Currently, refractive surgery is a safe and effective procedure, and considered as a risk for development of dry eye. The aim of study is to analyze the scientific publications in the field of ocular dryness secondary to refractive surgery through a bibliometric approach. The temporal period goes since 2001–2019, years in which first references appeared and search limited selection is done, respectively. The set of publications ranges from the first publication appeared in 2001, to the last one selected in 2019.
MethodsA search of references was made through Scopus, using “refractive surgery” as main descriptor, and «dry eye» as secondary one; both descriptors were limited to those available in the chosen field for the title, abstract, and keywords. The most common indicators and bibliometric maps were applied for to the selected publications.
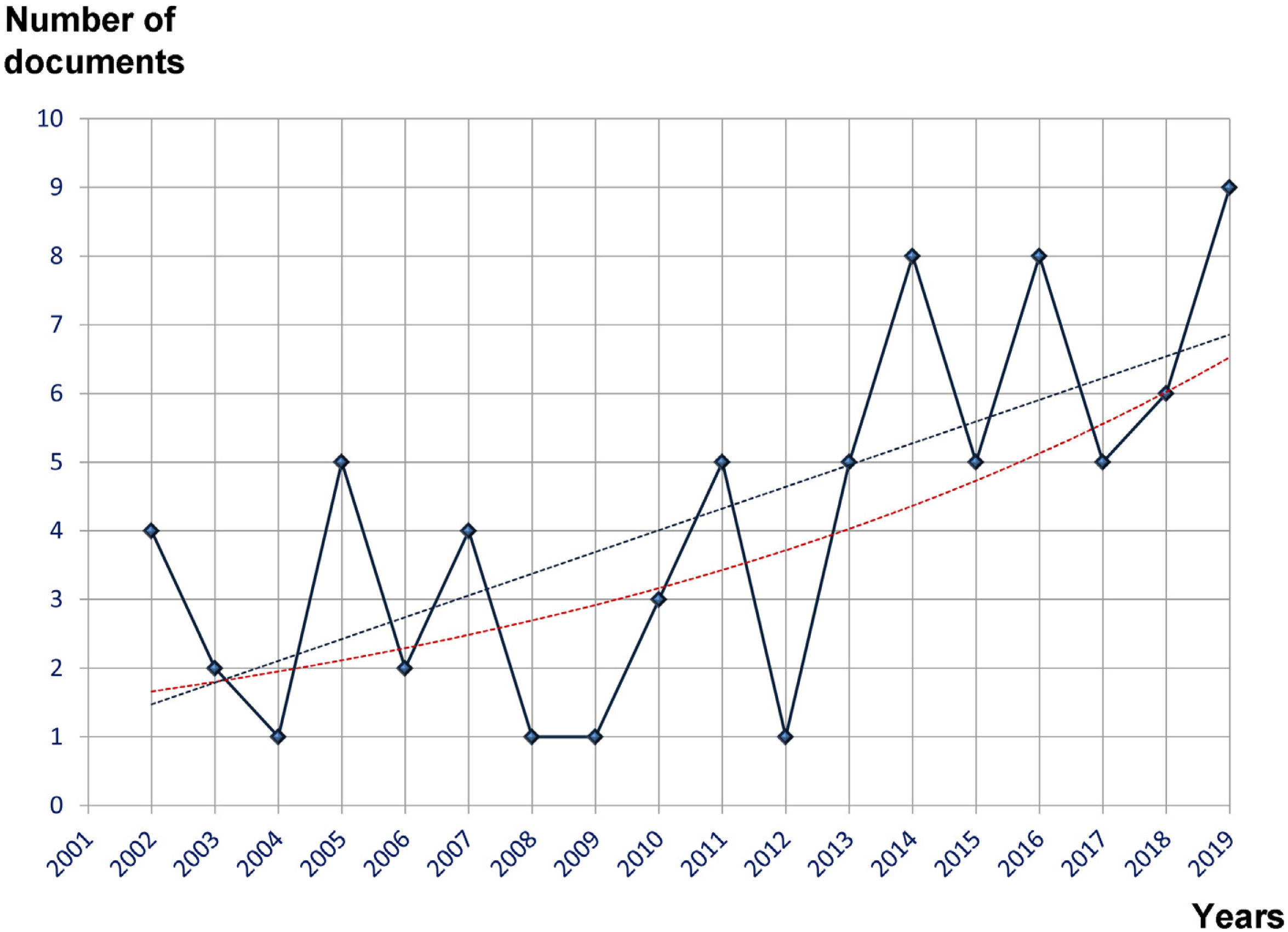
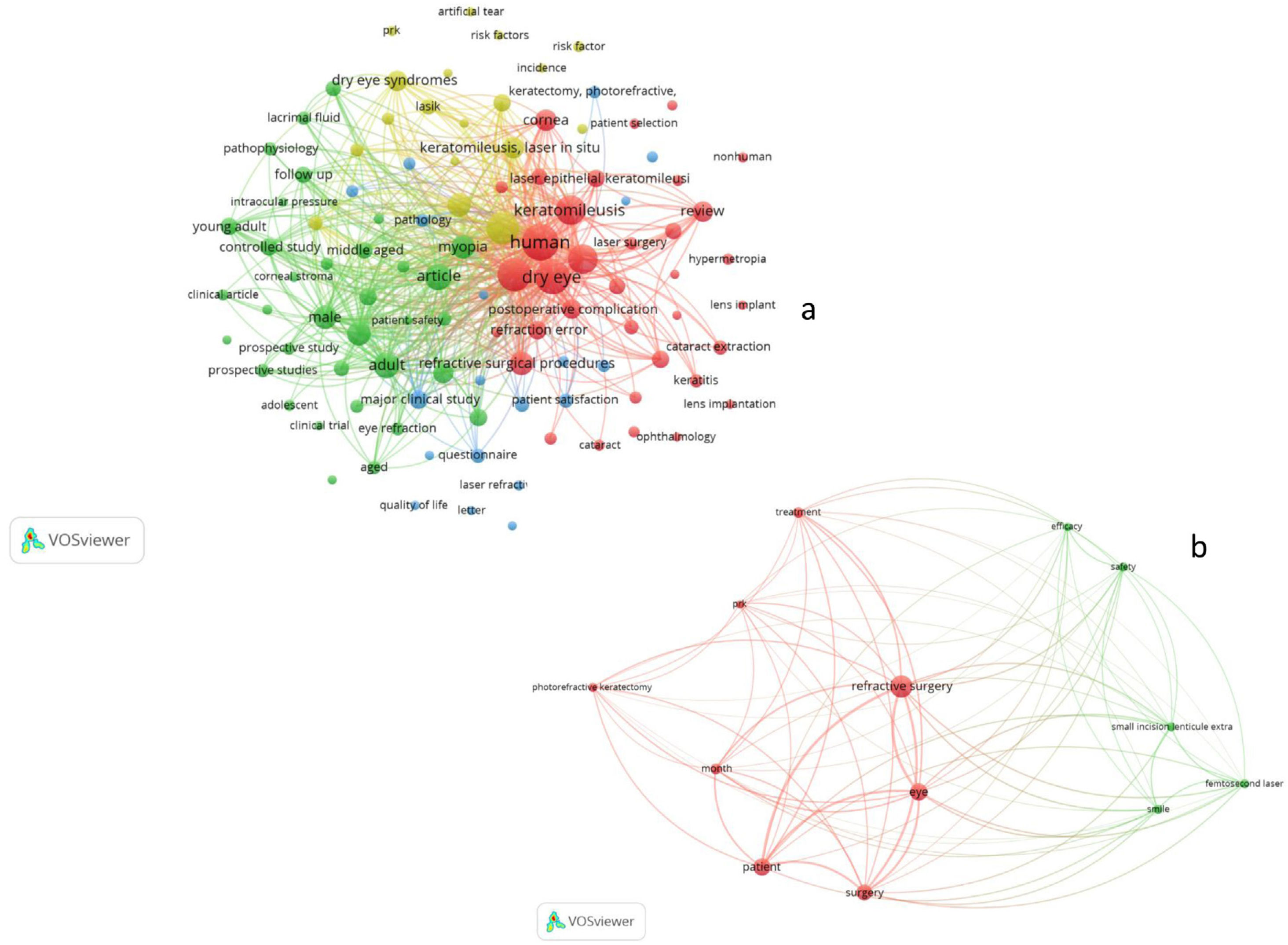
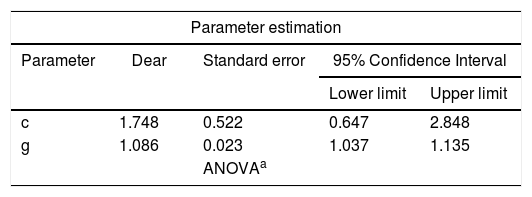
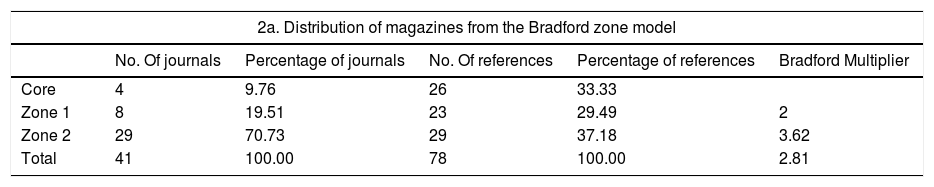
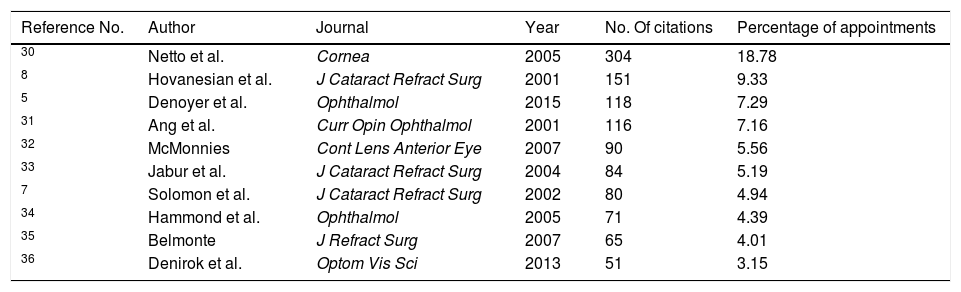
ResultsA total of 78 original articles were collected from the timeframe 2001−2019. According to the Price's law, the growth of literature production was linear turned out in a linear growth of literature production. The annual growth rate was 8.6% with a literature doubling time of 8.4 years. The Bradford core, preferred journals chosen by authors were 4 with offered four preferred journals by the authors, all of them with an impact factor >2. These were Ophthalmology, Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Journal of Glaucoma and British Journal of Ophthalmology. Regarding geographical distribution, the United States had the highest production.
ConclusionsThe scientific production of dry eye after refractive surgery follows a linear growth. In this instance, postulates of the Price’s growth law of science are not fulfilled. In addition, there is a high rate of transience. That may indicate low productivity or presence of researchers from other related subjects disciplines, who have published occasionally in this topic.
La cirugía refractiva es actualmente un procedimiento seguro y eficaz, y es reconocida como factor de riesgo para el desarrollo del ojo seco. El objetivo del estudio es analizar la producción e identificar el estado de conocimiento sobre el ojo seco secundario a cirugía refractiva, sus inicios y su evolución, así como cuales son los autores e instituciones más notorios.
Material y métodosSe realizó una búsqueda de referencias a través de la base de datos Scopus, utilizando «cirugía refractiva» como descriptor principal y «ojo seco» como secundario; unidos ambos por el operador booleano AND, y limitándose el campo a la disponibilidad de título, resumen y palabras clave. A las publicaciones seleccionadas se le aplicaron los indicadores y los mapas bibliométricos habituales.
ResultadosSe recopilaron 78 artículos del periodo 2001−2019. Según la ley de Price, el crecimiento de la producción de la literatura fue lineal. La tasa de crecimiento anual fue del 8,6% con un tiempo de duplicación de 8,4 años. El núcleo de Bradford ofreció 4 revistas, todas con factor de impacto>2. Estas fueron: Journal of Ophthalmology, Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Journal of Glaucoma y The British Journal of Ophthalmology. El país con mayor producción fue EE. UU.
ConclusionesLa producción científica sobre el ojo seco secundaria a cirugía refractiva sigue un crecimiento lineal, no cumpliéndose los postulados de Price. Existe una alta transitoriedad de autores. Esto puede indicar una baja productividad por autor, o bien la presencia alta de investigadores que hayan publicado publican ocasionalmente sobre este tema.