To describe visual function, macular integrity, and fixation stability using MAIA microperimetry (macular integrity assessment) after retinal detachment surgery. Evaluate if there are statistically significant differences between surgical approaches.
Materials and methodsA prospective, comparative, interventional study was conducted, recruiting a total of 21 patients with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and macula-off. Eleven patients underwent surgery using pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), and 10 patients underwent scleral buckle surgery. Clinical examinations and optical coherence tomography (OCT) were performed post-surgery. MAIA microperimetry was conducted at 6 months.
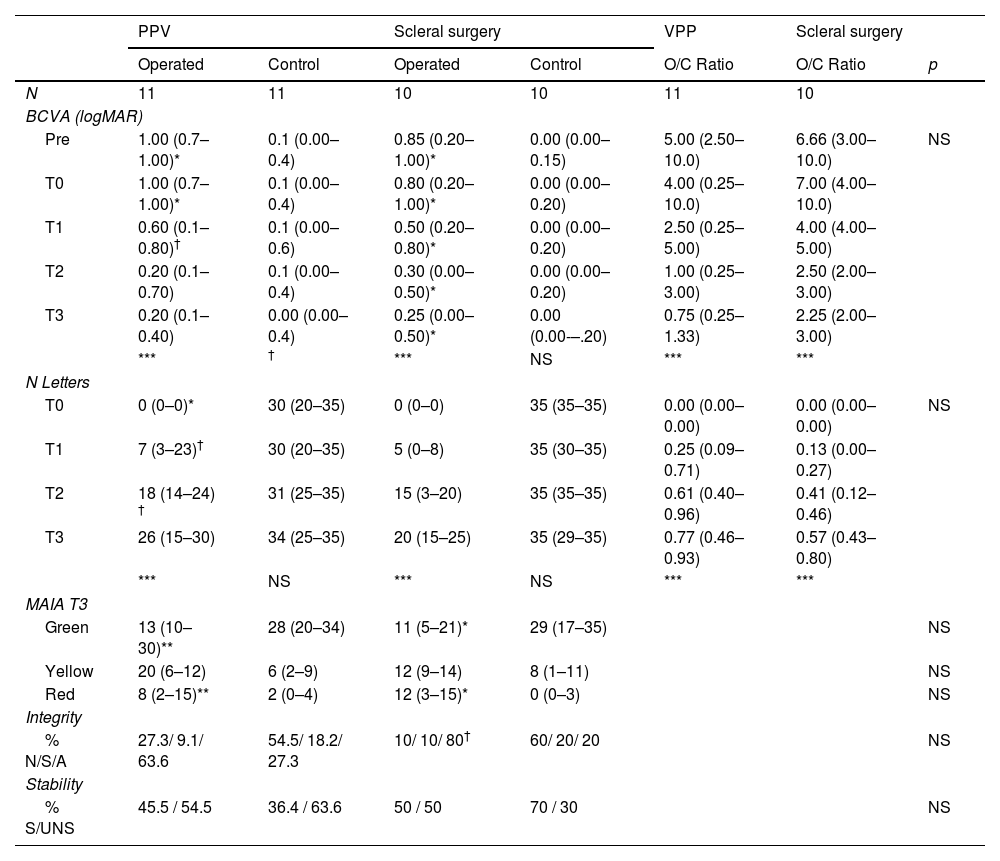
ResultsBest-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and the number of letters read improved over time in the operated eye but did not reach the level of the control eye (p = 0.001). No significant differences were found between the two surgical approaches in BCVA (p = 0.230) or the number of letters read (p = 0.608). Macular integrity in the operated eye did not match that of the control eye in both procedures (p = 0.05). No differences were detected between the two surgeries, either in macular integrity (p = 0.512) or fixation stability (p = 0.835).
ConclusionsFollowing retinal detachment surgery, a decrease in BCVA and the number of letters read occurs, which does not reach the level of the control eye. No significant differences were observed between the two surgical approaches. Macular integrity in the operated eye does not match that of the control eye.
Describir la función visual, integridad macular y la estabilidad de fijación mediante microperimetría MAIA (macular integrity assessment) tras la cirugía de desprendimiento de retina. Valorar si existen diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre cirugías.
Materiales y métodosSe confeccionó un estudio prospectivo, comparativo, intervencionista, reclutando un total de 21 pacientes con desprendimiento regmatógeno de retina y mácula off. 11 pacientes fueron intervenidos mediante vitrectomía vía pars plana (VPP) y 10 pacientes mediante cirugía escleral segmentaria. Se realizaron controles clínicos y mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) tras la cirugía. A los 6 meses se practicó una microperimetría MAIA.
ResultadosLa mejor agudeza visual corregida (MAVC) y el número de letras leídas mejoran a lo largo del tiempo en el ojo intervenido, sin llegar a igualar el ojo control (p = 0,001). No existen diferencias entre ambas cirugías en la MAVC (p = 0.230) ni en número de letras leídas (p = 0,608). La integridad macular en el ojo intervenido no llega a igualar al ojo control en ambos procedimientos (p = 0.05). No se detectan diferencias entre ambas cirugías, ni en integridad macular (p = 0,512) ni en estabilidad de fijación (p = 0,835).
ConclusionesTras la operación del desprendimiento de retina Se produce una disminución en la MAVC y en el número de letras leídas, que no llega a igualar al ojo control. No existen diferencias entre ambas cirugías. La integridad macular no llega a igualar en el ojo intervenido al ojo control.