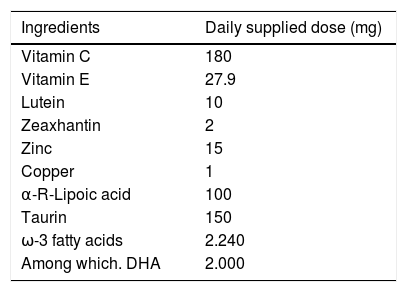
To analyse the safety and effectiveness of the oral administration of a commercialised supplement containing R-alpha lipoic acid (ALA), taurine, vitamins C and E, lutein, zeaxanthin, zinc, copper and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), and in control subjects.
Material and methodsA prospective study of cases and controls was carried out, including 30 participants of both genders that were divided into: POAG Group (n=15) and a control group (CG; n=15), assigned to the oral intake of NuaDHA preparations Vision® (1 pill/day)+NuaDHA 1000 (2 pills/day) for 6 months. Participants were interviewed, ophthalmologically examined, and peripheral blood was taken for routine analysis and the determination of the pro-oxidant [malondialdehyde (MDA)] and total antioxidant status (TAS). Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 22.0 program.
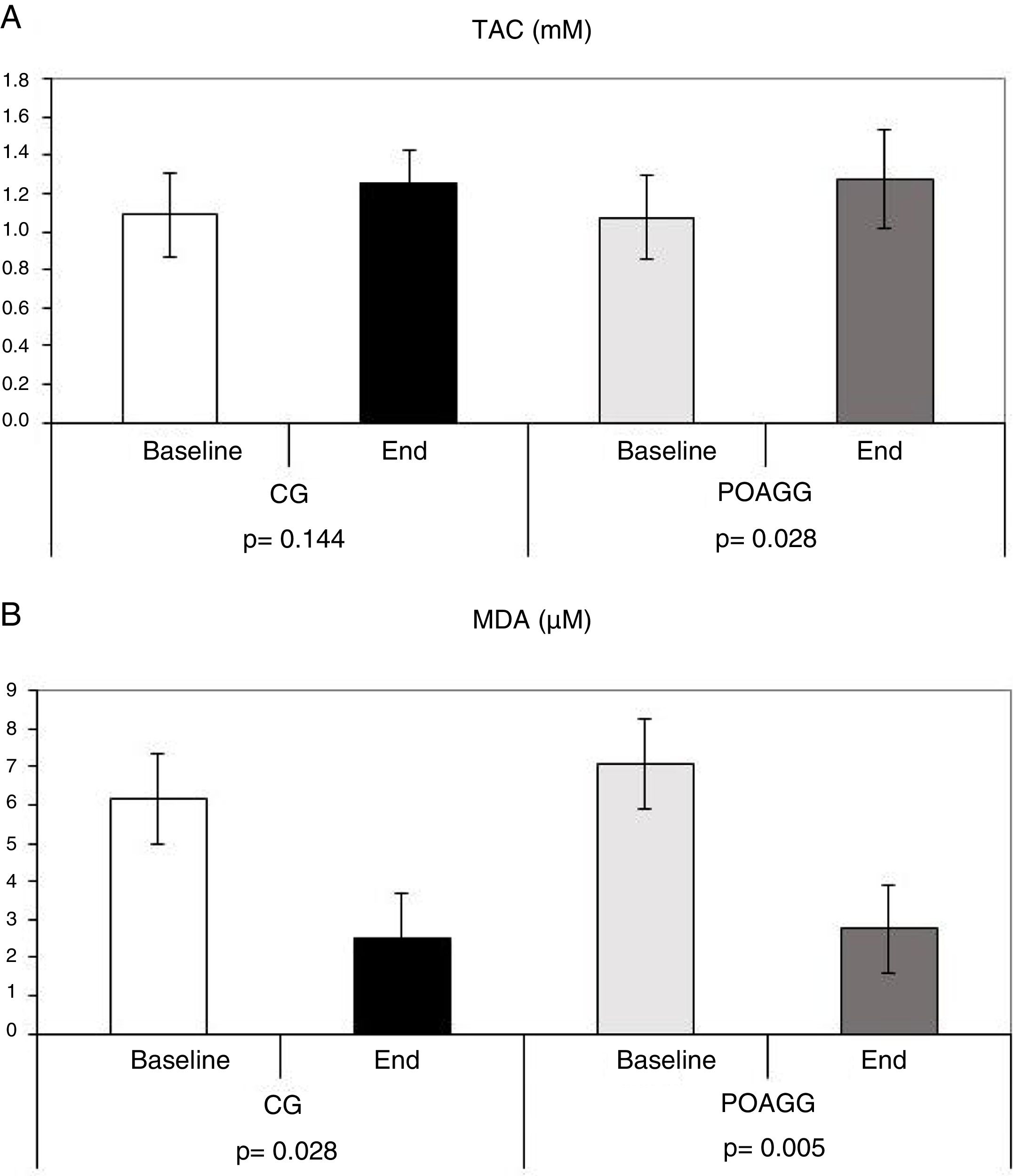
ResultsAfter 6 months of supplementation, there was a significant increase in the plasma TAS (1.073±0.090mM vs 1.276±0.107mM, P=.028), along with a parallel decrease in MDA (7.066±1.070μM vs 2.771±0.462μM, P=.005) in the POAG group. The MDA also decreased in the control group (6.17±1.336 vs. 2.51±0.391, P=.028). The Schirmer test improved (20–30%) and the subjective dry eye signs/symptoms noticeably decreased in the POAG group versus the CG.
ConclusionsFormulations containing antioxidant vitamins, ALA and DHA, administered for 6 consecutive months, counteracted the oxidative stress by further stabilising the morphological/functional parameters of both the ocular surface and the glaucoma, without presenting with adverse effects or intolerances.
Analizar la seguridad y efectividad de la administración oral de un suplemento comercializado que contiene ácido alfa-R-Lipoico (ALA), taurina, vitaminas C y E, luteína, zeaxantina, zinc, cobre y ácido docosahexaenoico (DHA) en pacientes con glaucoma primario de ángulo abierto (GPAA) y sujetos control.
Material y MétodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo de casos y controles que incluyó 30 participantes de ambos sexos, divididos en: pacientes con GPAA (GGPAA; n=15) y sujetos sanos (GC; n=15) asignados a tomar durante 6 meses los preparados NuaDHA Visión® (1 comp./dia) + NuaDHA 1000 (2 comps./dia). Los participantes fueron entrevistados, examinados oftalmológicamente, extrayendo sangre periférica que fue procesada para analítica convencional y determinación de actividades pro-oxidante [malonildialdehido (MDA)] y estado antioxidante total (EAT). El análisis estadístico se realizó mediante el programa SPSS 22.0.
ResultadosTras 6 meses de suplementación los niveles plasmáticos de EAT aumentaron significativamente 1,073±0,090mM vs 1276±0,107mM, p=0,028, disminuyendo en paralelo los de MDA 7,066±1,070 μM vs 2761±0,462 μM, p=0.005 en el GGPAA. El MDA también descendió significativamente en el GC 6,17±1336 vs 2,51±0,391, p=0,028. Los pacientes con GPAA mostraron valores del test de Schirmer notablemente mayores 20-30%) y mejoraron subjetivamente los signos/síntomas de ojo seco, frente a los resultados del GC.
ConclusionesLas formulaciones que contienen vitaminas antioxidantes, ALA y DHA administradas durante 6 meses consecutivos contrarrestaron el estrés oxidativo, y estabilizaron los parámetros morfológicos/funcionales de la superficie ocular y del glaucoma, sin presentar efectos adversos o intolerancias.