Low-protein diet (less than 0.8g/kg/day) has been practiced in the management of chronic kidney disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]<60ml/min/1.73m2 or urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios [UACR] ≥30mg/g) for decades. However, its effect on all-cause mortality is unclear. We investigated the association between a low-protein intake and all-cause mortality in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment.
Materials and methodsWe analyzed participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2003 to 2010. They were divided into four groups according to their eGFR (≥60 or <60ml/min/1.73m2) and UACR (≥30 or <30mg/g). Daily protein intake of the NHANES participants could be assessed using information from the dietary interview questionnaires. The mortality data was retrieved by linking to the National Death Index till the end of 2011. The hazard ratios for all-cause mortality were evaluated by the weighted Cox proportional hazards regression models.
ResultsA total of 8093 participants were analyzed. During a median follow-up of 4.7 years, participants with UACR≥30mg/g (with or without eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2) had a higher risk of all-cause mortality compared with those having UACR<30mg/g and eGFR≥60ml/min/1.73m2 (reference group). The higher risk of mortality in participants with UACR≥30mg/g was consistently observed in those with or without a low-protein intake.
ConclusionsA low-protein intake was not associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment.
Desde hace décadas se utiliza una dieta baja en proteínas (menos de 0,8g/kg/día) para el control de la enfermedad renal crónica (filtración glomerular estimada [FGe]<60ml/min/1,73m2 o cociente albúmina/creatinina en orina [ACR]≥30mg/g). Sin embargo, se desconoce su efecto en la mortalidad por todas las causas. Investigamos la asociación entre una ingesta baja de proteínas y la mortalidad por todas las causas en sujetos con diversos grados de insuficiencia renal.
Materiales y métodosAnalizamos a los participantes de la Encuesta Nacional de Examen de Salud y Nutrición (NHANES, por las siglas en inglés de National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) desde 2003 a 2010. Los dividimos en 4 grupos según su FGe (≥60 o <60ml/min/1,73m2) y ACR (≥30 o <30mg/g). La ingesta diaria de proteínas de los participantes en la NHANES podía evaluarse utilizando información procedente de los cuestionarios de entrevistas sobre alimentación. Los datos de mortalidad se obtuvieron por vinculación con el registro nacional de defunciones hasta finales de 2011. Los cocientes de riesgos instantáneos para la mortalidad por todas las causas se evaluaron mediante modelos de regresión de riesgos proporcionales de Cox ponderados.
ResultadosSe analizaron 8.093 participantes en total. Durante una mediana de seguimiento de 4,7 años, los participantes con un ACR≥30mg/g (con o sin un valor de FGe<60ml/min/1,73m2) presentaron un riesgo mayor de mortalidad por todas las causas que aquellos que presentaron un ACR<30mg/g y una FGe≥60ml/min/1,73m2 (grupo de referencia). El mayor riesgo de mortalidad en los participantes con un ACR≥30mg/g correspondió al observado en los participantes con o sin una ingesta baja de proteínas.
ConclusionesUna ingesta baja de proteínas no se asoció con un menor riesgo de mortalidad por todas las causas en sujetos con diversos grados de insuficiencia renal.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was one of the most prevalent non-communicable diseases contributing to increasing disease burden between 1990 and 2019,1 making it become an international health challenge. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 60ml/min/1.73m2 or urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios (UACR) greater than 30mg/g for more than three months according to the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI) clinical practice guidelines.2 The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration illustrated that CKD affected 697.5 million of people worldwide with 29.3% of change in prevalence between 1990 and 2017, and that CKD accounted for 35.8 million disability-adjusted life-years in 2017.3 Several researches had confirmed a U-shaped association between eGFR change and all-cause mortality, indicating change in eGFR over time as a predictor of mortality risk.4 Similarly, albuminuria had been documented to be an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality.5
Lifestyle modification, including exercise and nutritional therapy, is fundamental for the management of CKD.6 With respect to nutritional therapy, dietary protein restriction to less than 0.8g/kg/day (low-protein diet) has been recommended for patients with CKD.7 Dating back to the past century, low-protein diet was first introduced to alleviate uremic symptoms8 that were derived from the retention of toxic catabolites of proteins.9 In 1984, Rosman et al.10 demonstrated that early moderate dietary protein restriction retarded the progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in patients with various renal diseases. In 2008, Cianciaruso et al.11 further reported that more restricted protein intake guaranteed a better metabolic control with decreased 24-h urinary urea nitrogen and lower excretion of creatinine. However, low-protein diet may have potential harmful impact for patient with CKD (such as malnutrition), and its implementation needs careful consideration.
Although plenty of studies12–14 had praised the effects of low-protein diet on limiting loss of renal function and ameliorating complications of CKD, there was limited data investigating the impact of dietary protein restriction on all-cause mortality.15 Inconclusive results reported in some studies13,16 led to uncertainty about the effect of low-protein diet on all-cause mortality. In this study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), we investigated risk of all-cause mortality in people with CKD (eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2 or UACR≥30mg/g or both), and whether the mortality risks associated with CKD differed in people with or without a low-protein intake.
Materials and methodsOur study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan (approval number: CE18312A). We conducted this study in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and all participants in the NHANES signed informed consent. The NHANES was a series of cross-sectional examinations conducted by National Center for Health Statistics of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The examinations investigated the health and nutritional status of general population in the United States by home interview, health examination and laboratory testing. A total of 41156 participants from 2003 to 2010 were enrolled (Fig. 1). Participants were excluded if they were younger than 18 years old, had missing data on questionnaires or relevant information, or due to uncertain vital status. Eventually, 8093 participants were analyzed in this study. The mortality data of all participants was retrieved by linking to the National Death Index till the end of 2011.
Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation17 was used to determine eGFR. We divided the study population into four groups by whether they had eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2 or UACR ≥30mg/g. Participants who had eGFR ≥60ml/min/1.73m2 with UACR<30mg/g served as the reference group to determine the risks of all-cause mortality in those who had eGFR≥60ml/min/1.73m2 with UACR≥30mg/g (UACR group), eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2 with UACR<30mg/g (eGFR group), and eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2 with UACR≥30mg/g (combined group). Daily protein intake of the NHANES participants could be assessed using information from the dietary interview questionnaires (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Search/DataPage.aspx?Component=Dietary&CycleBeginYear=2005). The risks of all-cause mortality in the aforementioned subgroups were further examined in participants who had protein intake ≥0.8g/kg/day and <0.8g/kg/day, respectively, to determine whether the mortality risks associated with CKD differed in people with or without low-protein diet (<0.8g/kg/day). Healthy Eating Index-2010 (HEI-2010)18 was used to assess diet quality of the study population. The higher the HEI-2010 total score, the closer congruence to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
We employed Statistical Analysis System survey procedures (SAS version 9.4, 2013, Cary, NC, USA) to analyze all of the statistics. Continuous and categorical variables were presented with mean (95% confidence interval [CI]) and numbers (percentages), respectively. ANOVA was applied to explore the significant difference of characteristics between groups. The hazard ratio (HR) for all-cause mortality among the CKD groups were evaluated by the weighted Cox proportional hazards regression models with adjustment of age, sex, and other risk factors.
ResultsAmong 41156 participants in the NHANES from 2003 to 2010, 8093 participants were analyzed in this study after excluding those who had missing data on eGFR, UACR, and relevant information (Fig. 1). Study participants were divided into four groups based on their renal function (eGFR ≥60ml/min/1.73m2 or eGFR <60ml/min/1.73m2) and albuminuria status (UACR <30mg/g or UACR≥30mg/g) (Table 1):
- •
Reference group was characterized as eGFR≥60ml/min/1.73m2 and UACR<30mg/g (n=6566);
- •
UACR group was characterized as eGFR≥60ml/min/1.73m2 and albuminuria (UACR≥30mg/g) (n=752); eGFR group was characterized as decreased eGFR (<60ml/min/1.73m2) and UACR<30mg/g (n=508); and
- •
Combined group was characterized as decreased eGFR and albuminuria (n=267).
Characteristics of study participants by eGFR level and albuminuria status.
| Variable | ReferenceeGFR≥60, UACR<30 | UACReGFR≥60, UACR≥30 | eGFReGFR<60, UACR<30 | CombinedeGFR<60, UACR≥30 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 6566 | 752 | 508 | 267 | <0.001 |
| Age, year | 45.5 (45.0–46.1) | 53.8 (52.3–55.3) | 70.8 (69.3–72.2) | 72.9 (71.0–74.8) | 0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 3837 (56.0) | 451 (55.1) | 270 (45.0) | 186 (64.2) | <0.001 |
| Race/ethnicity, n (%) | |||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 3734 (76.8) | 379 (71.2) | 362 (86.4) | 173 (82.0) | |
| Non-Hispanic black | 1108 (8.6) | 170 (13.1) | 79 (8.0) | 56 (10.8) | |
| Mexican American/others | 1724 (14.6) | 203 (15.7) | 67 (5.6) | 38 (7.3) | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.1 (27.9–28.3) | 29.6 (28.8–30.3) | 28.7 (28.1–29.3) | 29.6 (28.7–30.5) | <0.001 |
| CVD, n (%) | 265 (3.5) | 76 (9.3) | 68 (12.4) | 52 (20.0) | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP, mmHg | 121.7 (121.1–122.3) | 133.5 (131.3–135.6) | 133.2 (131.1–135.2) | 144.4 (139.5–149.3) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | 70.9 (70.4–71.3) | 73.3 (71.8–74.8) | 64.9 (63.7–66.1) | 64.6 (61.1–68.2) | <0.001 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 3245 (49.7) | 358 (51.4) | 89 (18.2) | 45 (18.5) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dl | 200.6 (199.2–202.0) | 200.5 (196.2–204.7) | 194.3 (189.9–198.7) | 180.9 (173.5–188.3) | <0.001 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dl | 52.4 (51.7–53.1) | 52.4 (50.3–54.4) | 52.5 (51.0–54.1) | 50.7 (48.2–53.3) | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dla | 128.1 (125.3–130.9) | 146.7 (136.6–157.5) | 143.9 (136.2–152.0) | 141.6 (129.3–155.1) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.49 (5.46–5.51) | 6.11 (5.96–6.25) | 5.84 (5.73–5.94) | 6.20 (6.05–6.34) | <0.001 |
| FPG, mg/dl | 95.8 (94.9–96.6) | 115.0 (110.7–119.3) | 105.8 (101.0–110.6) | 118.2 (112.9–123.6) | <0.001 |
| Calorie intake, kcal/day | 2339 (2303–2374) | 2126 (2034–2217) | 1791 (1675–1906) | 1727 (1599–1854) | <0.001 |
| % from carbohydrate | 49.1 (48.7–49.6) | 48.7 (47.8–49.7) | 49.4 (48.0–50.7) | 47.5 (46.1–49.0) | |
| % from fat | 34.8 (34.5–35.2) | 35.2 (34.4–35.9) | 34.8 (33.7–35.9) | 36.0 (34.8–37.2) | |
| % from protein | 16.0 (15.8–16.2) | 16.1 (15.6–16.6) | 15.8 (15.3–16.4) | 16.5 (15.9–17.0) | |
| Low-protein diet, n (%) | 2351 (32.8) | 338 (42.6) | 258 (47.5) | 149 (53.8) | <0.001 |
| HEI-2010 total score | 46.9 (46.2–47.6) | 47.3 (46.0–48.5) | 51.5 (49.8–53.2) | 49.1 (47.0–51.1) | <0.001 |
| eGFR, ml/min/1.73m2 | 97.4 (96.7–98.1) | 92.3 (90.5–94.0) | 49.9 (48.9–50.9) | 42.7 (40.5–44.9) | <0.001 |
| UACR, mg/ga | 6.0 (5.8–6.2) | 83.5 (76.9–90.7) | 7.7 (7.0–8.4) | 140.4 (116.2–169.6) | <0.001 |
Data are presented as mean (95% confidence interval, CI) or n (%). CVD, cardiovascular disease; BP, blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HEI, healthy eating index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; UACR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio.
The average value of eGFR and UACR was 97.4 (96.7–98.1) and 6.0 (5.8–6.2) in the reference group, 92.3 (90.5–94.0) and 83.5 (76.9–90.7) in the UACR group, 49.9 (48.9–50.9) and 7.7 (7.0–8.4) in the eGFR group, and 42.7 (40.5–44.9) and 140.4 (116.2–169.6) in the combined group, respectively (Table 1). Compared with the others, the combined group was the eldest (mean age 72.9 years), having the highest prevalence of cardiovascular disease (20.0%) and diabetes (45.0%), the poorest control of systolic blood pressure (mean 144.4mmHg), and the least calorie (mean 1727kcal/day) and protein intake (53.8% had protein intake less than 0.8g/kg/day).
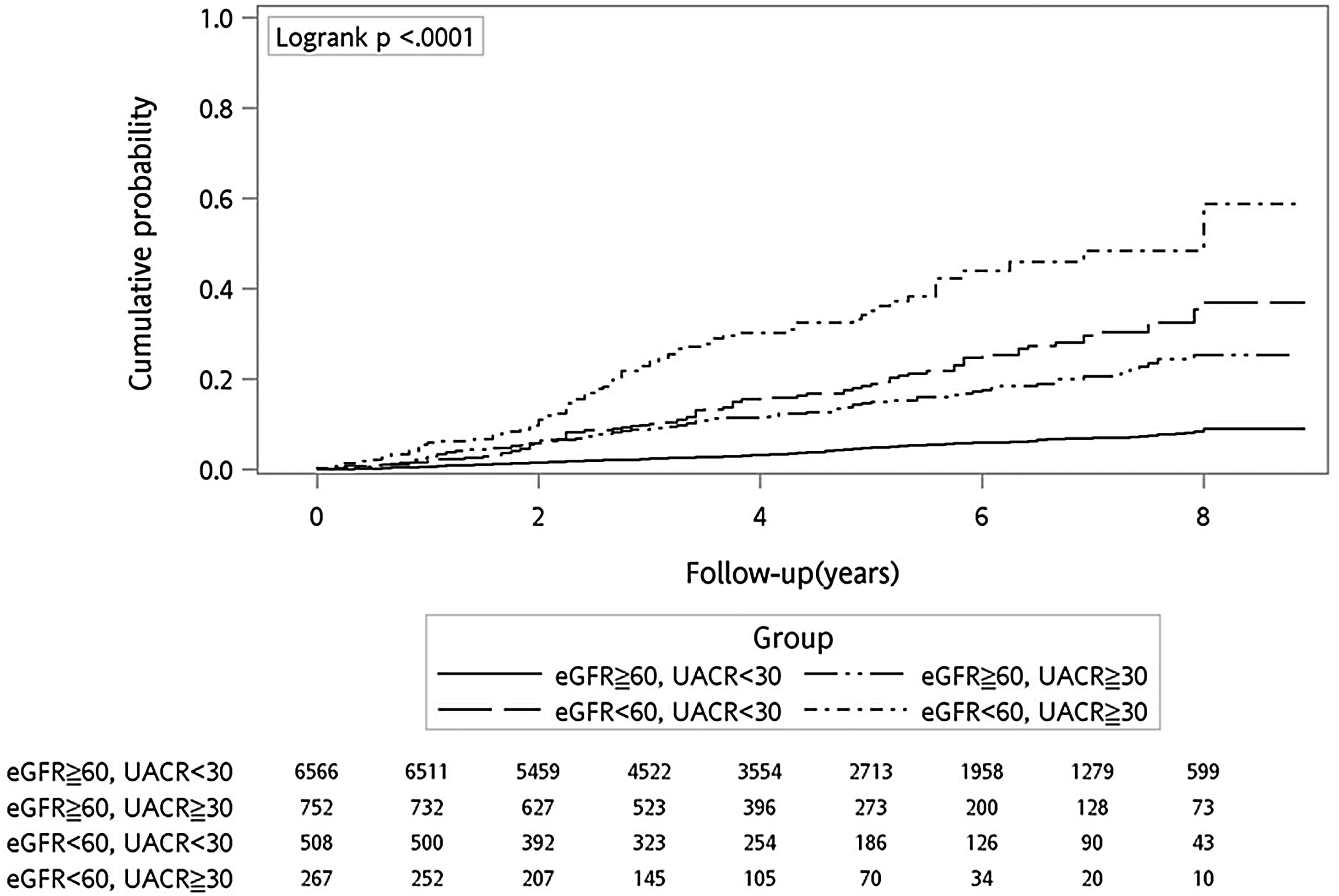
Fig. 2 shows the cumulative probability of all-cause mortality in the study participants after a median follow-up of 4.7 years. Combined group had the highest cumulative mortality rate (88.8 per 1000 person-years) among the four groups, followed by the eGFR group (32.1 per 1000 person-years) and the UACR group (22.8 per 1000 person-years). After adjustment for age, sex and other risk factors, the combined group (HR 2.591, 95% CI 1.894–3.544, p<0.001) and the UACR group (HR 1.655, 95% CI 1.197–2.288, p=0.003) had significantly higher risk of mortality compared with the reference group (Table 2).
All-cause mortality in participants with various degrees of renal impairment.
| Mortality (per 1000 person-years) | HR (95% CI)a | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR≥60, UACR<30 | 6.7 | ref | |
| eGFR≥60, UACR≥30 | 22.8 | 1.655 (1.197–2.288) | 0.003 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 32.1 | 1.008 (0.740–1.373) | 0.958 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≥30 | 88.8 | 2.591 (1.894–3.544) | <0.001 |
| Protein intake ≥0.8 g/kg/day | |||
| eGFR≥60, UACR<30 | 5.6 | ref | |
| eGFR≥60, UACR≥30 | 17.7b | 1.343 (0.865–2.086) | 0.186 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 24.8 | 0.929 (0.558–1.548) | 0.775 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≥30 | 84.7 | 2.376 (1.644–3.432) | <0.001 |
| Protein intake <0.8g/kg/day | |||
| eGFR≥60, UACR<30 | 9 | ref | |
| eGFR≥60, UACR≥30 | 29.8b | 2.072 (1.267–3.388) | 0.004 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 40.4 | 1.066 (0.748–1.519) | 0.720 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≥30 | 92.4 | 2.859 (1.774–4.607) | <0.001 |
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. HR, hazard ratio. UACR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio.
We then examined the association of CKD with all-cause mortality in participants with or without a low-protein intake (Table 2). The mortality rates (per 1000 person-years) in the four groups who had a protein intake ≥0.8g/kg/day were 5.6, 17.7, 24.8, and 84.7, respectively. Among participants having a protein intake <0.8g/kg/day, the respective mortality rates were 9.0, 29.8, 40.4, and 92.4. The mortality rate in the UACR group who had a protein intake <0.8g/kg/day was even higher than those who had a protein intake ≥0.8g/kg/day after multivariable adjustment (HR 1.678, 95% CI 1.027–2.741, p=0.039, data not shown in Table 2). In Table 3, we updated vital status of the participants to 2015, and the results were similar to the findings in Table 2.
All-cause mortality (update to 2015) in subjects with various degrees of renal impairment.
| Mortality (per 1000 person-years) | HR (95% CI)a | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR≧60, UACR<30 | 8.4 | ref | |
| eGFR≧60, UACR≧30 | 29.1 | 2.024 (1.581–2.592) | <0.001 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 46.4 | 1.386 (1.053–1.825) | 0.021 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≧30 | 97.8 | 2.694 (1.977–3.671) | <0.001 |
| Protein intake ≧0.8g/kg/day | |||
| eGFR≧60, UACR<30 | 7.7 | ref | |
| eGFR≧60, UACR≧30 | 29.9 | 2.225 (1.525–3.246) | <0.001 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 31 | 1.030 (0.625–1.695) | 0.907 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≧30 | 86 | 2.506 (1.613–3.892) | <0.001 |
| Protein intake<0.8g/kg/day | |||
| eGFR≧60, UACR<30 | 9.8 | ref | |
| eGFR≧60, UACR≧30 | 28.1 | 1.855 (1.224–2.811) | 0.004 |
| eGFR<60, UACR<30 | 65.3 | 1.719 (1.195–2.471) | 0.004 |
| eGFR<60, UACR≧30 | 107.6 | 2.996 (1.775–5.057) | <0.001 |
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. HR, hazard ratio. UACR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio.
Table 4 shows nutrient intakes of study participants according to whether they had a low-protein intake. Participants who had a low-protein intake had a higher body mass index, while the differences in serum levels of albumin and total cholesterol were only modest. Although participants with a low-protein intake (<0.8g/kg/day) had lower consumption of total calorie, saturated and total fat, total sugar, and sodium, they had lower intake of fiber, fruit, and vegetable, with a lower diet quality (HEI-2010 total score), compared with those who had a protein intake ≥0.8g/kg/day.
Nutrient intakes of study participants according to low-protein intake.
| Variables | Low-protein intake (<0.8g/kg/day) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||
| n | 4997 | 3096 | |
| Protein intake per day, g/kg | 1.36 (1.34–1.38) | 0.57 (0.56–0.58) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 26.9 (26.7–27.1) | 30.8 (30.5–31.1) | <0.001 |
| Albumin, g/dl | 4.30 (4.29–4.32) | 4.19 (4.17–4.21) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dl | 199.6 (198.4–200.9) | 200.5 (198.2–202.7) | <0.001 |
| Calorie intake, kcal/day | 2663 (2622–2704) | 1573 (1544–1602) | <0.001 |
| % from carbohydrate | 47.0 (46.5–47.4) | 53.1 (52.6–53.6) | |
| % from fat | 35.8 (35.5–36.2) | 33.1 (32.7–33.6) | |
| % from protein | 17.2 (17.0–17.4) | 13.8 (13.5–14.0) | |
| Saturated fat, g/day | 34.3 (33.6–34.9) | 18.8 (18.2–19.3) | <0.001 |
| Total fat, g/day | 102.4 (100.6–104.2) | 57.1 (55.6–58.6) | <0.001 |
| Total sugars, g/day | 137.3 (132.9–141.6) | 98.7 (94.9–102.6) | <0.001 |
| Sodium, mg/day | 4267 (4197–4336) | 2435 (2379–2491) | <0.001 |
| Fiber, g/day | 17.7 (17.3–18.1) | 11.4 (11.0–11.7) | <0.001 |
| Fruit, cup/day | 0.95 (0.91–1.00) | 0.59 (0.54–0.63) | <0.001 |
| Vegetable, cup/day | 0.68 (0.64–0.73) | 0.55 (0.50–0.61) | <0.001 |
| HEI-2010 total score | 48.2 (47.5–48.9) | 45.2 (44.2–46.2) | <0.001 |
Data are presented as mean (95% confidence interval). HEI, healthy eating index.
In this study involving 8093 participants from NHANES, we demonstrated that CKD was associated with increased mortality risk (Fig. 1), especially in those with albuminuria. Having a daily protein intake less than 0.8g/kg/day showed no benefit on survival, irrespective of participants’ albuminuria status or renal function (Table 2). A low-protein intake was even associated with a higher risk of mortality in the UACR group. Given our research findings and the inconclusive results from previous studies13,16 regarding the effect of low-protein diet on all-cause mortality in patients with CKD, whether low-protein diet with protein intake <0.8g/kg/day should be recommended to people with CKD deserves careful consideration.
Several clinical guidelines, including KDIGO19 and American Diabetes Association guidelines,14 advocated protein restriction to 0.8g/kg/day in patients with kidney damage. A variety of studies had shown benefits of dietary protein restriction in CKD,9,12–14 including retarding decline in eGFR, ameliorating proteinuria, preventing progression to ESRD, and impeding the need for renal replacement therapy by improving glomerular hyperfiltration/hypertension,20 and reducing tubulo-interstitial inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis.21
However, the relationship between dietary protein restriction and mortality risk in patients with CKD remained uncertain. In a meta-analysis22 including 16 controlled trials in patients with CKD, each having at least 30 subjects, low-protein diet (<0.8g/kg/day) was related to higher serum bicarbonate, lower phosphorus levels, and deferring progression to ESRD in non-dialysis-dependent CKD. Although a trend toward lower risk of all-cause death (absolute risk reduction −0.01, 95% CI −0.04–0.02) was found in subjects on low-protein diet, the finding was not significant. Similarly, a meta-analysis23 including 17 randomized controlled trials with 2996 non-diabetic and non-dialysis-dependent CKD (stage 3–5) participants reported that low-protein diets (0.55–0.6g/kg/day) probably had no influence on all-cause death (risk ratio 0.77, 95% CI 0.51–1.18) when compared with normal protein intake (0.8–1g/kg/day). In another meta-analysis24 including 19 randomized controlled trials with 2492 CKD participants, protein restriction ranging from 0.29 to 0.9g/kg/day reduced the risk of ESRD and deterioration of renal function, but there was not a clear beneficial effect on all-cause mortality (odds ratio 1.17, 95% CI 0.67–2.06). In our study, we reported a higher risk of all-cause mortality in people with albuminuria (with or without eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2, Table 2), and the risk remained significant in those who had a low-protein intake. We suggested that dietary protein restriction had no benefit on improving survival irrespective of people's albuminuria status or eGFR level. Our finding using data from a general population was in agreement with previous studies22–24 in patients with CKD, and more evidence is required before recommendation of dietary protein restriction to less than 0.8g/kg/day for patients with CKD.
On the other hand, there is a growing sense of concern about protein-energy wasting owing to dietary protein restriction. People on low-protein diet are more likely to consume sparingly or even avoid some high-protein foods, such as meat, eggs, beans or cheese. Limited food choices might result in anorexia, malnutrition or uneven caloric distribution. Noce et al.25 demonstrated that low-protein diet (0.7g/kg/day) contributed to a significant reduction in serum albumin and body mass index, and a significant impairment of lean mass in patients with CKD. In a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Yue et al.26 reported that low-protein diet increased the risk of malnutrition (a decline in body weight and body mass index), and the impacts of low-protein diet were much more obvious on aged, obesity, moderate or severe renal impairment, and diabetic nephropathy patients. Especially in the elderly,27 having defect in protein synthesis with aging, taking low-protein diet may increase risk of sarcopenia, frailty, disability, hospitalization and death.28 On top of that, people taking low-protein diet may increase carbohydrate or fat intake in order to maintain the daily caloric requirement. The increase in carbohydrate or fat intake may have undesirable effects.29 Our study participants with a low-protein intake had more than 50% of their daily calorie from carbohydrate (Table 4). Although they had a lower consumption of saturated and total fat, as well as total sugar and daily calorie, compared with those who had a protein intake ≥0.8g/kg/day, the former also had lower consumption of fiber, fruit, and vegetable, with a lower diet quality, compared with the latter. How to maintain diet quality along with a low-protein intake merits further investigation.
The following limitations should be taken into consideration when interpreting our findings. First, there might be some bias for data collected by questionnaires or home interview. Nevertheless, all interviewers in the NHANES were required to complete a training course and to minimize data collection bias. Thus, the quality of data should be acceptable. Second, this was an observational study. Although we found that having a low-protein intake (<0.8g/kg/day) might be detrimental in people with albuminuria, the causal relationship is yet to be proved. Third, types of carbohydrate and sources of protein (plant- or animal-based) were not investigated in this study, while both of which were related to patients’ outcomes.30 Although we considered diet quality as a confounder and adjusted for HEI-2010 total score19 in our analyses, quality of carbohydrate and protein may have confounded our results.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that the mortality risk associated with CKD was consistent in people with or without a low-protein intake (<0.8g/kg/day). A low-protein intake was even associated with a higher risk of mortality in people with albuminuria. High-quality prospective randomized control trials are needed to confirm our findings. Before that, whether low-protein diet (<0.8g/kg/day) should be recommended to people with CKD deserves careful consideration.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
We would like to thank the participants in the NHANES, and the members of the National Center for Health Statistics for collecting the data and making it publicly available. This work was supported by Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan [grant numbers TCVGH-1083505C, 2019; TCVGH-1093504C, 2020]. The funder was not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of the results, or preparation of the article.