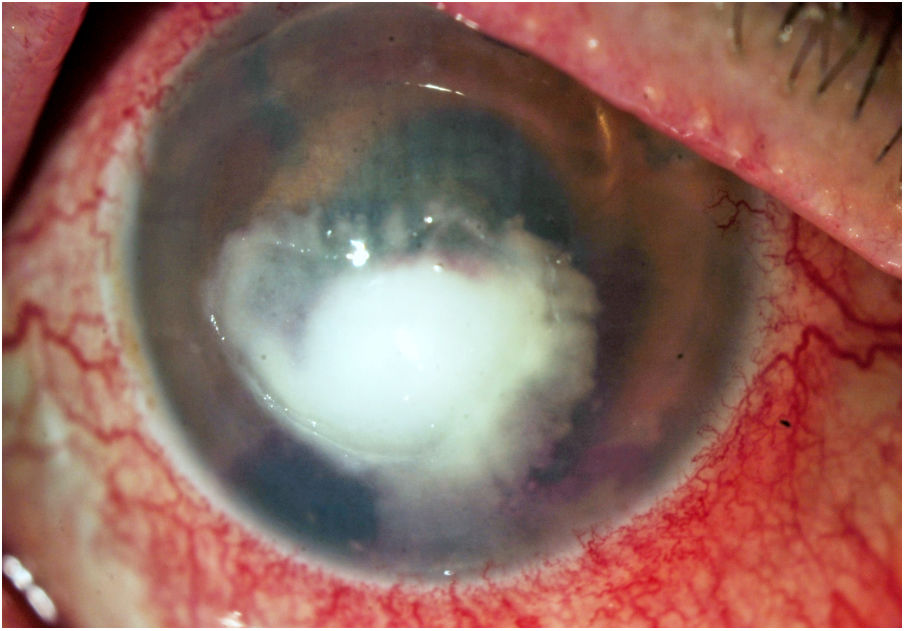
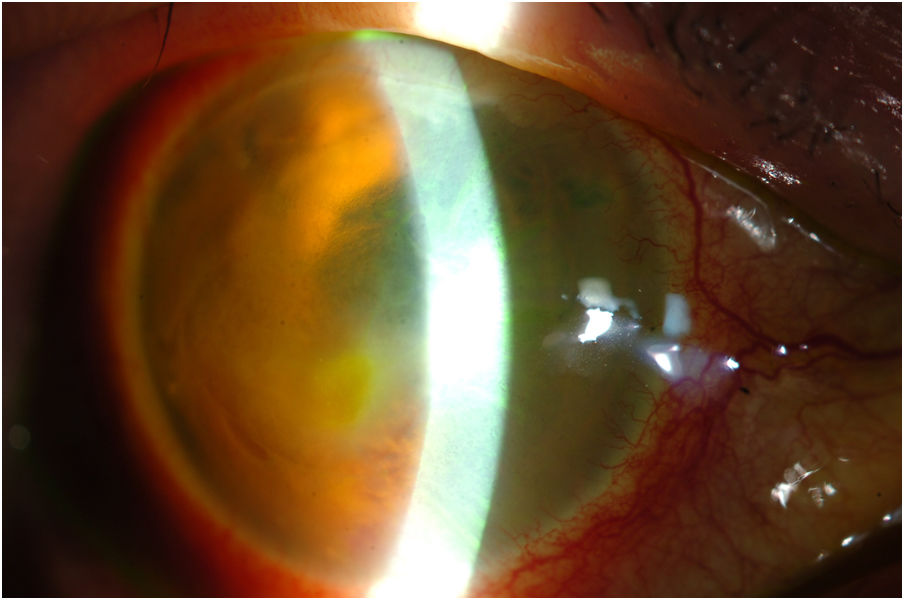
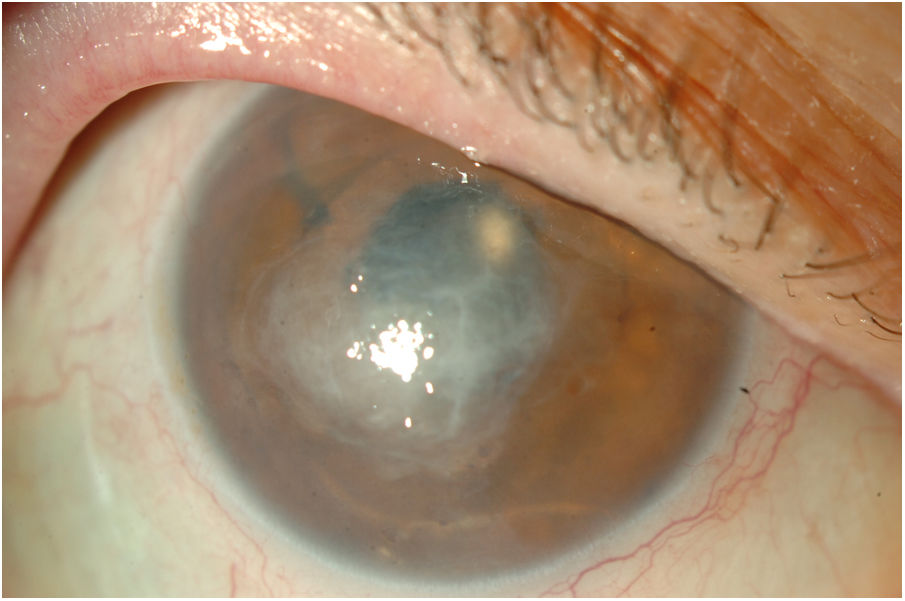
Moraxella keratitis can lead to important complications. Moraxella nonliquefaciens (M. nonliquefaciens) has the worst prognosis. Only three cases of corneal infections due to M. nonliquefaciens have been published. The case presented is of a 79-year-old man with bullous keratopathy, recently affected with severe infectious keratitis. Dense, deep, and central stromal infiltrates and hyphaema were detected. After the identification of M. nonliquefaciens in the culture, and given the progression of the condition, the initial empirical treatment was modified to topical ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime in accordance with the antibiogram, combining oral ciprofloxacin and amoxicillin-clavulanate. After 27 days, there was total resolution of the lesion, with central residual leucoma.
Keratitis caused by M. nonliquefaciens is rare and must be suspected in elderly patients with local predisposing factors, such as corneal damage or previous eye surgery. Early antibiogram-guided treatment and close monitoring are important to avoid complications and poor compliance.
La queratitis bacteriana por Moraxella spp. puede producir importantes complicaciones, siendo la producida por la Moraxella nonliquefaciens (M. nonliquefaciens) la de peor pronóstico. Solo existen tres publicaciones de queratitis por M. nonliquefaciens.
Presentamos el caso clínico de un hombre de 79 años, con queratopatía bullosa, recientemente afectado con queratitis infecciosa grave. En la exploración se observa infiltrado estromal denso, profundo y central con hifema. Tras la identificación en cultivo de M. nonliquefaciens y dada la progresión se modifica el tratamiento empírico, según antibiograma, a ciprofloxacino y ceftazidima tópicos, asociando ciprofloxacino y amoxicilina clavulánico orales. Tras 27 días se aprecia resolución total de la lesión con leucoma residual central. La queratitis infecciosa por M. nonliquefaciens es rara y se debe sospechar en pacientes mayores con factores locales predisponentes como daño corneal o cirugía ocular previa. Es importante un tratamiento precoz guiado por antibiograma y un seguimiento cercano para evitar complicaciones y mal cumplimiento.