Adjustable suture procedures allow addressing the unpredictability of some postoperative results in strabismus surgery. The purpose of the study was to compare the effectiveness of adjustable and non-adjustable suture in the treatment of horizontal strabismus in children and adults.
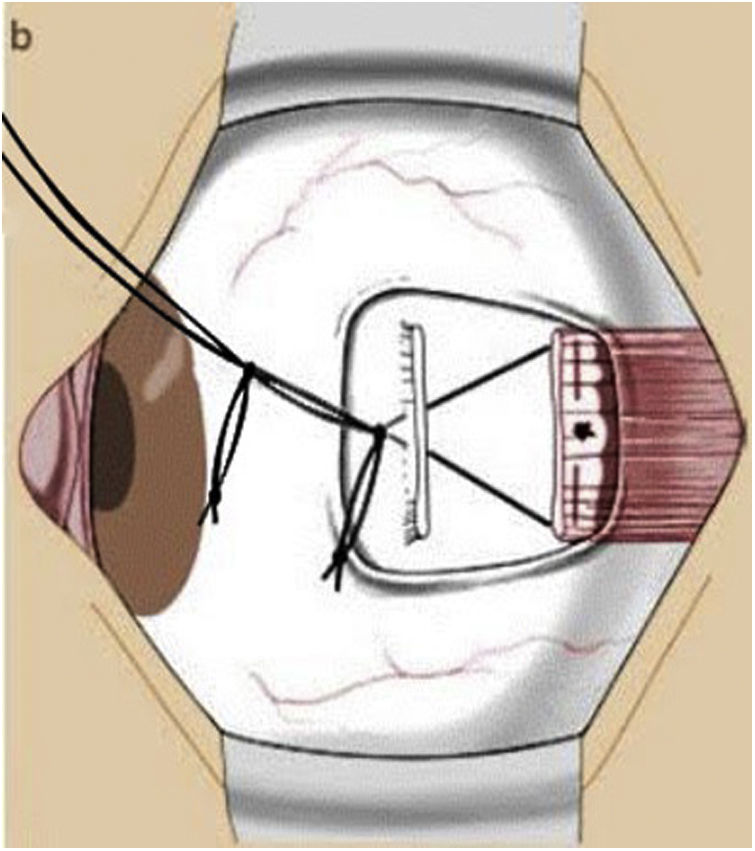
MethodsProspective study including patients undergoing strabismus surgery to correct horizontal strabismus with fixed hanging suture (non-adjustable suture group) and adjustable suture. Visual acuity, amblyopia, deviation, oblique muscle involvement, previous surgeries, nystagmus, need for adjustment, and complications were recorded. The variables were recorded in the immediate postoperative period, at one week and at 3 and 6 months.
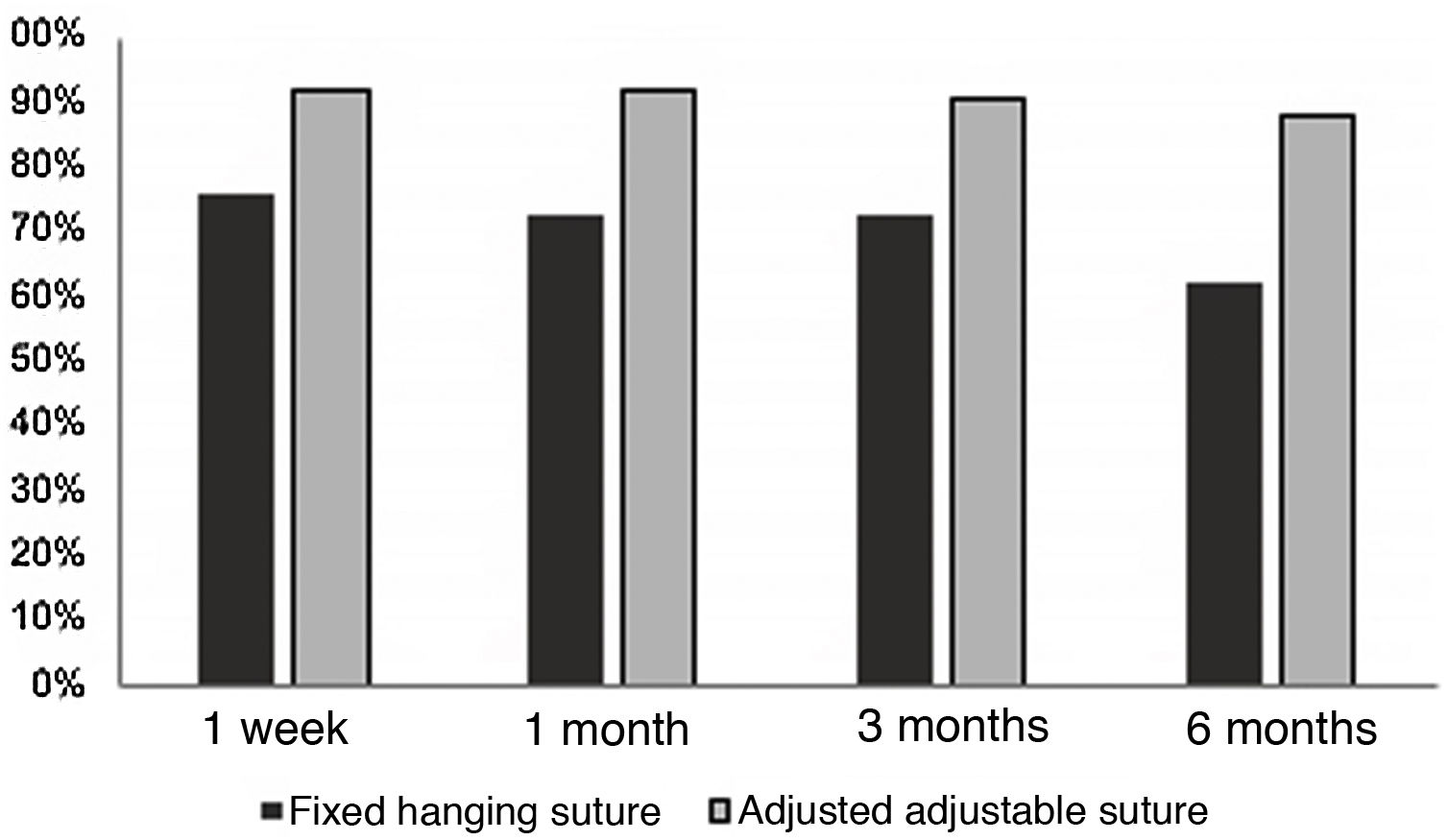
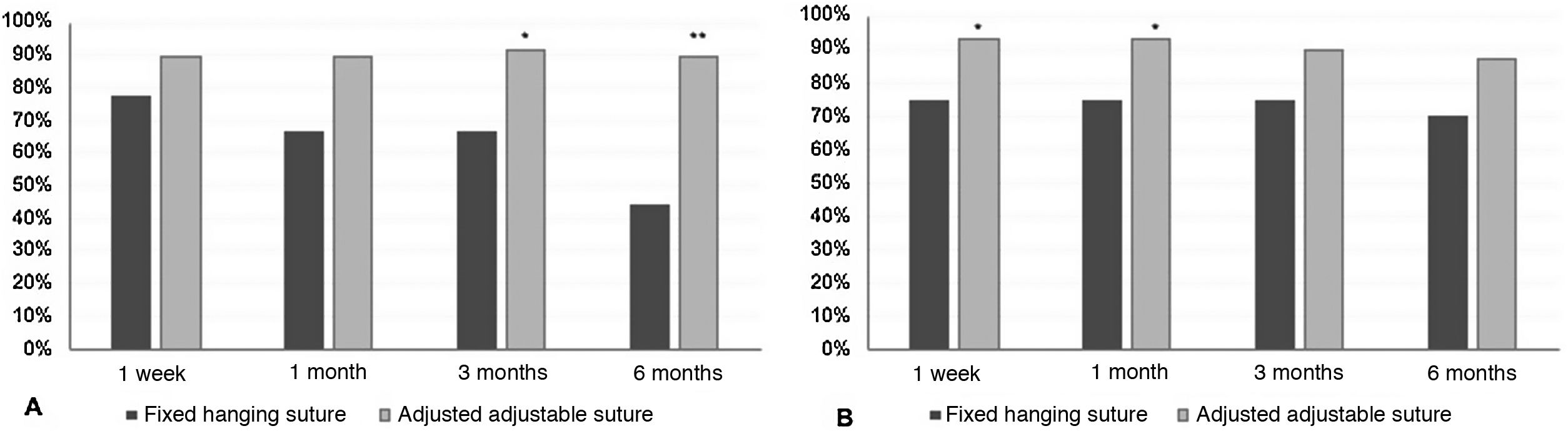
Results186 patients were included: 157 (84.4%) with adjustable suture and 29 (15.6%) with non-adjustable suture, of which 119 were children and 67 were adults. Postoperatively, 19 children (16.0%) and 19 adults (28.4%) required adjustment (p = 0.044). Of 157 patients with adjustable suture, it was adjusted in 20% (32/157). Success after adjustment was higher for adjustable suture (91.72% vs 79.31%; p = 0.043) and remained for 6 months (p < 0.05). Previous surgery (p = 0.004) and exotropia (p = 0.018) correlated with the need for adjustment.
Conclusions20% of patients with horizontal strabismus can benefit from a postoperative adjustment to improve the surgical result. The adjustable suture was shown to be superior to the fixed hanging suture and is an excellent surgical option, both in children and adults.
Los procedimientos con sutura ajustable permiten abordar la imprevisibilidad de algunos resultados postoperatorios en la cirugía de estrabismo. El propósito del estudio fue comparar la efectividad de la sutura ajustable y no ajustable en el tratamiento del estrabismo horizontal en niños y adultos.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo en el que se incluyeron pacientes sometidos a cirugía de estrabismo para la corrección de un estrabismo horizontal con sutura colgante fija (grupo de sutura no ajustable) y sutura ajustable. Se registró la agudeza visual, la ambliopía, la desviación, la afectación de músculos oblicuos, cirugías previas, el nistagmo, la necesidad de ajuste y las complicaciones. Las variables se registraron en el postoperatorio inmediato, a la semana y a los 3 y 6 meses.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 186 pacientes: 157 (84.4%) con sutura ajustable y 29 (15.6%) con sutura no ajustable, de los cuales 119 eran niños y 67 adultos. En el postoperatorio, 19 niños (16,0%) y 19 adultos (28,4%) requirieron un ajuste (p = 0,044). De 157 pacientes con sutura ajustable, se ajustó al 20% (32/157). El éxito tras el ajuste fue superior para la sutura ajustable (91,72% vs 79,31%; p = 0,043) y se mantuvo los 6 meses (p < 0.05). La cirugía previa (p = 0,004) y la exotropía (p = 0,018) se relacionaron con la necesidad de ajuste.
ConclusionesUn 20% de pacientes con estrabismo horizontal se pueden beneficiar de un ajuste postoperatorio para mejorar el resultado quirúrgico. La sutura ajustable mostró ser superior frente a la sutura colgante fija y supone una excelente opción quirúrgica tanto en niños como en adultos.