In 2013 we implemented an asynchronous telemedicine circuit for the diagnosis of eyelid diseases (tele-eyelid), connecting the outpatient primary healthcare with the hospital's specialists. The purpose of this study is to assess the use of telemedicine in the diagnosis of eyelid diseases by primary care teams, to evaluate its usefulness and to analyse the epidemiology of the pathological conditions referred to the tertiary level hospital, as well as the need for surgery.
Materials and methodsThis study was carried out in the Spanish public health system, in a mainly rural area assisted by the Institut Català de la Salut (ICS) and Althaia Xarxa Assistencial Universitària de Manresa. This is a retrospective, descriptive analysis of the telematic consultations undertaken between 2013 and 2019. The consultations between 2018 and 2019 underwent a further descriptive retrospective-prospective analysis to assess the conditions referred to the hospital.
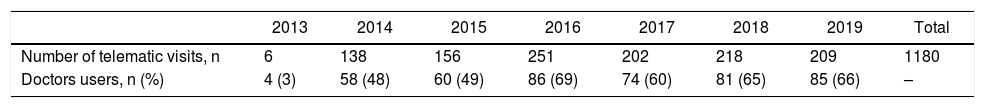
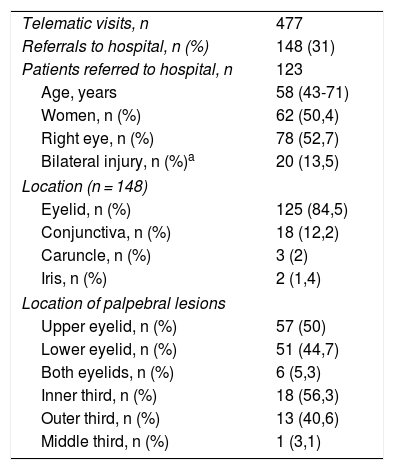
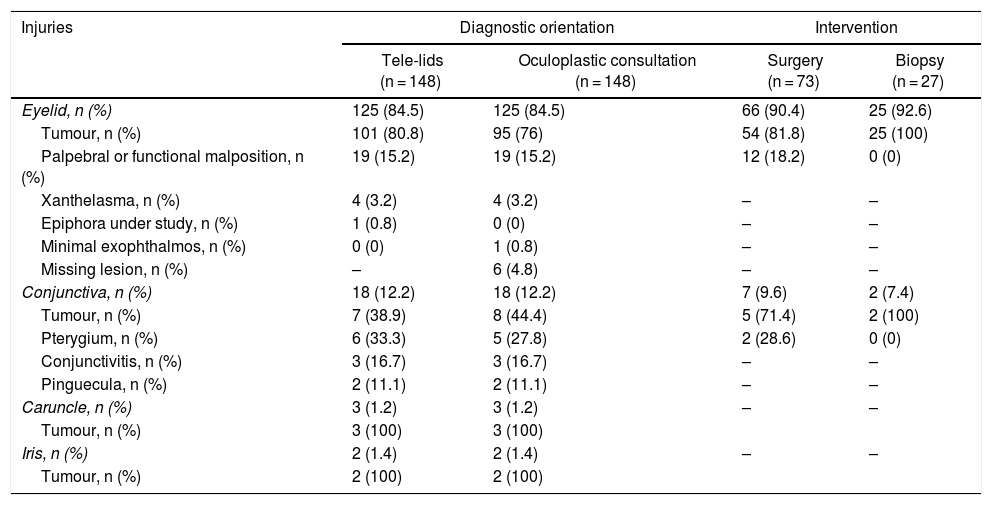
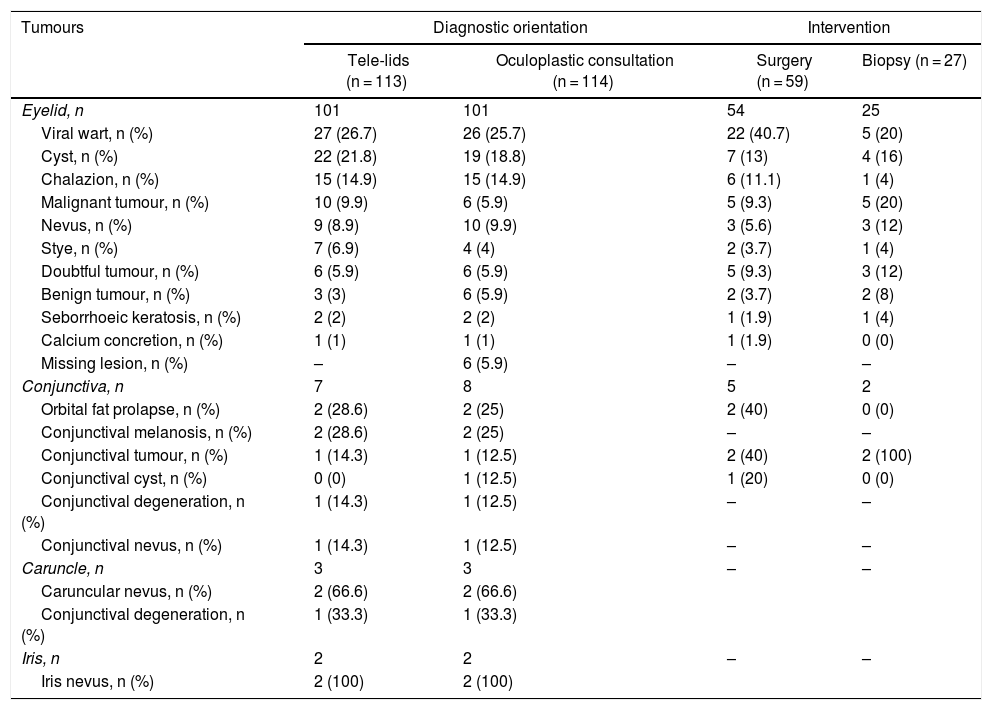
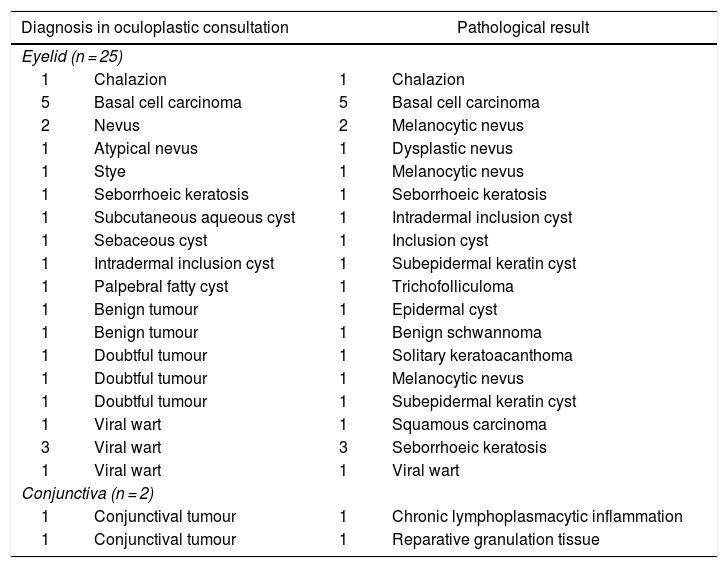
ResultsUnnecessary referrals were avoided in 72% of telematic consultations. More than 50% of primary care practitioners used tele-eyelid. Up to 68% of the referrals were due to eyelid tumours, 50% needed surgery and 18%, a biopsy. Moreover, we found a high reliability between telematic and face-to-face diagnosis.
ConclusionsTeleophthalmology applied to eyelid pathology is a useful tool to improve access to specialized care and helps solving pathological conditions. It avoids unnecessary consultations and increases efficiency, both in primary and hospital care.
En 2013 implementamos un circuito de telemedicina asincrónica centrada en la patología palpebral (telepárpados), conectando la atención primaria ambulatoria con la especializada de ámbito hospitalario. El objetivo de este estudio es valorar el uso por parte de los Equipos de Atención Primaria de la telemedicina en el diagnóstico de las enfermedades palpebrales, evaluar su utilidad y analizar la epidemiología de las patologías derivadas al hospital de tercer nivel de referencia, así como la necesidad de cirugía.
Materiales y métodosEste estudio se desarrolló en el sistema público de salud español, en un territorio principalmente rural asistido por el Institut Català de la Salut (ICS) y Althaia Xarxa Assistencial Universitària de Manresa. Se realizó un análisis descriptivo retrospectivo de las visitas telemáticas realizadas entre 2013 y 2019, y se seleccionaron las realizadas entre 2018 y 2019 para practicar un análisis descriptivo retrospectivo-prospectivo más específico centrado en las consultas derivadas al hospital.
ResultadosSe evitaron derivaciones innecesarias en el 72% de las consultas telemáticas. Más de un 50% de los/las médicos de atención primaria utilizaron telepárpados. El 68% de las derivaciones al hospital correspondieron a tumoraciones palpebrales, el 50% requirió cirugía y el 18%, biopsia. Además, hallamos una elevada concordancia entre el diagnóstico telemático y el presencial.
ConclusionesLa telemedicina aplicada a la patología palpebral es una herramienta útil para mejorar el acceso a la atención especializada, así como la resolución de los procesos. Permite evitar visitas innecesarias y aumenta la eficiencia, tanto en atención primaria como hospitalaria.