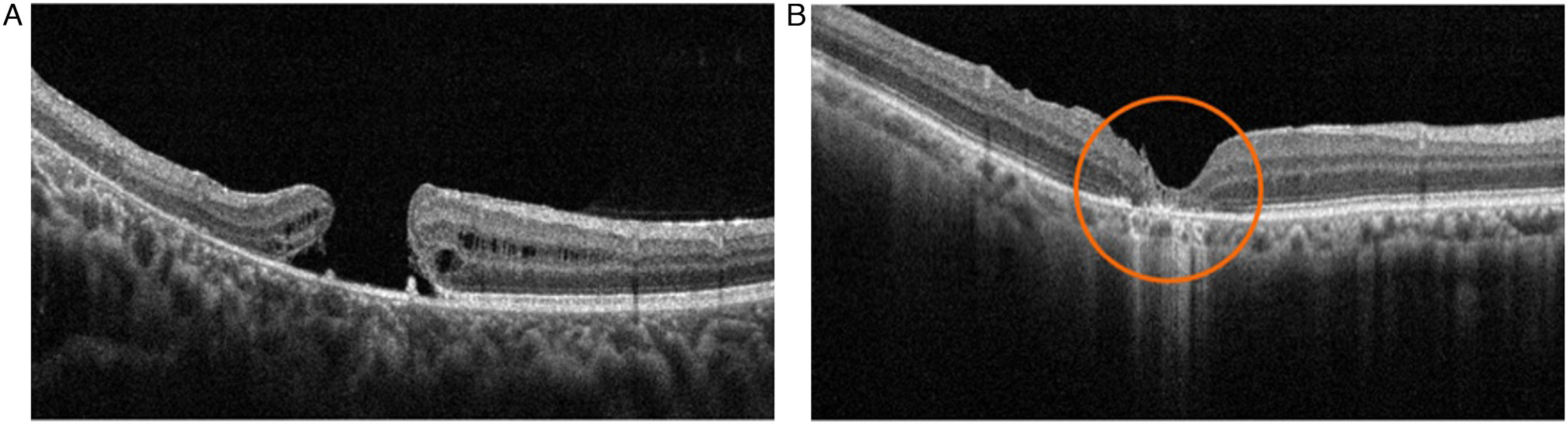
To evaluate the presence of subfoveal hyperreflective dots (SfHD) using optical coherence tomography (OCT) in macular holes (MH) and establish whether there is a relationship with postoperative anatomical and functional outcomes.
MethodsAn observational cross-sectional study was conducted at the Dr. Elías Santana Hospital. Sixty-eight eyes of 67 patients with a tomographic diagnosis of full-thickness MH who underwent pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) and internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling were included. Preoperative and postoperative measurements were obtained using radial macular scans and HD raster scans with Optovue and Cirrus 5000 (Zeiss) OCT machines. The main outcome measures were anatomical closure by OCT and functional outcome through best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA).
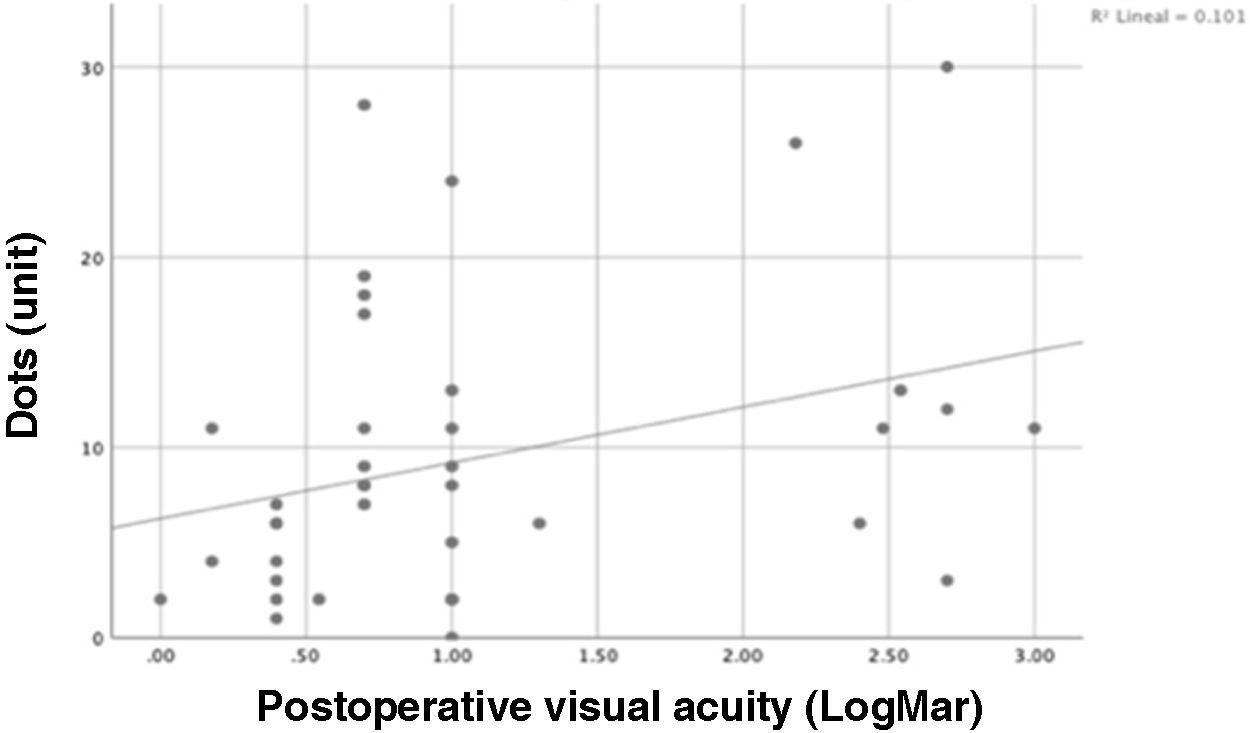
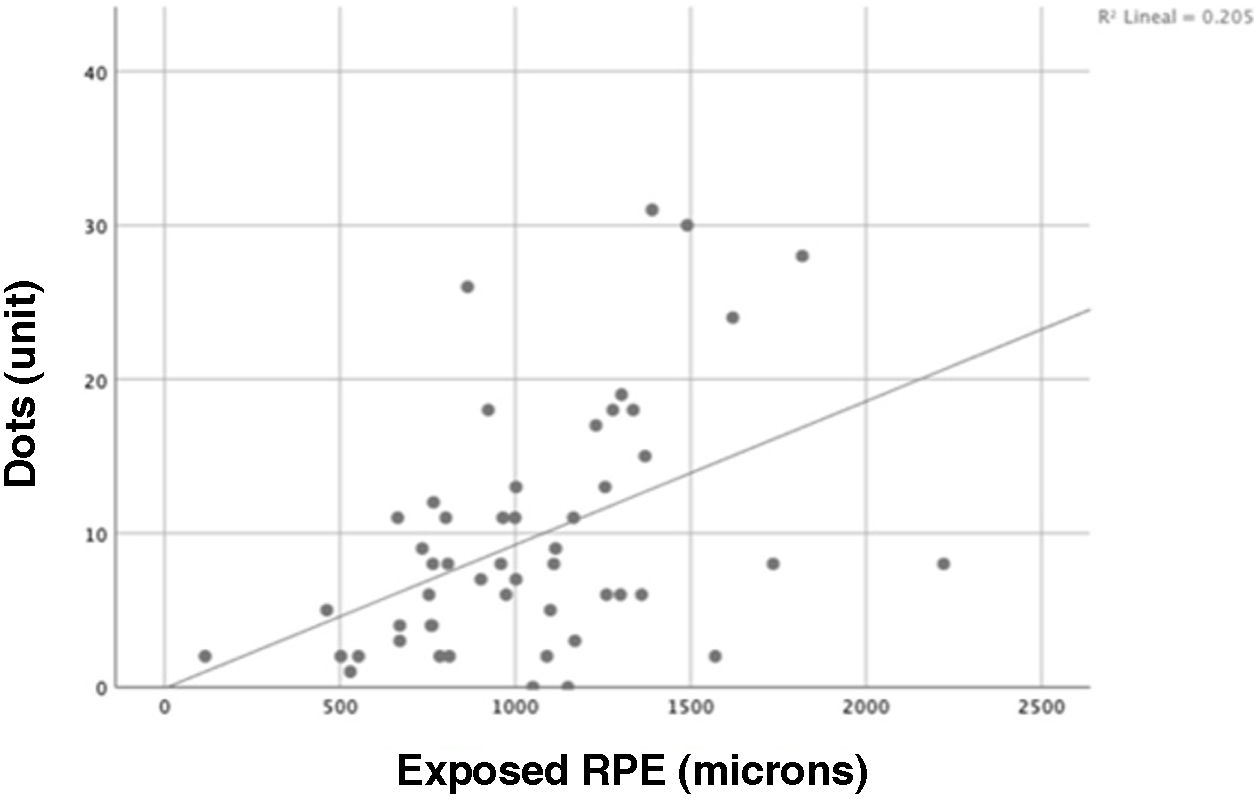
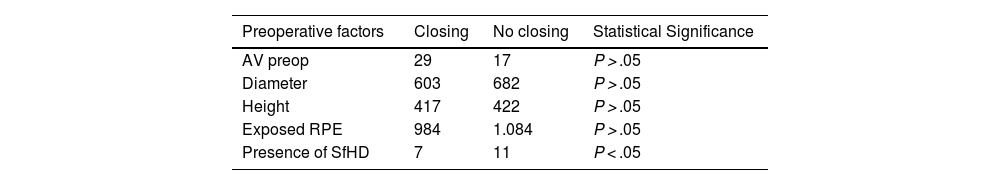
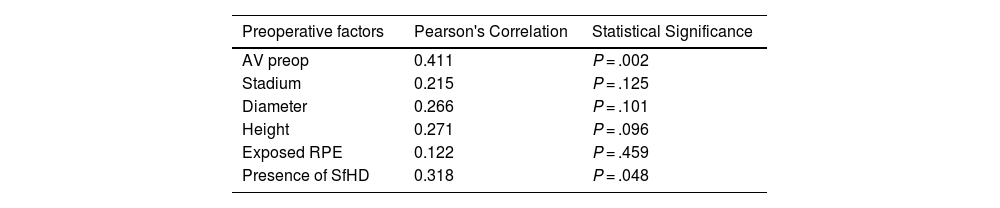
ResultsThe anatomical closure rate in our study was 63%. MHs that failed to achieve anatomical closure exhibited a higher number of hyperreflective dots and worse postoperative BCVA. A statistically significant association was found between exposed retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in microns and the number of SfHD (P = .001).
ConclusionSfHD is a common tomographic finding in MH, and the presence of a higher number of these points is associated with poorer anatomical and functional outcomes. This imaging finding is a potential prognostic biomarker in this pathology.
Evaluar la presencia de puntos hiperreflectivos subfoveales (PHSf) por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) en agujero macular (AM) y establecer si existe relación con los resultados anatómicos y funcionales postoperatorios.
MetodologíaEstudio observacional, de corte transversal realizado en el Hospital Dr. Elías Santana. Se incluyeron 68 ojos de 67 pacientes con diagnóstico tomográfico de AM de espesor total, que fueron sometidos a cirugía de vitrectomía posterior vía pars plana (VPP) y pelado de membrana limitante interna (MLI). Las medidas preoperatorias y postoperatorias se obtuvieron por medio de cortes maculares radiales y HD raster utilizando los equipos OCT Optovue y el Cirrus 5000 (Zeiss). Las medidas de resultados principales fueron el cierre anatómico por OCT y el resultado funcional por medio de la agudeza visual mejor corregida (AVMC).
ResultadosLa tasa de cierre anatómico en nuestro estudio fue de 63%. Para los AM con fallo en el cierre anatómico, se encontró una mayor cantidad de puntos hiperreflectivos y peor AVMC postoperatoria. Se encontró una asociación estadísticamente significativa entre el EPR expuesto en micras y la cantidad de PHSf (P = ,001).
ConclusiónLos PHSf son un hallazgo tomográfico común en AM y la presencia de una mayor cantidad éstos se relaciona con peores resultados anatómicos y funcionales. Este hallazgo imagenológico es un potencial biomarcador pronóstico en esta patología.