Combined oral contraceptives (COCs), use in individuals are associated with increased risk of thrombotic events. This highlights the significance of assessing the impact of COC on promoting coagulation and endothelial activation in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed Sprague Dawley rats.
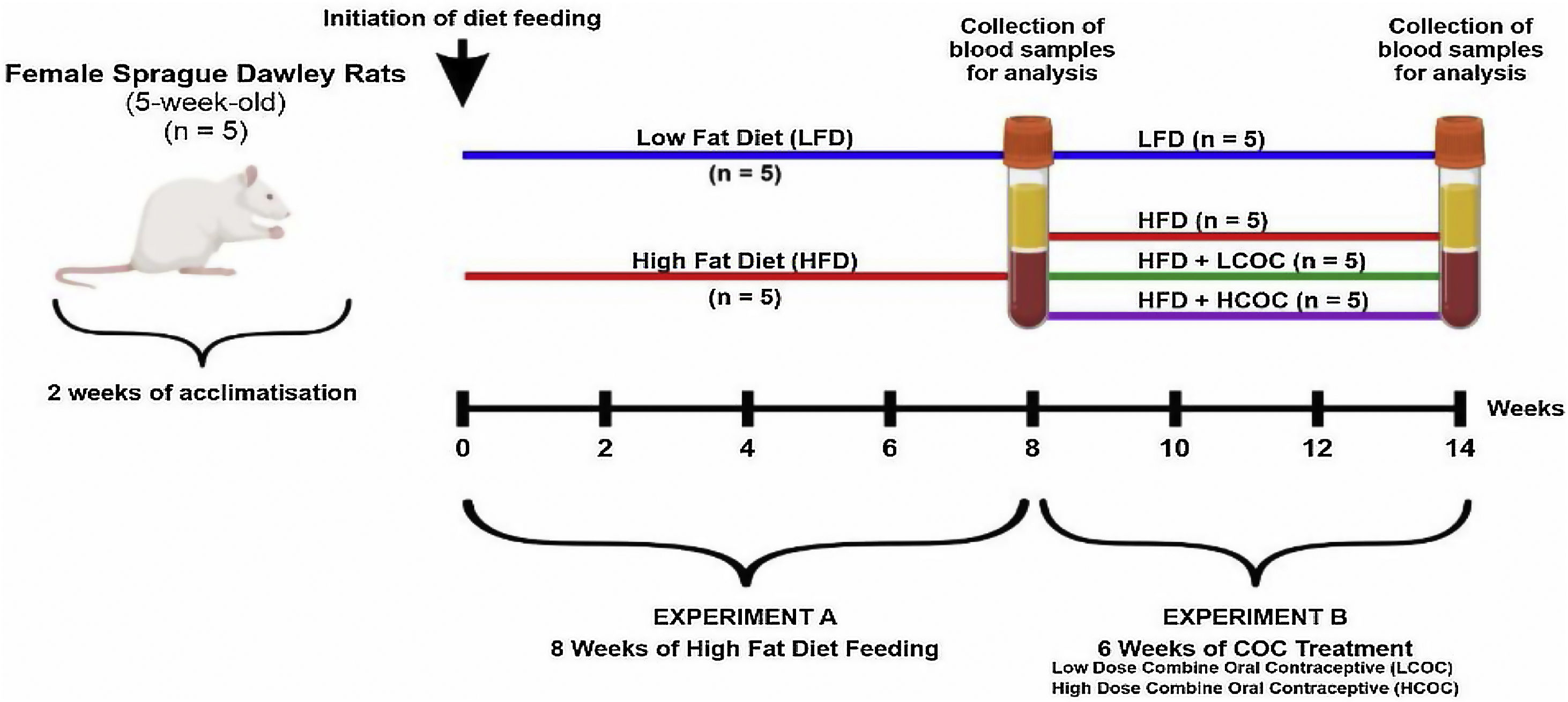
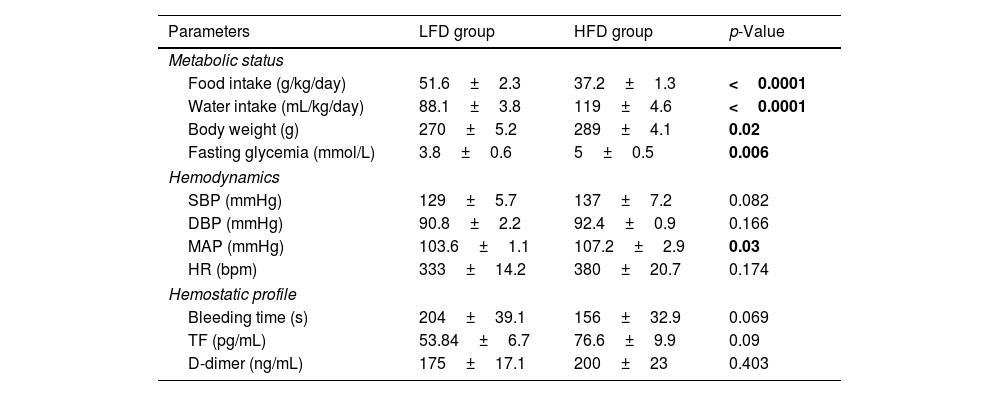
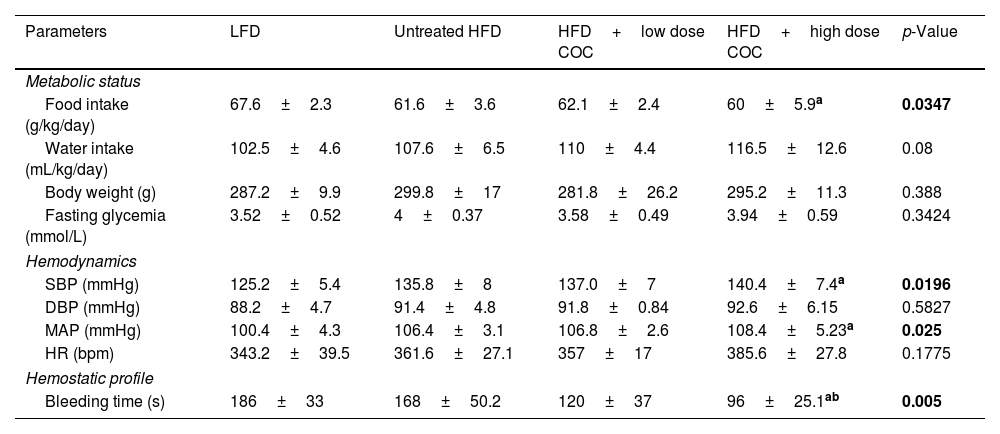
MethodsTwenty (20) five-weeks-old female Sprague Dawley rats weighing between 150 and 200g were subjected to both LFD and HFD-feeding for 8-weeks to determine its influence on basic metabolic status, hemostatic profile, hemodynamic parameters (blood pressure and heart rate), as well as selected biomarkers of coagulation (tissue factor and D-dimer) and endothelial activation (Von Willebrand factor and nitric oxide). Thereafter HFD-fed animals were treated with receive high dose combined oral contraceptive (HCOC) and low dose combine oral contraceptive (LCOC) for 6 weeks.
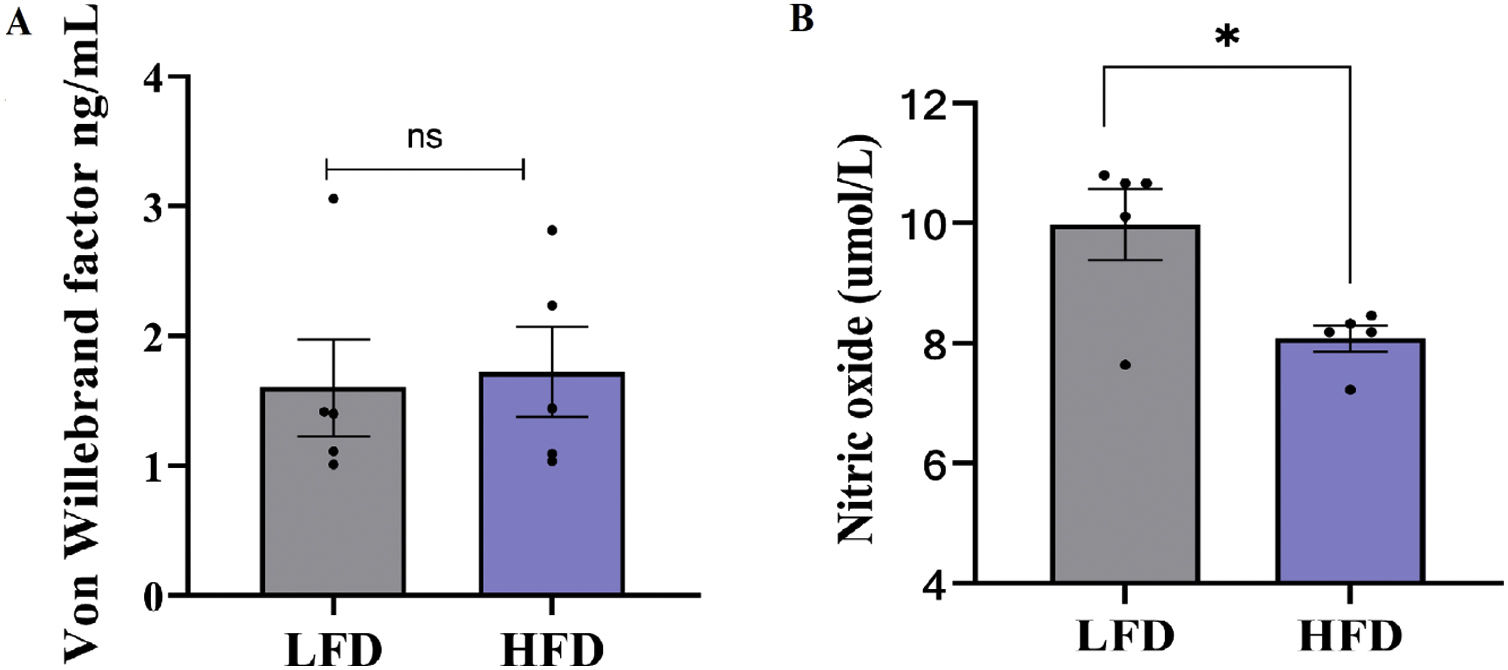
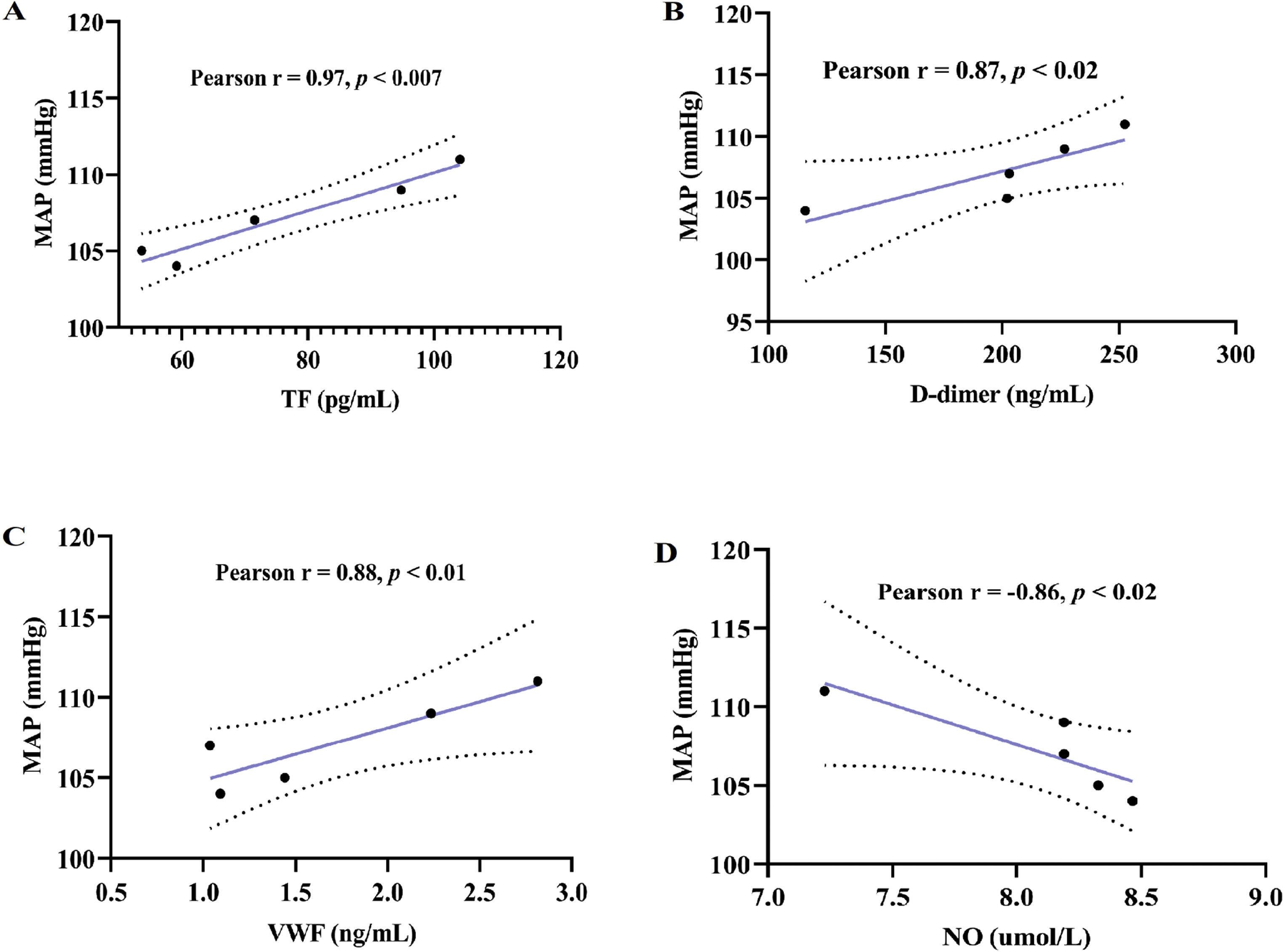
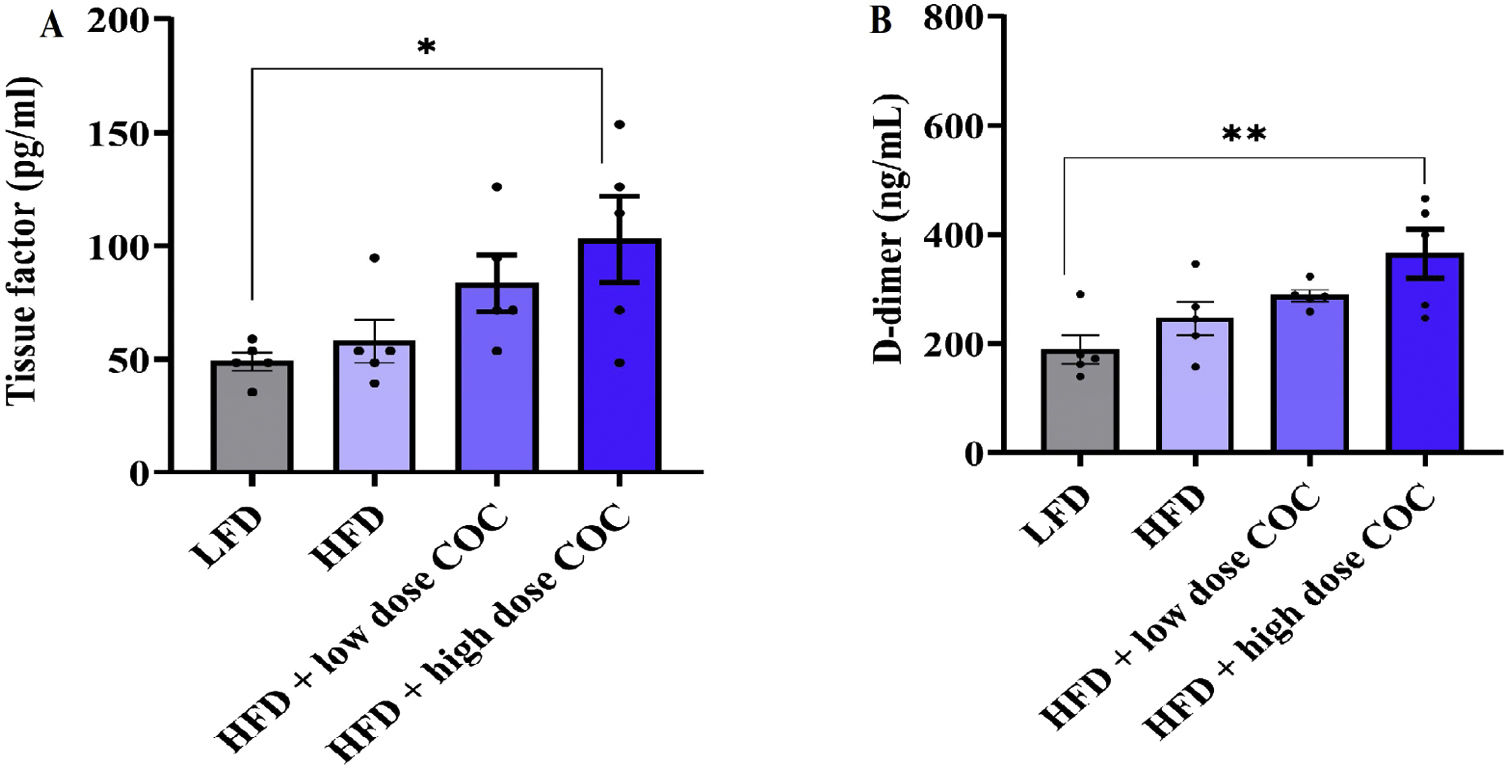
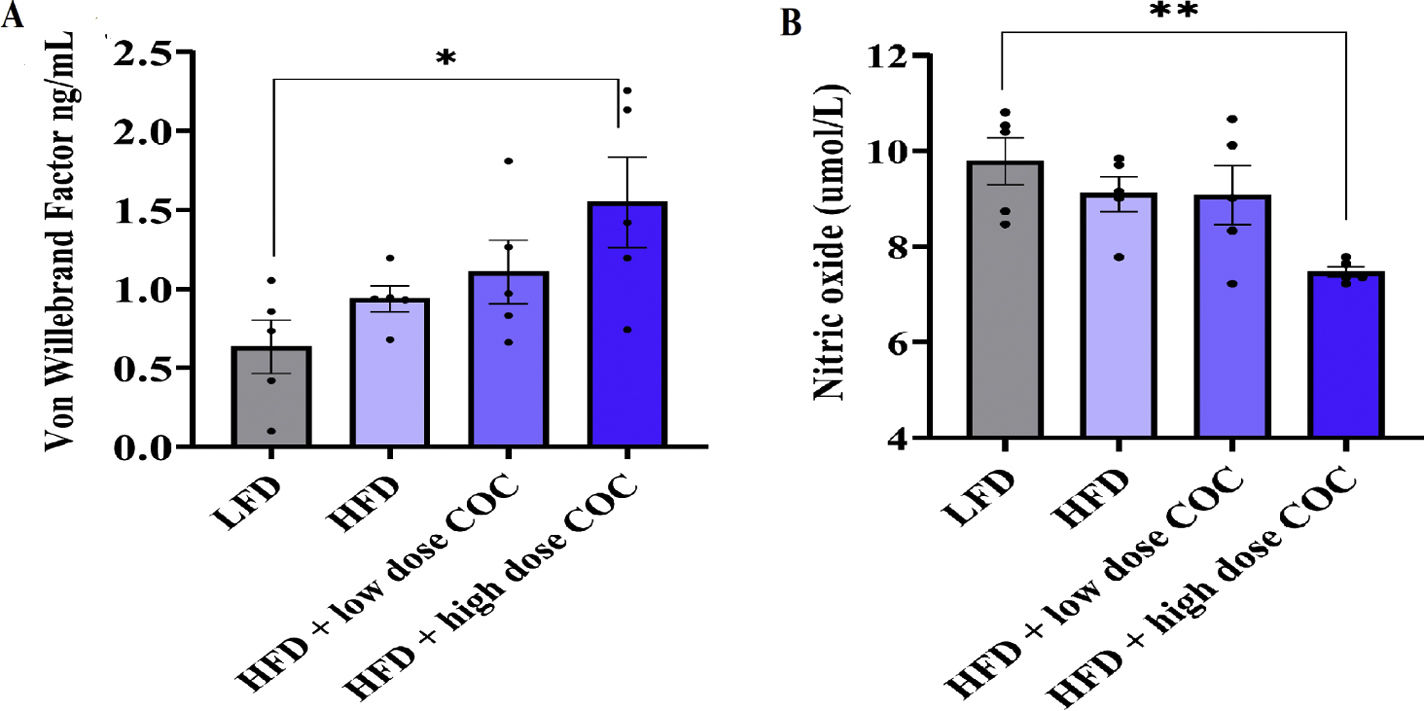
ResultsOur results showed that beyond weight gain, HFD-feeding was associated with hyperglycemia, increased mean arterial pressure, and reduced nitric oxide levels when compared with LFD group (p<0.05). Interestingly, treatment with high dose of COC for 6-weeks did not significantly alter atherothrombotic markers (p>0.05). However, this study is not without limitation as regulation of these markers remains to be confirmed within the cardiac tissues or endothelial cells of these animals.
ConclusionHFD-feeding orchestrate the concomitant release of pro-coagulants and endothelial activation markers in rats leading to haemostatic imbalance and endothelial dysfunction. Short-term treatment with COC shows no detrimental effects in these HFD-fed rats. Although in terms of clinical relevance, our findings depict the notion that the risk of CVD in association with COC may depend on the dosage and duration of use among other factors especially in certain conditions. However, additional studies are required to confirm these findings, especially long-term effects of this treatment within the cardiac tissues or endothelial cells of these animals in certain conditions relating to postmenopausal state.
El uso de anticonceptivos orales combinados (AOC) en individuos se asocia con un mayor riesgo de eventos trombóticos. Esto resalta la importancia de evaluar el impacto de los AOC en la promoción de la coagulación y la activación endotelial en ratas Sprague Dawley alimentadas con una dieta alta en grasas (HFD).
MétodosVeinte (20) ratas Sprague Dawley hembra de 5semanas de edad con un peso entre 150-200g fueron tratadas mediante una alimentación con dieta baja en grasas (LFD) y alta en grasas (HFD) durante 8 semanas para determinar su influencia en el estado metabólico básico, perfil hemostático, parámetros hemodinámicos (presión arterial y frecuencia cardíaca), así como biomarcadores seleccionados de coagulación (factor tisular y D-dímero) y activación endotelial (factor de von Willebrand y óxido nítrico). Posteriormente, los animales alimentados con HFD fueron tratados con dosis alta de anticonceptivo oral combinado (AOC-AL) y dosis baja de anticonceptivo oral combinado (AOC-BL) durante 6 semanas.
ResultadosNuestros resultados mostraron que, además del aumento de peso, la alimentación con HFD se asoció con hiperglucemia, aumento de la presión arterial media y niveles reducidos de óxido nítrico en comparación con el grupo LFD (p<0,05). Curiosamente, el tratamiento con dosis alta de AOC durante 6 semanas no alteró significativamente los marcadores aterotrombóticos (p>0,05). Sin embargo, este estudio no está exento de limitaciones, ya que la regulación de estos marcadores aún debe confirmarse en los tejidos cardíacos o las células endoteliales de estos animales.
ConclusiónLa alimentación con HFD orquesta la liberación concomitante de procoagulantes y marcadores de activación endotelial en ratas, lo que conduce a un desequilibrio hemostático y disfunción endotelial. El tratamiento a corto plazo con AOC no muestra efectos perjudiciales en estas ratas alimentadas con HFD. Aunque, en términos de relevancia clínica, nuestros hallazgos representan la idea de que el riesgo de enfermedad cardiovascular en relación con el AOC puede depender de la dosis y la duración de uso, entre otros factores, especialmente en ciertas condiciones. Sin embargo, se requieren estudios adicionales para confirmar estos hallazgos, especialmente los efectos a largo plazo de este tratamiento en los tejidos cardíacos o las células endoteliales de estos animales en ciertas condiciones relacionadas con el estado posmenopáusico.