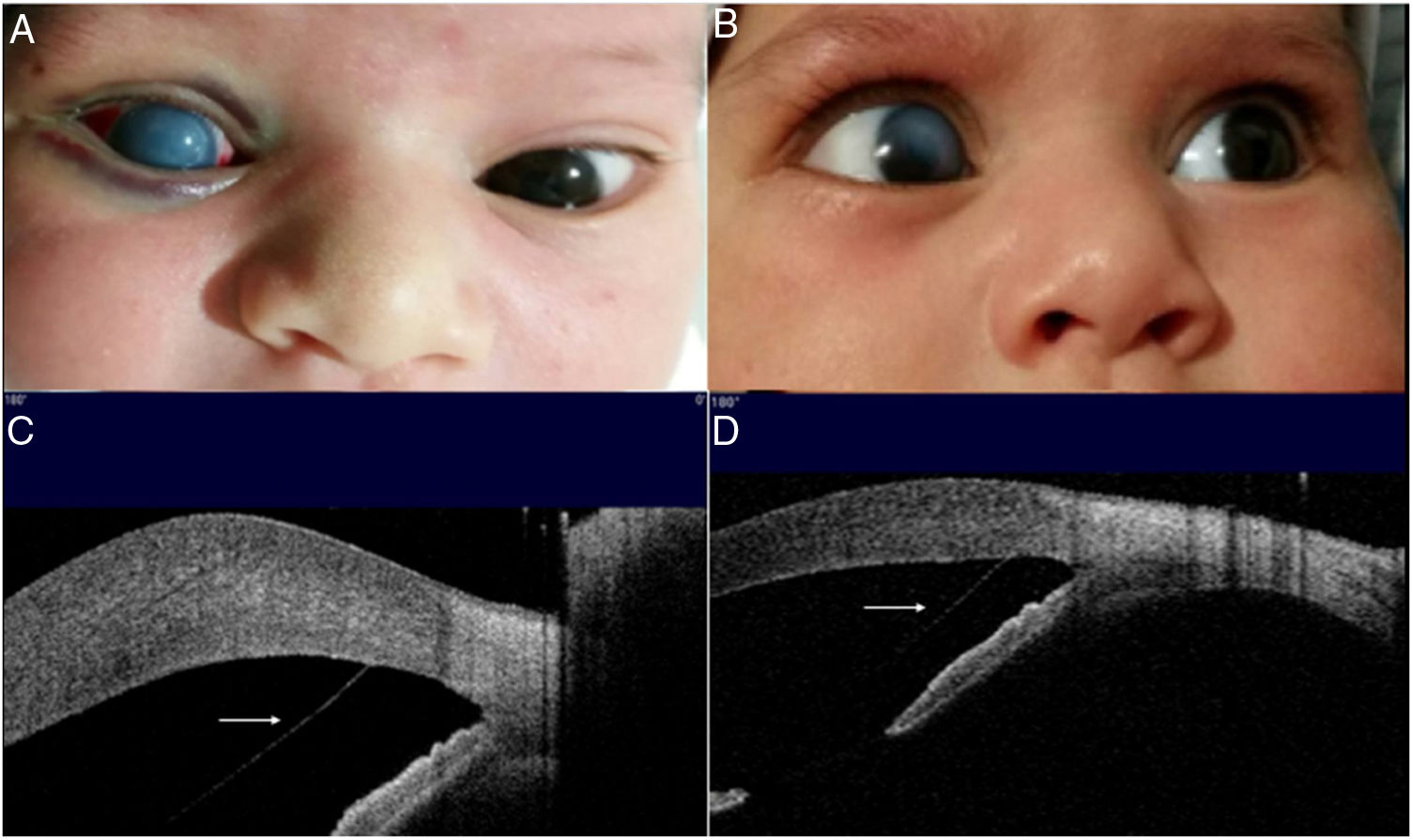
To describe the clinical signs and management of Descemet membrane (DM) detachment after forceps-related trauma during birth. A 2-day-old term infant presented with right eye corneal clouding and history of forceps assisted delivery. Ophthalmic assessment was consistent for corneal trauma and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT Visante®) revealed DM detachment. Prolonged topical treatment considerably reduced edema, but after four months of treatment superior DM detachment persisted, anterior chamber air injection at this point also failed to achieve apposition. Central visual axis remained partially spared in the months to follow, and intensive amblyopia treatment was indicated. Prolonged topical treatment may be helpful to reduce edema and risk of severe amblyopia in DM tears secondary to forceps traumatism at birth, but insufficient in cases of large DM detachment.
Describir los signos clínicos y el manejo del desprendimiento de la membrana de Descemet (MD) secundario a un traumatismo relacionado a fórceps durante el parto. Un recién nacido de término de 2 días de edad se presentó con opacidad corneal del ojo derecho y antecedentes de parto con fórceps. La evaluación oftalmológica fue consistente para traumatismo corneal y en la tomografía de coherencia óptica del segmento anterior (OCT-SA Visante®) se objetivó un desprendimiento de la membrana de Descemet (MD). El tratamiento tópico prolongado redujo considerablemente el edema, y después de cuatro meses con este, el desprendimiento persistía en su porción superior, la inyección de aire en la cámara anterior llegado a este punto tampoco logró la reaplicación. El eje visual se mantuvo parcialmente transparente durante los meses siguientes, y se indicó terapia visual intensiva para evitar la ambliopía. El tratamiento tópico prolongado puede ser útil para reducir el edema y el riesgo de ambliopía severa en las lesiones de la MD secundarias al traumatismo por fórceps durante el parto, pero puede ser insuficiente en casos donde coexista también un desprendimiento de esta.