The aim of this study was to investigate presence of subclinical atherosclerosis by measuring carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) in patients with Helicobacter pylori (HP) and to assess effects of HP on atherosclerosis by evaluating markers of atherosclerosis and blood growth differentiation factor (GDF-15) levels.
Materials and methodsThis cross-sectional study included 59 patients without comorbid disease who had HP and 30 healthy controls without HP in upper endoscopic biopsy. In order to assess atherosclerosis, the CIMT measurement was performed by sonography. Serum GDF-15 level was measured by ELISA method. In all patients, atherosclerosis markers were recorded. Atherogenic indices were calculated, including Castelli risk index I and II (TG/HDL-c and LDL-c/HDL-c, respectively), plasma atherogenic index (PAI; log TG/HDL-c), non-HDL-c (TH-HDL-c) and atherogenic coefficient (AC; non-HDL-HDL-c).
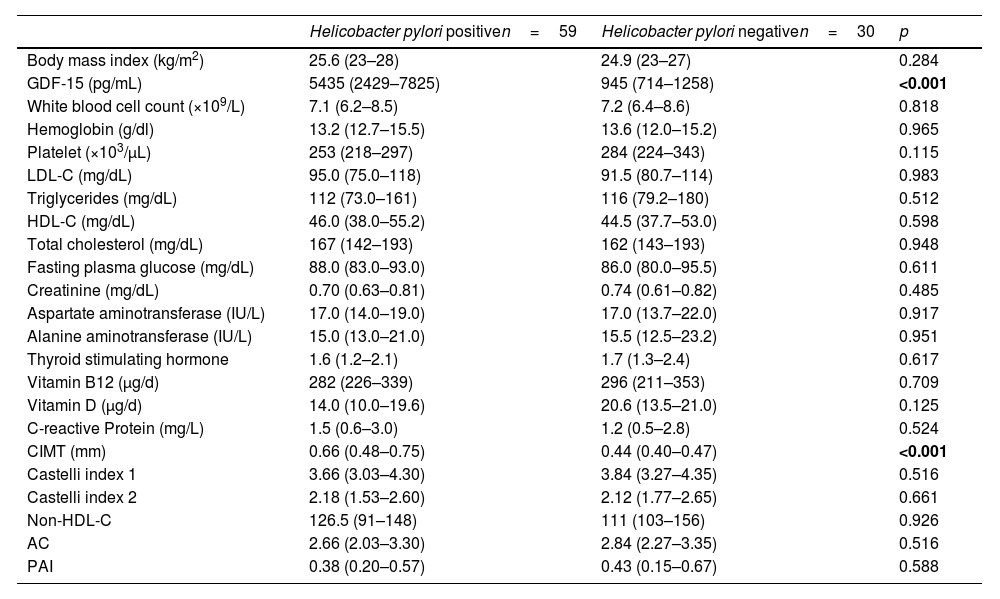
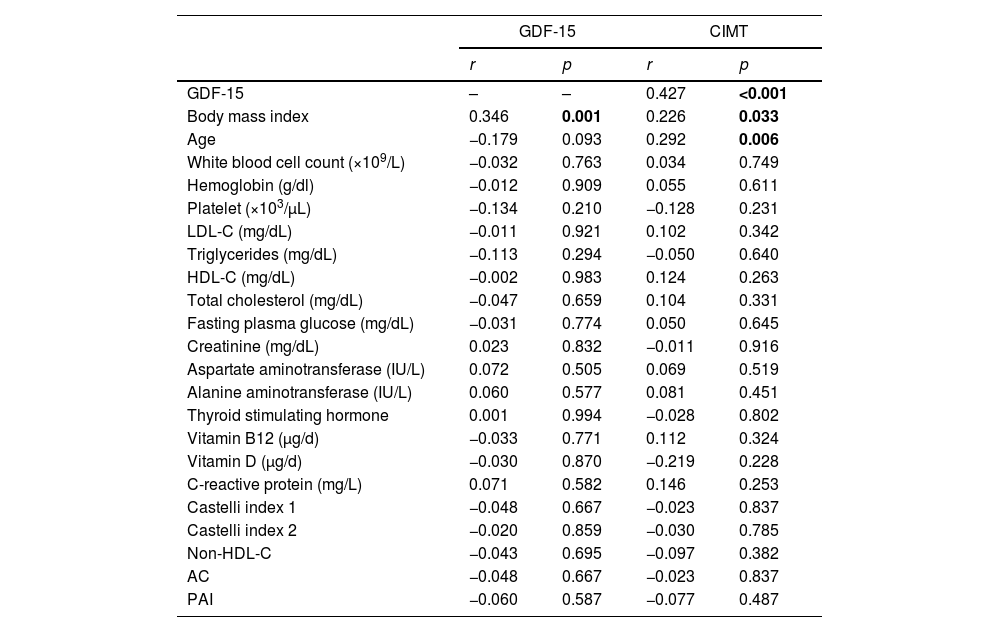
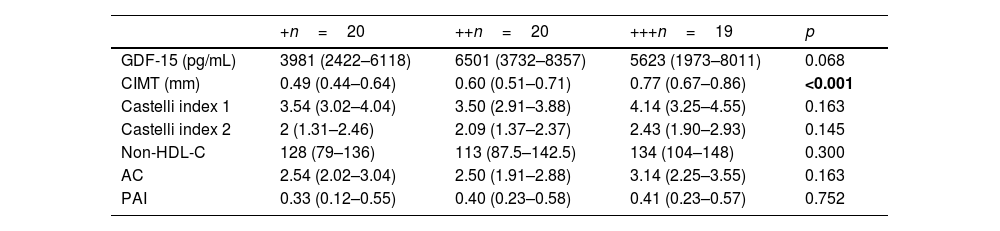
ResultsThe GDF-15 level and CIMT were significantly higher in HP-positive group when compared to HP-negative group (p≤0.001). There was a significant correlation between serum GDF-15 level and CIMT (r=0.445; p≤0.001). There was no correlation between other atherosclerosis markers and serum GDF-15 level or CIMT. The bacterial intensity on endoscopic specimen was only correlated with CIMT (p<0.001). Vitamin B12 and D levels were comparable among groups.
ConclusionThis study suggested that there was a correlation between GDF-15 level and subclinical atherosclerosis development in patients with HP. However, GDF-15 level, which was found to be elevated while atherogenic indices were normal, can be an earlier marker for subclinical atherosclerosis.
El objetivo de este estudio fue investigar la presencia de aterosclerosis subclínica mediante la medición del grosor íntima-media de la carótida (GIMC) en pacientes con Helicobacter pylori y evaluar los efectos de H.pylori sobre la aterosclerosis mediante la evaluación de marcadores de aterosclerosis y de niveles de factor de diferenciación del crecimiento sanguíneo (growth differentiation factor 15 [GDF-15]).
Materiales y métodosEste estudio transversal incluyó 59 pacientes sin enfermedad comórbida que tenían H.pylori y 30 controles sanos sin H.pylori en la biopsia endoscópica superior. Para evaluar la aterosclerosis, la medición de GIMC se realizó mediante ecografía. El nivel de GDF-15 en suero se midió mediante el método ELISA. En todos los pacientes se registraron marcadores de aterosclerosis. Se calcularon los índices aterogénicos, incluyendo el índice de riesgo de Castelli I y II (TG/cHDL y cLDL-cHDL, respectivamente), el índice aterogénico plasmático (PAI; log TG/HDL-c), no-cHDL (TH-cHDL) y el coeficiente aterogénico (no-HDL-cHDL).
ResultadosLos niveles de GDF-15 y de GIMC fueron significativamente más altos en el grupo H.pylori positivo en comparación con el grupo H.pylori negativo (p≤0,001). Hubo una fuerte correlación entre el nivel sérico de GDF-15 y el GIMC (r=0,445; p≤0,001). No hubo correlación entre otros marcadores de aterosclerosis y el nivel sérico de GDF-15 o GIMC. La intensidad bacteriana en la muestra endoscópica solo se correlacionó con GIMC (p≤0,001). Los niveles de vitaminaB12 y de vitaminaD fueron comparables entre los grupos.
ConclusiónEste estudio sugirió que había una correlación entre el nivel de GDF-15 y el desarrollo de aterosclerosis subclínica en pacientes con H.pylori. Sin embargo, el nivel de GDF-15, que se encontró elevado mientras que los índices aterogénicos eran normales, puede ser un marcador temprano de aterosclerosis subclínica.