To compare the success rate of two laser dacryocystorhinostomy (L-DCR) techniques.
Materials and methodsA retrospective study of patients who underwent surgery for acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) between 2000 and 2021, carried out in a third level hospital, using L-DCR and modifications of this technique. Intraoperative findings, complications, and anatomical and functional success rate of the 2 techniques were analyzed. The follow-up time was 1 year.
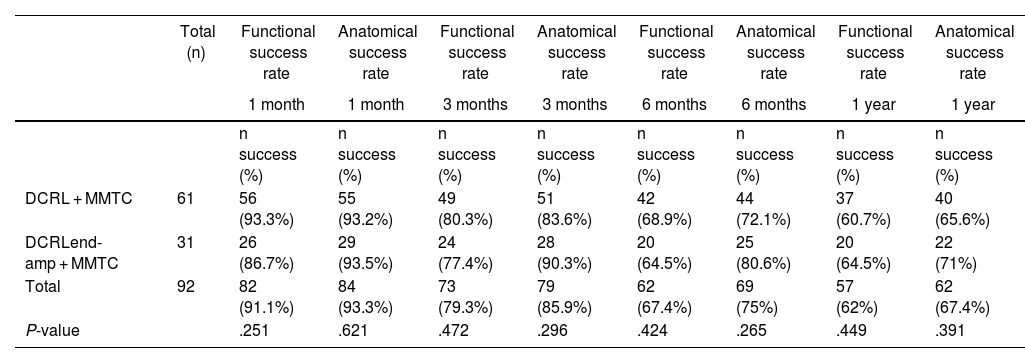
ResultsWe included 92 lacrimal ducts with NLDO. 66 (71.7%) were women. 78 (84.8%) underwent unilateral surgery. The mean age was 62.77 ± 13.08 years.
61 (66.3%) underwent intraoperative laser dacryocystorhinostomy with MMTC (L-DCR + MMTC) and 31 (33.6%) L-DCR associated with endoscopic ostium enlargement (L-DCRend-amp).
The one-year anatomical/functional success rate of the L-DCRend-amp + MMTC was 71%/64,5%. L-DCR + MMTC obtained a lower success rate, 65.6/60,7% (P = .391).
There were no differences throughout the follow-up between the anatomical or functional success rates of the 2 techniques, nor between the different visits (P > ,05).
Intraoperative findings rate was 3.63% in L-DCR + MMTC, and 32.26% in L-DCRend-amp + MMTC.
Postoperative complication rate was 3.27% in L-DCR + MMTC, and 3.23% in L-DCRend-amp + MMTC.
ConclusionsThe L-DCRend-amp + MMTC gets a higher success rate than the L-DCR + MMTC. We must consider the surgical time-cost of the L-DCRend-amp + MMTC, as well as the learning curve of endoscopy techniques, and the skill of the surgeon, without a clear benefit in the success rate.
Comparar la tasa de éxito de dos técnicas de dacriocistorrinostomía láser (DCRL).
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de pacientes intervenidos por obstrucción adquirida de la vía lagrimal (OAVL) entre los años 2000 y 2021 en un hospital de tercer nivel, mediante DCRL con mitomicina intraoperatoria (DCRL + MMTC) y de DCRL asociada a ampliación de ostium con endoscopio y MMTC (DCRLend-amp + MMTC). Se analizaron hallazgos intraoperatorios, complicaciones y tasa éxito anatómico y funcional de las dos técnicas. El tiempo de seguimiento fue de un año.
ResultadosIncluimos 92 vías lagrimales con OAVL. 71,7% mujeres, 84,8% unilaterales y edad media de 62,77 ± 13,08 años.
En 61 vías lagrimales se realizó DCRL + MMTC (66,3%) y en 31 (33,6%) DCRLend-amp + MMTC. La tasa de éxito anatómica/funcional al año de la DCRLend-amp + MMTC fue del 71%/64,5%; la DCRL + MMTC obtuvo una menor tasa de éxito, 65,6%/60,7% (P = ,391). No existen diferencias, a lo largo del seguimiento, entre las tasas de éxito anatómicas ni funcionales de las dos técnicas, ni en las distintas visitas (P > ,05). La tasa de hallazgos intraoperatorios fue 1,63% en DCRL + MMTC y 32,26% en DCRLend-amp + MMTC.
La tasa de complicaciones postoperatorias fue 3,27% en DCRL + MMTC y 3,23% en DCRLend-amp + MMTC.
ConclusionesLa DCRLend-amp + MMTC obtiene una tasa de éxito ligeramente más alta que la DCRL + MMTC. Debemos tener en cuenta el tiempo-coste quirúrgico aumentado de la DCRLend-amp + MMTC, curva de aprendizaje, y destreza del cirujano, sin un beneficio claro en la tasa de éxito.