El objetivo de este estudio es comparar la visualización de la unión cisticocoledocal con verde de indocianina (ICG) entre 3 grupos de pacientes divididos según la dificultad preoperatoria de la colecistectomía laparoscópica electiva.
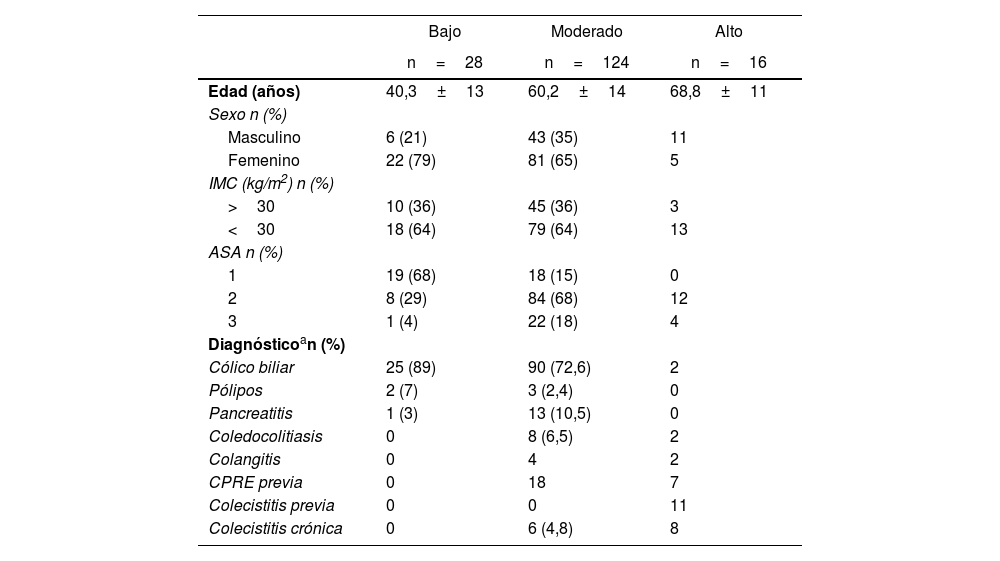
MétodosEstudio observacional, prospectivo no aleatorizado, realizado en un único centro con una cohorte de 168 pacientes sometidos a colecistectomía laparoscópica electiva a quienes se les calculó un score preoperatorio de riesgo predictivo de colecistectomía difícil publicado por A. Nassar en 2019 que incluyó datos clínicos y radiológicos. Se obtuvieron 3 grupos de riesgo: bajo, moderado y alto riesgo. Se administró 0,25mg de ICG i.v. durante la inducción anestésica y se evaluaron los diferentes objetivos.
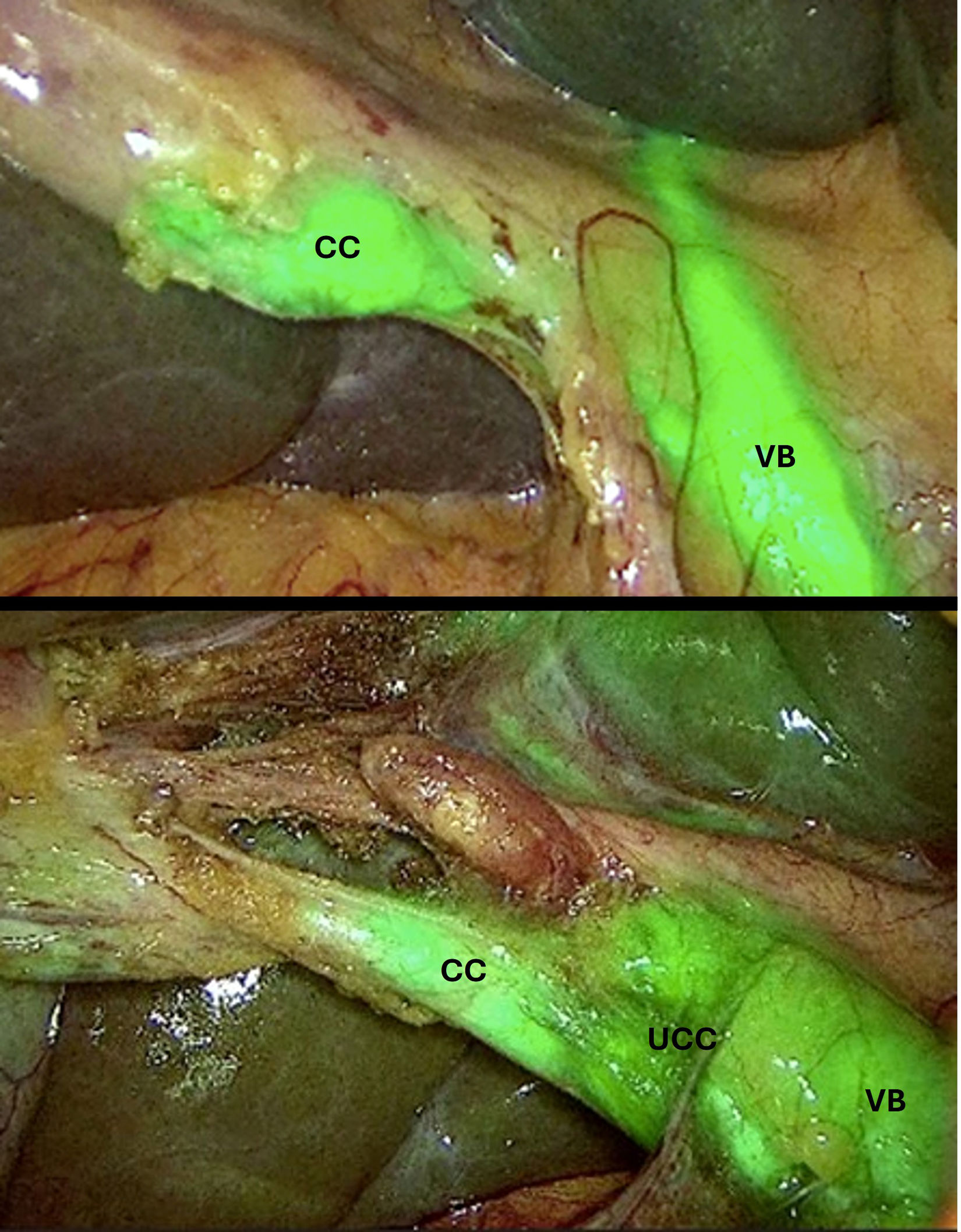
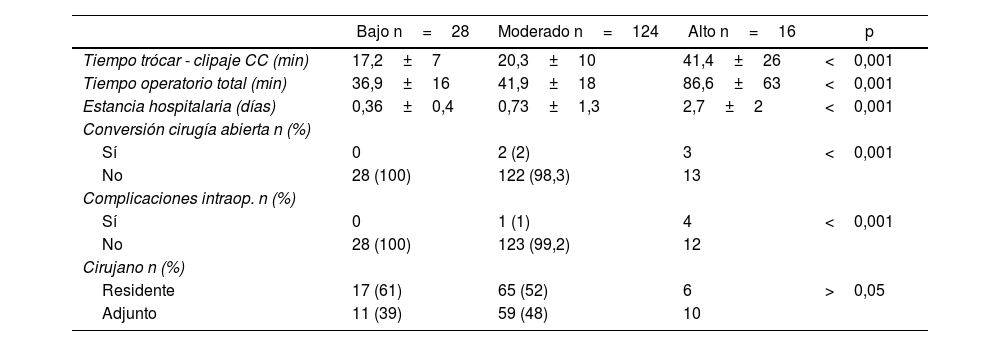
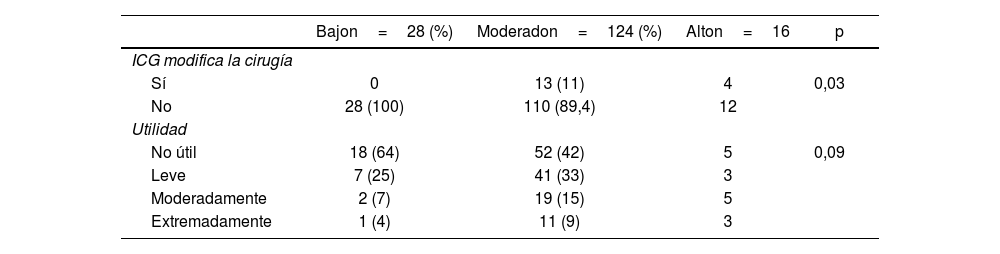
ResultadosLa visualización de la unión cisticocoledocal se consiguió en 28 (100%), 113 (91,1%) y 10 (63%) pacientes del grupo de bajo, moderado y alto riesgo, respectivamente. El grupo de alto riesgo presentó mayor tiempo quirúrgico, conversión a cirugía abierta, complicaciones y estancia hospitalaria. En cuanto a la valoración subjetiva del cirujano, el uso de ICG se consideró útil en el 36% de los pacientes de bajo riesgo, 58% de moderado riesgo y 69% de alto riesgo. Asimismo, modificó la estrategia quirúrgica en el 25% de los pacientes del grupo de alto riesgo comparado con el 11% del moderado y ninguno del bajo riesgo (p<0,01).
ConclusionesEn las colecistectomías difíciles la visualización de la unión cisticocoledocal se consigue en el 63% de los casos y condiciona una modificación del procedimiento quirúrgico en uno de cada 4 pacientes.
This study aims to compare the visualization of the cystic duct-common bile duct junction with indocyanine green (ICG) among 3 groups of patients divided according to the difficulty of elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
MethodsConducted at a single center, this non-randomized, prospective, observational study encompassed 168 patients who underwent elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy and were assessed with a preoperative risk score to predict difficult cholecystectomies, including clinical factors and radiological findings. Three groups were identified: low, moderate, and high risk. A dose of 0.25mg of IV ICG was administered during anesthesia induction and the different objectives were evaluated.
ResultsThe visualization of the cystic duct-common bile duct junction was achieved in 28 (100%), 113 (91.1%), and 10 (63%) patients in the low, moderate, and high-risk groups, respectively. The high-risk group had longer total operative time, higher conversion, more complications and longer hospital stay. In the surgeon's subjective assessment, ICG was considered useful in 36% of the low-risk group, 58% in the moderate-risk group, and 69% in the high-risk group. Additionally, there were no cases where ICG modified the surgeon's surgical approach in the low-risk group, compared to 11% in the moderate-risk group and 25% in the high-risk group (p<0.01).
ConclusionsThe results of this study confirm that in the case of difficult cholecystectomies, the visualization of the cystic duct-common bile duct junction is achieved in 63% of cases and prompts a modification of the surgical procedure in one out of four patients.