The classically named ‘choledochal cysts’ are cystic dilatations of the biliary tree. Since 1977, the Todani classification1 has divided them into 5 types: type I, choledochal cyst, which is subdivided into choledochal cyst alone (Ia), segmental dilatation (Ib) and diffuse or cylindrical dilatation (Ic); type II, supraduodenal diverticulum; type III, choledochocele; type IV, extrahepatic and intrahepatic fusiform dilatation (IVa) or multiple extrahepatic cysts (b); and type V multiple intrahepatic saccular dilatation or Caroli disease.
Rarely, the cystic dilation affects the cystic duct (CD), constituting type VI. The first of these well-documented cases dates from 1983,2 and its inclusion as a sixth type was proposed in 1991.3 Although some authors consider it a subtype of II, subtype VIa has recently been proposed for isolated CD dilation, and VIb if there are other associated cysts, mainly of the main bile duct (MBD).4 This lesion is a rarity, whose correct treatment is essential due to the oncogenic potential that extrahepatic biliary cysts entail.
We present a case of Todani type VIa treated by laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
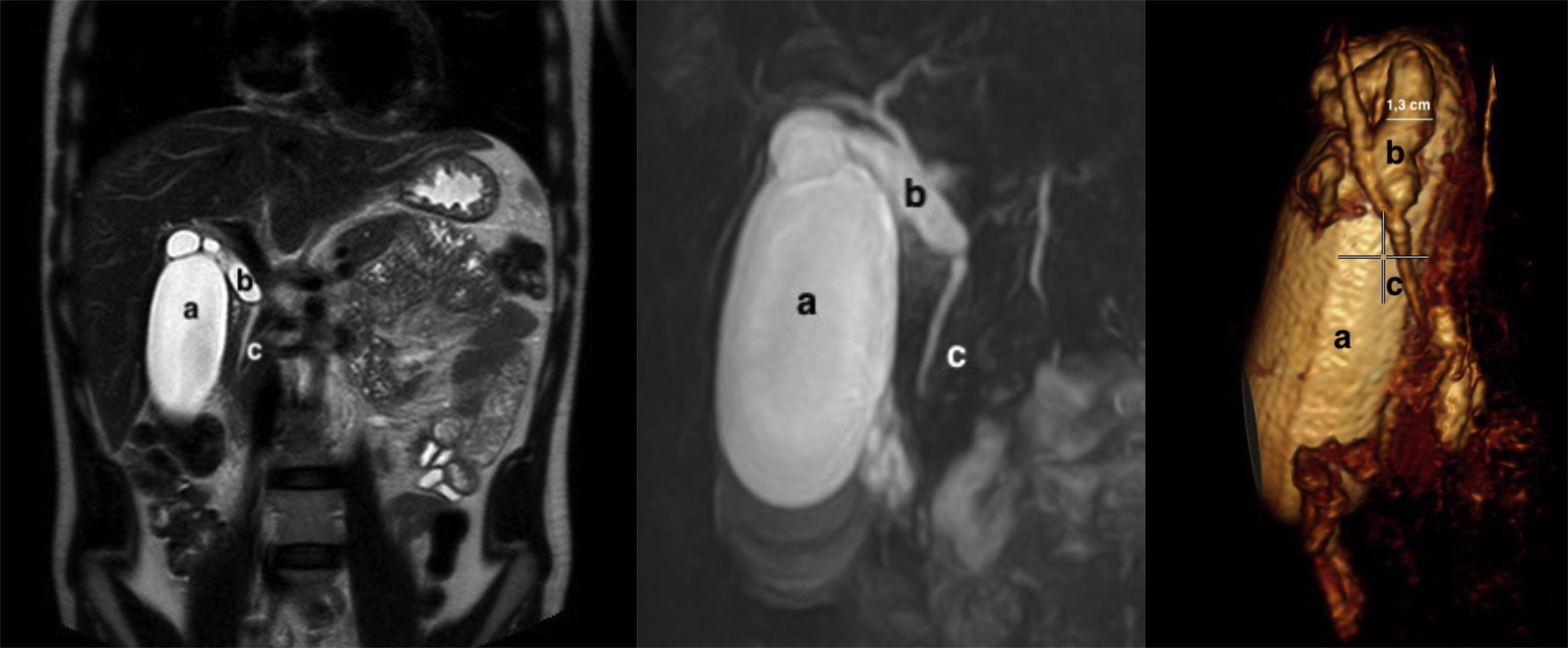
The patient is a 28-year-old man who was asymptomatic and had no medical-surgical history; he reported having discovered a palpable mass in the right hypochondrium. The only analytical alteration was total bilirubin 1.4mg/dL, with a conjugate fraction of 0.7mg/dL. Tumor markers were normal. Ultrasound showed a distended, thin-walled gallbladder measuring 4.5cm×12.3cm and a distended and redundant CD, with no clear cause of the obstruction. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) (Fig. 1) revealed a fusiform cystic dilation of the CD measuring 1.3cm, with a parallel pathway and low implantation. The intrahepatic BD and common bile duct were normal in size, and the distended gallbladder showed no signs of cholecystitis, cholelithiasis or choledocholithiasis. There were no lymphadenopathies or other lesions observed at the pancreatic-duodenal junction.
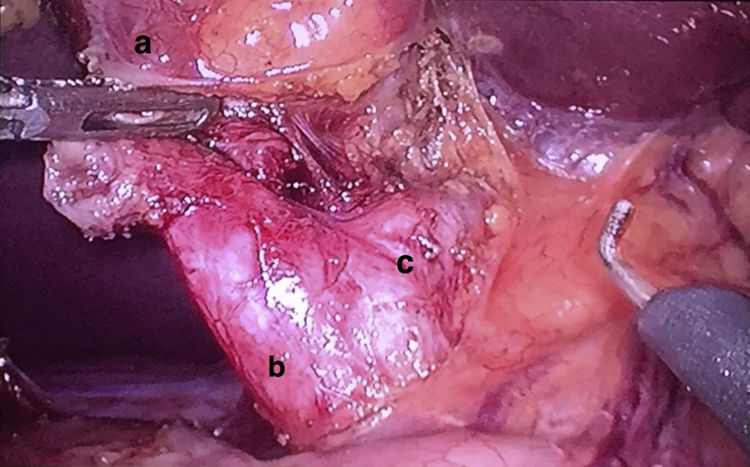
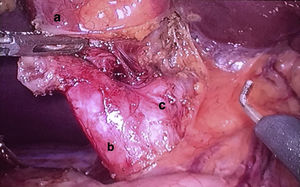
With the diagnosis of cystic malformation of CD (Todani type VI), a laparoscopic exploration was performed, finding a distended gallbladder that was normal in appearance, with a dilated CD up to its union with the BD. Cholecystectomy was performed and the CD was removed in its entirety (Fig. 2), closing the cystic duct with vascular Endo GIA® 45mm.
The pathology study reported a gallbladder measuring 8.5×4cm, with no lithiasis and a mucosa that was normal in appearance and thickness (0.2cm). The CD measured 2cm in length, 1.2cm in diameter and was dilated throughout, with no macroscopic wall lesions.
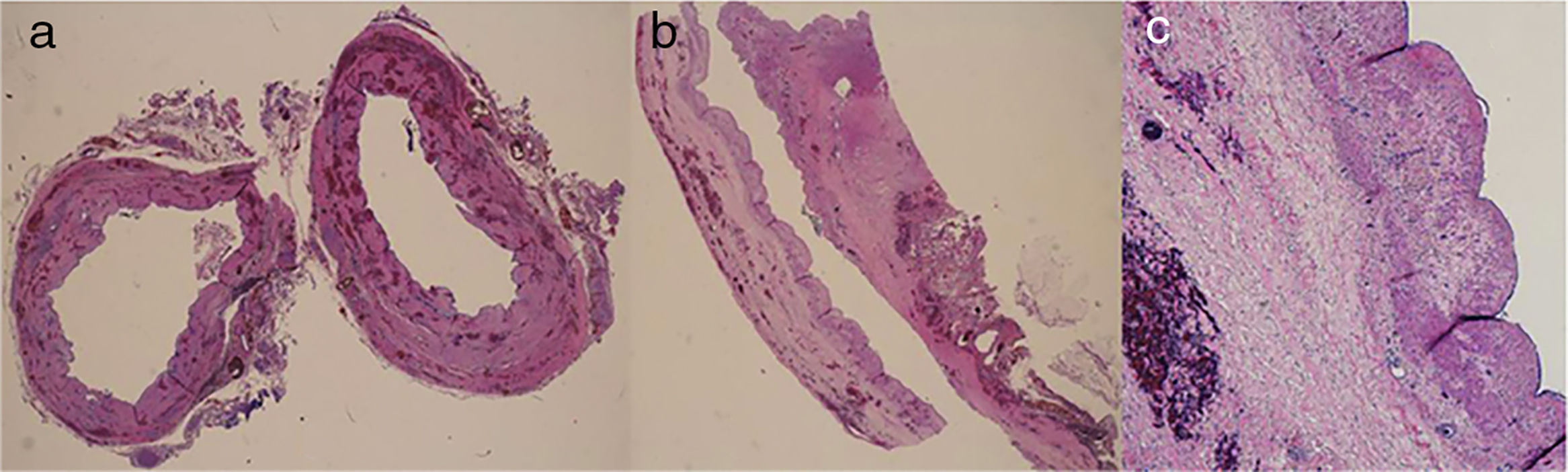
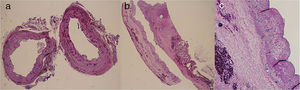
Microscopically, the biliary epithelium appeared flattened, with benign characteristics and no significant alterations (Fig. 3).
The patient was discharged on the second postoperative day, and 9 months later he was asymptomatic and had normal bilirubin levels. The planned follow-up will entail MRCP one year after the intervention and annual lab work with liver profile.
A choledochal cyst is an uncommon entity that is typically pediatric. The most widely accepted etiological hypotheses include: failed multiplication of embryological biliary tract cells, damage due to pancreatic reflux and the distal obstruction of the common bile duct.5 They predominantly affect women (4:1), with incidences from 1/100000 to 1/150000+ in Western societies and up to 1/1000 in Japan.6 The classic triad of jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium and palpable mass is only present in 20% of patients, with at least 2 of the 3 manifestations occurring in 80% of children and only in 25% of adults.6
The diagnostic methodology should preferably include hepatobiliary magnetic resonance and cholangio-resonance imaging, although intraoperative cholangiography or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography may later be indicated. The differential diagnosis includes Mirizzi syndrome, gallbladder duplication and duplicated BD.
Early treatment reduces the incidence of complications and the degree of malignancy, which ranges from 2.5% to 21%,7 especially when associated with anomalies in the biliopancreatic junction. The cyst must be completely resected, given its oncogenic potential,8 which makes it necessary for these cases to be treated by specialized units. The technique varies depending on the affected BD segment: types I, II and IVb require resection of the MBD and reconstruction with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy (RYHJ); type III has a lower malignant potential, therefore it is usually an exception to the general rule of excision, and can be treated by endoscopic sphincterotomy; for type IVa, in addition to resection of the MBD and RYHJ, liver resection of the affected segments is indicated; in localized Caroli disease, partial hepatectomy is indicated, considering transplantation for diffuse cases or those associated with hepatic insufficiency; in type VI, the surgical extension will depend on the union of the cystic duct-cyst with the MBD: in cases with a segment of normal CD at the union with the MBD, as well as in those where the breadth of this union between the cyst-CD and the common bile duct is not too wide, cholecystectomy with excision of the cyst and CD is sufficient from the oncological point of view.9 If there is involvement of the common bile duct or the drainage of the cyst to the MBD is excessively wide, total excision of the extrahepatic BD and bilioenteric reconstruction should be performed, usually with RYHJ.6,9,10 In uncertain cases, intraoperative biopsy may be considered. The postoperative study of surgical margins is required, since there have been cases of degeneration of cystic remnants, especially in the intrapancreatic bile duct, occurring up to 10 years after resection. Therefore, many authors recommend a life-long follow-up.
Thanks to Dr. Alberto Colina Alonso, Head of the Department and the Clinical Management Unit of General and Digestive Surgery at the Hospital Universitario Cruces, for his research and surgical training support.
Please cite this article as: Perfecto Valero A, Gastaca Mateo M, Prieto Calvo M, Ortiz de Urbina López J, Valdivieso López A. Quiste biliar del conducto cístico. Un caso de Todani tipo VI. Cir Esp. 2018;96:658–660.