The opinion of professionals about multidisciplinary teams (MDT) in thyroid cancer has not been studied in Spain. This study was intended to ascertain the opinion of specialists about the characteristics of the professionals and the advantages provided by these teams.
MethodsA survey was designed to assess the opinion about the characteristics of professionalism and the advantages of MDT for patients, professionals, and the health care system. The survey was posted online from November 15, 2017 to February 15, 2018.
ResultsA total of 226 surveys were evaluated. The ability for teamwork was considered the most important characteristic to be met by professionals by 37.2% of respondents, while scientific competence was the most important indicator of professionalism for 37.6%. More than two thirds of specialists felt that MDTs improve the choice of treatments and diagnostic procedures, decrease clinical variability, facilitate implementation of clinical guidelines, improve ongoing training, and increase patient satisfaction and hospital prestige. The degree of agreement with the advantages of MDTs was significantly higher among specialists who had a MDT at their hospitals.
ConclusionsThe overall opinion of professionals on the MDT model is highly favorable. Hospital managers and health care authorities should take these facts into account in order to encourage and support implementation of these teams.
En nuestro país no se ha estudiado la opinión de los profesionales sobre los equipos multidisciplinares en cáncer de tiroides. El objetivo de este estudio ha sido conocer la opinión de los especialistas sobre las características de los profesionales y las ventajas que aportan estos estos equipos.
MétodosSe diseñó una encuesta para valorar la opinión sobre las características de profesionalidad y las ventajas de los equipos multidisciplinares para pacientes, profesionales y sistema sanitario. La encuesta se mantuvo activa online del 15 de noviembre de 2017 al 15 de febrero de 2018.
ResultadosSe recibieron 226 encuestas. La capacidad para trabajar en equipo fue considerada la característica más importante que deben cumplir los profesionales por el 37,2% de los encuestados, mientras que la competencia científica fue el indicador de profesionalidad más importante para el 37,6%. Más de 2/3 de los especialistas opinan que los equipos multidisciplinares mejoran la elección de tratamientos y procedimientos diagnósticos, reducen la variabilidad clínica, facilitan la implementación de las guías clínicas, mejoran la formación continuada y aumentan la satisfacción de los pacientes, así como el prestigio del hospital. El grado de acuerdo con las ventajas de los EMD fue significativamente superior entre los especialistas que contaban con un EMD en su hospital.
ConclusionesEstos resultados muestran una opinión globalmente muy favorable de los profesionales hacia el modelo de trabajo multidisciplinar. Los responsables de los hospitales y las autoridades sanitarias deberían tener en cuenta estos hechos para favorecer y apoyar la implantación de estos equipos.
Multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) are currently considered to be an optimum model for the care of cancer patients, since they offer decisions based on consensus among different specialists experienced in the management of neoplastic disease, and allow a holistic approach to patients and their disease from diagnosis and over long-term follow-up.1–3 In the area of thyroid cancer, the Spanish Society of Endocrinology and Nutrition (Sociedad Española de Endocrinología y Nutrición [SEEN]) has recently published a consensus document on the definition, composition, requirements, structure and functioning of a MDT for the integral care of thyroid cancer patients. The document establishes requirements for specialists in MDTs, as well as objective indicators of professional quality.4
Multidisciplinary teams offer clinicians a cross-sectional organization model whose effectiveness in a real life setting largely depends on the motivation, interest, skills and professionalism of the participating members. It is therefore essential to directly know the opinion of the professionals regarding the requirements of the participating members and the advantages afforded by MDTs in the management of thyroid cancer. Although some studies have been published analyzing professional perception of MDTs in reference to different tumor types,5,6 to the best of our knowledge this aspect has not been explored to date in thyroid cancer. We therefore designed this research project in order to ascertain the opinion of the professionals involved in the management of patients with thyroid cancer regarding the usefulness and advantages of MDTs.
MethodsStudy designOur aim was to ascertain the opinion of the different specialists regarding the characteristics required of those professionals wishing to belong to MDTs in thyroid cancer, as well as the advantages which such teams offer patients, professionals and the healthcare system. With this aim in mind, we prepared a survey model that was evaluated in several discussion rounds among the authors through e-mail contact. A survey was finally designed, composed of three parts: one referring to personal and professional data; another addressing the professional characteristics of the team members; and a third part on the advantages of these teams. The design of the questionnaire and the specific aspects that the responders were asked about were based on a literature review which we carried out before the aforementioned consensus document, and which is reflected in Tables 1 and 2 of the final article.4
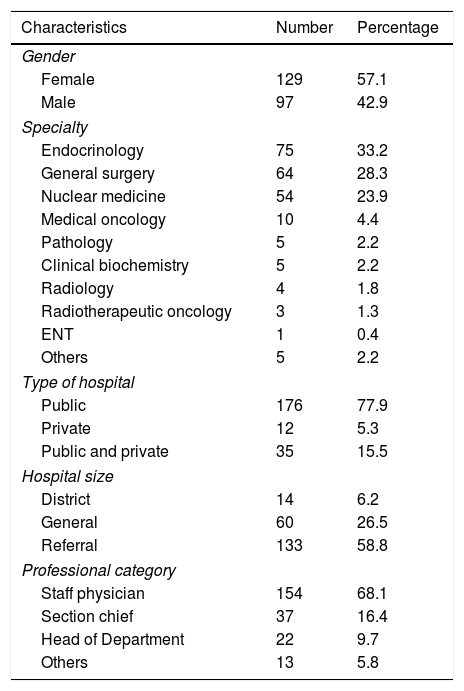
General characteristics of the professionals surveyed.
| Characteristics | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 129 | 57.1 |
| Male | 97 | 42.9 |
| Specialty | ||
| Endocrinology | 75 | 33.2 |
| General surgery | 64 | 28.3 |
| Nuclear medicine | 54 | 23.9 |
| Medical oncology | 10 | 4.4 |
| Pathology | 5 | 2.2 |
| Clinical biochemistry | 5 | 2.2 |
| Radiology | 4 | 1.8 |
| Radiotherapeutic oncology | 3 | 1.3 |
| ENT | 1 | 0.4 |
| Others | 5 | 2.2 |
| Type of hospital | ||
| Public | 176 | 77.9 |
| Private | 12 | 5.3 |
| Public and private | 35 | 15.5 |
| Hospital size | ||
| District | 14 | 6.2 |
| General | 60 | 26.5 |
| Referral | 133 | 58.8 |
| Professional category | ||
| Staff physician | 154 | 68.1 |
| Section chief | 37 | 16.4 |
| Head of Department | 22 | 9.7 |
| Others | 13 | 5.8 |
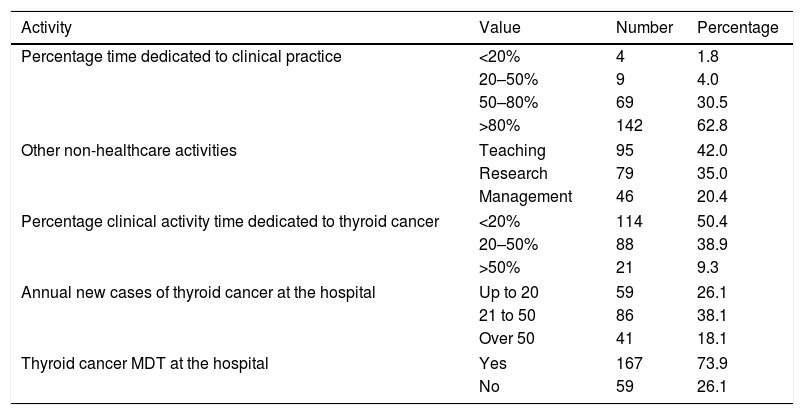
General clinical activity and activity related to thyroid cancer.
| Activity | Value | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage time dedicated to clinical practice | <20% | 4 | 1.8 |
| 20–50% | 9 | 4.0 | |
| 50–80% | 69 | 30.5 | |
| >80% | 142 | 62.8 | |
| Other non-healthcare activities | Teaching | 95 | 42.0 |
| Research | 79 | 35.0 | |
| Management | 46 | 20.4 | |
| Percentage clinical activity time dedicated to thyroid cancer | <20% | 114 | 50.4 |
| 20–50% | 88 | 38.9 | |
| >50% | 21 | 9.3 | |
| Annual new cases of thyroid cancer at the hospital | Up to 20 | 59 | 26.1 |
| 21 to 50 | 86 | 38.1 | |
| Over 50 | 41 | 18.1 | |
| Thyroid cancer MDT at the hospital | Yes | 167 | 73.9 |
| No | 59 | 26.1 | |
The questionnaire was distributed through the SEEN website, since in Spain endocrinologists are the reference specialists in the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid cancer. However, although this study was carried out under the auspices of the SEEN, its scope was not limited to its membership but was extended to all specialists dedicated to the care of patients with thyroid cancer. Accordingly, the questionnaire was also distributed through direct contact with surgeons, specialists in nuclear medicine, oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, radiotherapists, ear, nose and throat specialists, and biochemists. After the pertinent authorizations had been obtained, the survey was posted on the websites of the SEEN and the Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular [SEMNIM]) from 15 November 2017 to 15 February 2018. A direct link to the survey was enabled for those specialists who were not members of the SEEN or SEMNIM.
Statistical analysisQuantitative variables were reported as the mean and standard deviation for data with a normal distribution, and as the median and interquartile range (IQR) for nonparametric data. Normal distribution of variables was checked using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Quantitative variables were reported as absolute values and percentages. The chi-squared test and Fisher exact test were used for the comparison of proportions. A multivariate logistic regression model was used to assess the dependence of the presence of a MDT in the hospital upon other qualitative and quantitative variables. Two-tailed tests were used in all cases, and statistical significance was considered for p<0.05.
ResultsCharacteristics of the surveyed specialistsThe survey was completed by 226 specialists (129 women) aged 28–70 years (mean 43.3±9.6). Their personal and professional characteristics are reported in Table 1. The dominant specialties were endocrinology, general surgery, nuclear medicine and medical oncology. Only 9.3% of those surveyed dedicated more than 50% of their time to thyroid cancer (Table 2). A total of 73.9% of the participants reported the presence of a thyroid cancer MDT at their hospital.
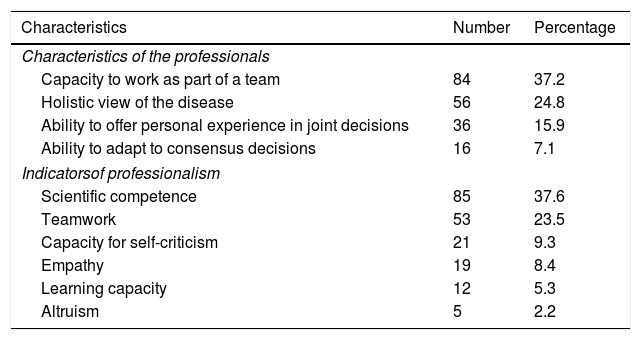
Professionalism characteristics and indicatorsA total of 37.2% of those surveyed considered the most important characteristic required of professionals in order to belong to an MDT to be the capacity to work as part of a team, while a holistic perspective of the disease was cited by 24.8% (Table 3).
Specialist opinion regarding the characteristics required of professionals. belonging to an MDT and the indicators of professionalism considered important in such teams.
| Characteristics | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of the professionals | ||
| Capacity to work as part of a team | 84 | 37.2 |
| Holistic view of the disease | 56 | 24.8 |
| Ability to offer personal experience in joint decisions | 36 | 15.9 |
| Ability to adapt to consensus decisions | 16 | 7.1 |
| Indicatorsof professionalism | ||
| Scientific competence | 85 | 37.6 |
| Teamwork | 53 | 23.5 |
| Capacity for self-criticism | 21 | 9.3 |
| Empathy | 19 | 8.4 |
| Learning capacity | 12 | 5.3 |
| Altruism | 5 | 2.2 |
The data indicate the number and percentage of specialists who consider each characteristic or indicator to be the most important of its group. The professional characteristics and indicators of professionalism appear in hierarchical order.
Of the 6 professionalism indicators explored, scientific competence was considered to be the most important by 37.6% of the responders, while 23.5% considered teamwork to be the most important indicator (Table 3).
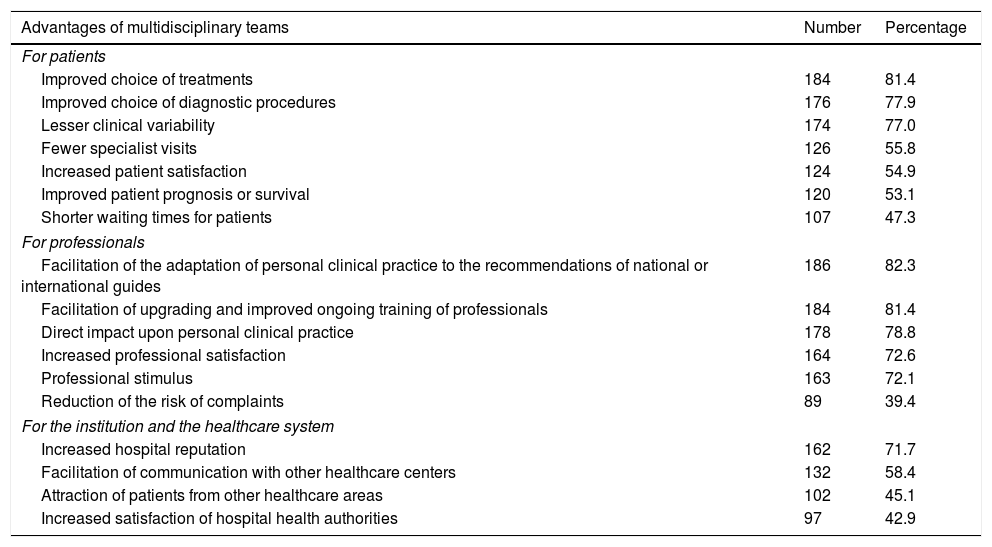
Advantages of multidisciplinary teamsTable 4 shows the degree of agreement of the professionals with the different advantages afforded by MDTs. With regard to the advantages for the patients, over two-thirds of the responders agreed on the following characteristics: an improved choice of treatments and diagnostic procedures, and lesser clinical variability. Over half of the responders agreed that MDTs reduce the number of consultations, increase patient satisfaction, and improve prognosis or survival. With regard to advantages for the professionals, over two-thirds of the responders agreed on all the items, except for the reduction of the risk of complaints. With regard to the advantages for the healthcare system, agreement by over two-thirds of the responders was only recorded with reference to the increased prestige of the hospital.
Agreement of the surveyed specialists regarding the benefits of MDTs for patients, professionals and the healthcare system.
| Advantages of multidisciplinary teams | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| For patients | ||
| Improved choice of treatments | 184 | 81.4 |
| Improved choice of diagnostic procedures | 176 | 77.9 |
| Lesser clinical variability | 174 | 77.0 |
| Fewer specialist visits | 126 | 55.8 |
| Increased patient satisfaction | 124 | 54.9 |
| Improved patient prognosis or survival | 120 | 53.1 |
| Shorter waiting times for patients | 107 | 47.3 |
| For professionals | ||
| Facilitation of the adaptation of personal clinical practice to the recommendations of national or international guides | 186 | 82.3 |
| Facilitation of upgrading and improved ongoing training of professionals | 184 | 81.4 |
| Direct impact upon personal clinical practice | 178 | 78.8 |
| Increased professional satisfaction | 164 | 72.6 |
| Professional stimulus | 163 | 72.1 |
| Reduction of the risk of complaints | 89 | 39.4 |
| For the institution and the healthcare system | ||
| Increased hospital reputation | 162 | 71.7 |
| Facilitation of communication with other healthcare centers | 132 | 58.4 |
| Attraction of patients from other healthcare areas | 102 | 45.1 |
| Increased satisfaction of hospital health authorities | 97 | 42.9 |
The data indicate the number and percentage of specialists who agree with each of the proposed advantages.
A logistic regression analysis with the presence of MDT as the dependent variable showed the latter to be directly related to hospital size (OR 6.82 [95%CI: 1.89–24.61]; p=0.003, for referral hospitals versus regional hospitals) and the type of hospital (OR 7.85 [1.19–51.76]; p=0.032, for public hospitals versus private hospitals), but not to the number of new cases of thyroid cancer seen annually (OR 0.99 [0.98–1.01]; p=0.274). We therefore sought to analyze the differences in the opinions of the different groups of professionals classified not only by specialty, but also according to these variables (size and type of hospital, number of new cases per year and the presence of MDT).
No significant differences were found in the opinion of the participants regarding the characteristics of the professionals and the professionalism indicators in the three main specialties (endocrinology, general surgery and nuclear medicine), or in terms of hospital size, the type of hospital, the number of new cases per year, and the presence of MDT (data not shown).
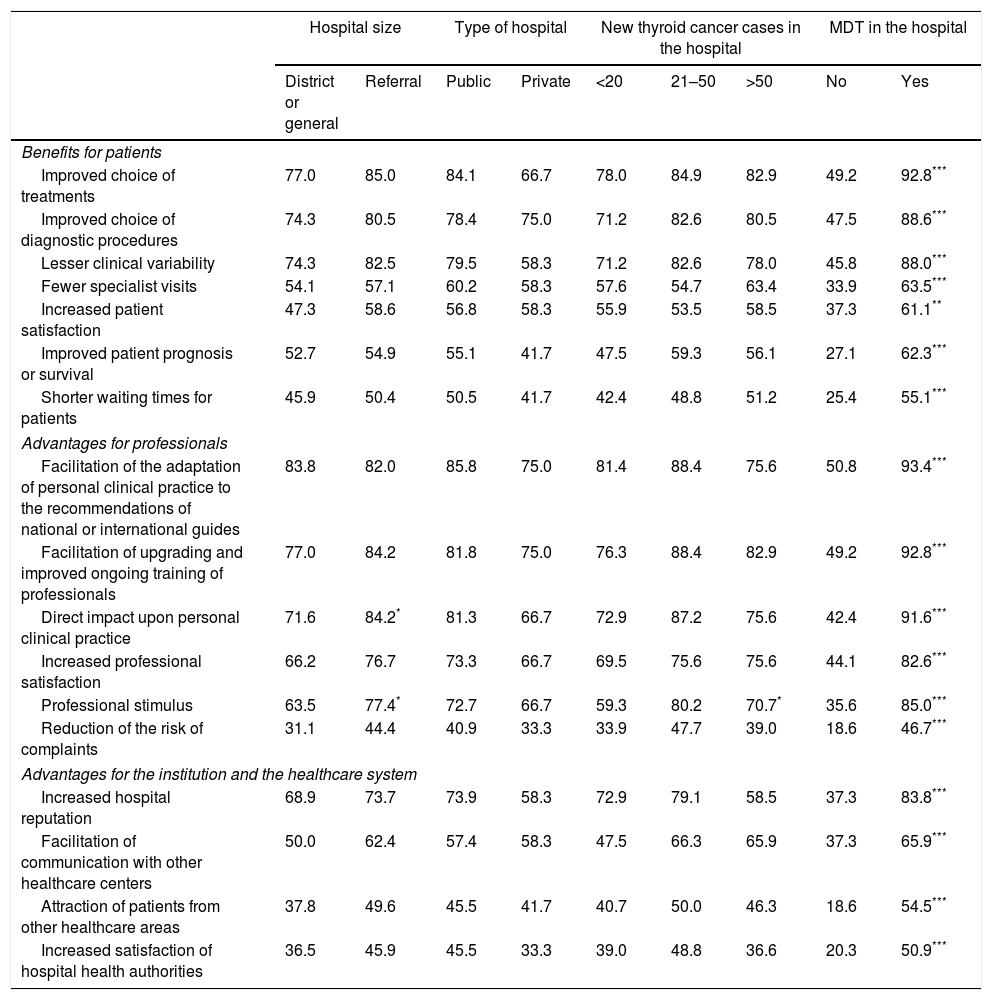
Hospital size, type of hospital, and the number of new cases per year had a minimal influence upon the opinion of the professionals regarding the advantages of MDT (Table 5). However, the degree of agreement regarding the advantages analyzed was highly significant in the group of professionals with a MDT at their hospital (Table 5).
Agreement with the benefits of MDTs among the surveyed specialists classified by groups according to the hospitals’ characteristics.
| Hospital size | Type of hospital | New thyroid cancer cases in the hospital | MDT in the hospital | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District or general | Referral | Public | Private | <20 | 21–50 | >50 | No | Yes | |
| Benefits for patients | |||||||||
| Improved choice of treatments | 77.0 | 85.0 | 84.1 | 66.7 | 78.0 | 84.9 | 82.9 | 49.2 | 92.8*** |
| Improved choice of diagnostic procedures | 74.3 | 80.5 | 78.4 | 75.0 | 71.2 | 82.6 | 80.5 | 47.5 | 88.6*** |
| Lesser clinical variability | 74.3 | 82.5 | 79.5 | 58.3 | 71.2 | 82.6 | 78.0 | 45.8 | 88.0*** |
| Fewer specialist visits | 54.1 | 57.1 | 60.2 | 58.3 | 57.6 | 54.7 | 63.4 | 33.9 | 63.5*** |
| Increased patient satisfaction | 47.3 | 58.6 | 56.8 | 58.3 | 55.9 | 53.5 | 58.5 | 37.3 | 61.1** |
| Improved patient prognosis or survival | 52.7 | 54.9 | 55.1 | 41.7 | 47.5 | 59.3 | 56.1 | 27.1 | 62.3*** |
| Shorter waiting times for patients | 45.9 | 50.4 | 50.5 | 41.7 | 42.4 | 48.8 | 51.2 | 25.4 | 55.1*** |
| Advantages for professionals | |||||||||
| Facilitation of the adaptation of personal clinical practice to the recommendations of national or international guides | 83.8 | 82.0 | 85.8 | 75.0 | 81.4 | 88.4 | 75.6 | 50.8 | 93.4*** |
| Facilitation of upgrading and improved ongoing training of professionals | 77.0 | 84.2 | 81.8 | 75.0 | 76.3 | 88.4 | 82.9 | 49.2 | 92.8*** |
| Direct impact upon personal clinical practice | 71.6 | 84.2* | 81.3 | 66.7 | 72.9 | 87.2 | 75.6 | 42.4 | 91.6*** |
| Increased professional satisfaction | 66.2 | 76.7 | 73.3 | 66.7 | 69.5 | 75.6 | 75.6 | 44.1 | 82.6*** |
| Professional stimulus | 63.5 | 77.4* | 72.7 | 66.7 | 59.3 | 80.2 | 70.7* | 35.6 | 85.0*** |
| Reduction of the risk of complaints | 31.1 | 44.4 | 40.9 | 33.3 | 33.9 | 47.7 | 39.0 | 18.6 | 46.7*** |
| Advantages for the institution and the healthcare system | |||||||||
| Increased hospital reputation | 68.9 | 73.7 | 73.9 | 58.3 | 72.9 | 79.1 | 58.5 | 37.3 | 83.8*** |
| Facilitation of communication with other healthcare centers | 50.0 | 62.4 | 57.4 | 58.3 | 47.5 | 66.3 | 65.9 | 37.3 | 65.9*** |
| Attraction of patients from other healthcare areas | 37.8 | 49.6 | 45.5 | 41.7 | 40.7 | 50.0 | 46.3 | 18.6 | 54.5*** |
| Increased satisfaction of hospital health authorities | 36.5 | 45.9 | 45.5 | 33.3 | 39.0 | 48.8 | 36.6 | 20.3 | 50.9*** |
The data indicate the percentage of those surveyed who agree with each of the cited advantages in each group.
The present study offers the first analysis in Spain of the opinions of the different specialists regarding the professional characteristics required of members of MDTs and the advantages of MDTs for thyroid cancer management. The average profile of those surveyed corresponds to specialists working in public referral hospitals and involved in eminently clinical activities, though many of them combine the latter with other activities such as teaching and research. Overall, the results obtained reflect a very positive attitude among the professionals toward MDTs, as has also been seen with reference to other tumor types.5,7
The growing complexity of the management of medical information can turn healthcare professionals into technicians who merely apply algorithms automatically. This risk was intuited at the turn of the millennium by a number of scientific bodies that published the Physicians’ Charter.8 The principles established in this charter defined the need to create MDTs to treat complex diseases (such as thyroid cancer), and rendered obsolete the concept of the “owning physician” as someone who views his or her patients as personal property and whose intervention is decided upon based on personal criteria alone. According to the charter, the patient comes first.9 We also emphasize that the participants in our survey considered the ability to work as part of a team to be the main requirement of an MDT member, followed by a holistic view of the disease. Scientific competence and teamwork were the most important indicators of professionalism of the 6 proposed. This suggests that the surveyed specialists consider that professionals must not only be competent, but should also meet a series of requirements regarding attitudes and commitment in order to carry out the tasks inherent to MDTs. These opinions persisted when analysis was made by subgroups according to specialty, hospital characteristics, and the number of new patients received annually. The availability of an MDT in the hospital likewise had no influence upon the opinion of the responders regarding the indicators of professionalism. All this suggests that MDTs require extra effort from the professionals, but also facilitate higher quality medical practice as a result of the professionalism of their members. Multidisciplinary teams improve how we practice medicine and generate better quality care.
In agreement with what is seen in other types of cancer, the responders considered MDTs to offer many benefits for patients, especially in terms of an improved choice of treatments10,11 and diagnostic procedures,12 lesser clinical variability,11 and increased patient satisfaction.13–15 Most of the responders agreed on these aspects. Improved survival has been suggested by several authors in patients with breast,2 colorectal,16 esophageal17 and head and neck malignancies.18 However, some recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been unable to demonstrate a cause–effect relationship between MDT care and patient survival.19,20 It is therefore curious that over half of our responders agreed that MDTs improve patient prognosis or survival given that this is particularly difficult to demonstrate in the concrete case of thyroid cancer. However, it is also true that the concentration of cases in centers with MDTs may improve the outcomes, as reflected by the fact that surgeons with a larger number of thyroidectomies achieve fewer complications, shorter stays, and a lower cost per procedure.21
We again found no relevant differences in these opinions on dividing the patients according to the characteristics of the hospitals, with the exception of belonging to an MDT. Our results clearly show that specialists with an MDT at their center have a much more favorable opinion of the advantages of this model. This suggests that the professional experience of working in a multidisciplinary environment is the key factor that makes the advantages of this cross-sectional decision-making model more visible to professionals, while patient volume or hospital size has only a minimum impact upon specialist opinion.
Our data also indicate that the majority of the responders agreed on all the considered benefits for professionals, with the exception of a decrease in the risk of complaints. The recent literature reports improved experience in cancer surgery22 and in the management of infrequent tumors23 among the specialists belonging to MDTs, as well as improved professional development and ongoing training,24 and overall greater professional satisfaction.12,25 As in the above case, the proportion of responders agreeing on these advantages was clearly higher among those specialists with MDTs in their workplace.
Lastly, the increased prestige of the hospital was considered to be the most relevant advantage of MDTs for the healthcare system. An important aspect of multidisciplinary care is that it allows for the better use of healthcare information and communication systems,26,27 an aspect that appears to be accepted by over half of the professionals surveyed. By contrast, there appears to be no great agreement regarding an increase in satisfaction on the part of the hospital authorities or regarding the degree to which patients were attracted to the hospital from other healthcare areas. Similar observations have been made in other studies.28
Our study is not without limitations. As expected, some specialties were underrepresented in our survey, which may condition the extrapolation of our results to healthcare professionals in general. The results of this study inherently reflect the subjective opinion of the surveyed professionals. Consequently, they do not offer objective clinical information as to the benefits for patients and the healthcare system. Moreover, the number of professionals working in private centers was relatively low, and so only limited conclusions regarding them can be drawn. Our survey did not explore the inconveniences of MDTs, the barriers or difficulties facing their implementation, or the ideas of the professionals for improving multidisciplinary decision-making processes.
As strengths of our study, mention should be made of the high number of responses obtained and the fact that the three key specialties in the diagnosis, the initial treatment and the follow-up of thyroid cancer were well represented in the survey. Despite the limitation posed by the lack of clinical data, our study shows that the responders appreciate the professionalism of the specialists and see the need and benefits of treating patients in a multidisciplinary context.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that the professionals participating in thyroid cancer management in Spain are aware of the importance of MDTs and have a very favorable opinion regarding the advantages of this health care model for patients, professionals and the healthcare system. We believe that hospital management should favor the creation and development of these teams, provide official coverage of their meetings, acknowledge meeting time as care working time, and afford administrative support.4 Our results may help healthcare managers and authorities to promote the incorporation of MDTs in thyroid cancer management in centers that still do not have this model of care.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
The authors thank Sanofi Genzyme for assistance in distributing our survey among the Spanish hospitals that treat patients with thyroid cancer. This study has not received funding from any public or private entity.
Please cite this article as: Díez JJ, Galofré JC, Oleaga A, Grande E, Mitjavila M, Moreno P. Características de profesionalidad de los especialistas y ventajas de los equipos multidisciplinares en cáncer de tiroides: resultados de una encuesta de opinión nacional. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2019;66:74–82.