Spinal epidural abscess (SEA) is a rare infection of the central nervous system with an incidence of 2–25 per 100,000 patients admitted to hospital.8 However, there has been an increase in its frequency in the past 30 years due to the increasing number of patients undergoing spinal invasive procedures, either as anesthetic procedures or for pain control, and also because of the improved resolution and/or increased number of imaging procedures. SEA poses a diagnostic challenge because its manifestations are nonspecific and a delay in diagnosis may lead to irreversible neurological sequelae and even death. Diabetes is considered as a risk factor for the occurrence of SEA, and should therefore be included in differential diagnosis of any diabetic patient with lumbar pain.
We report the case of a 70-year-old male Caucasian patient who attended the emergency department for a second consecutive time reporting mechanic pain refractory to standard analgesics in the left back region, irradiating to the lumbar spine, for approximately 15 days. Twenty days after the pain started, the patient experienced functional impotence with walking difficulty due to lower limb weakness. He had not experienced fever or sphincter changes, and did not report any other associated symptoms. There was no history of recent trauma, anesthetic block, or peripheral infection. The only remarkable history was amputation of the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones of the right foot for osteomyelitis with a microbiological report of the soft tissue culture positive for Pseudomonas sp.
The personal history of the patient included long-standing type 2 diabetes with fair chronic metabolic control, with an HbA1c value of 7.7% one month before admission, a slight worsening in metabolic control in laboratory tests at admission (HbA1c 7.9%), and multiple microvascular (non-proliferative retinopathy, nephropathy with stage 3B chronic renal disease, sensorimotor polyneuropathy, and Charcot arthropathy) and macrovascular (chronic ischemic cardiopathy, stroke some 25 years before with no sequelae, and Fontaine stage II intermittent claudication) complications. He was being treated with multiple insulin doses. The patient also had high blood pressure, adequately controlled with lercanidipine and irbesartan, and dyslipidemia treated with atorvastatin.
A physical examination revealed a good general condition, and the patient was afebrile and hemodynamically stable. There were no respiratory, cardiovascular, or abdominal pathological findings. A neurological examination found no motor or sensory deficits in the upper limbs or trunk. However, a lower limb examination revealed decreased patellar and ankle jerk reflexes in both limbs, as well as motor deficit 3/5, with no sensory changes. In addition, a large eschar was seen on the sacral region with a big central necrotic plaque 6cm×6cm in diameter and 1cm in depth with an evolution of approximately 6 months.
The most relevant laboratory test results included: WBC, 18,600 (3500–12,000g/L) with neutrophilia (86% neutrophils); hemoglobin, 7.79g/dL (12–16g/dL); hematocrit, 24% (33–53%); platelet count and coagulation within the normal range; urea, 74mg/dL (18–55mg/dL); creatine, 1.98mg/dL (0.72–1.25mg/dL); normal electrolytes and liver function; C-reactive protein, 273mg/L (1–5mg/L). ESR 94 (1–20mm/1h).
Chest X-rays showed no significant changes.
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was isolated from soft tissue culture (abscess sample taken by laminectomy) and from the sample taken from the smear of the sacral eschar. As both urine and blood cultures were negative, a transthoracic echocardiogram was not performed.
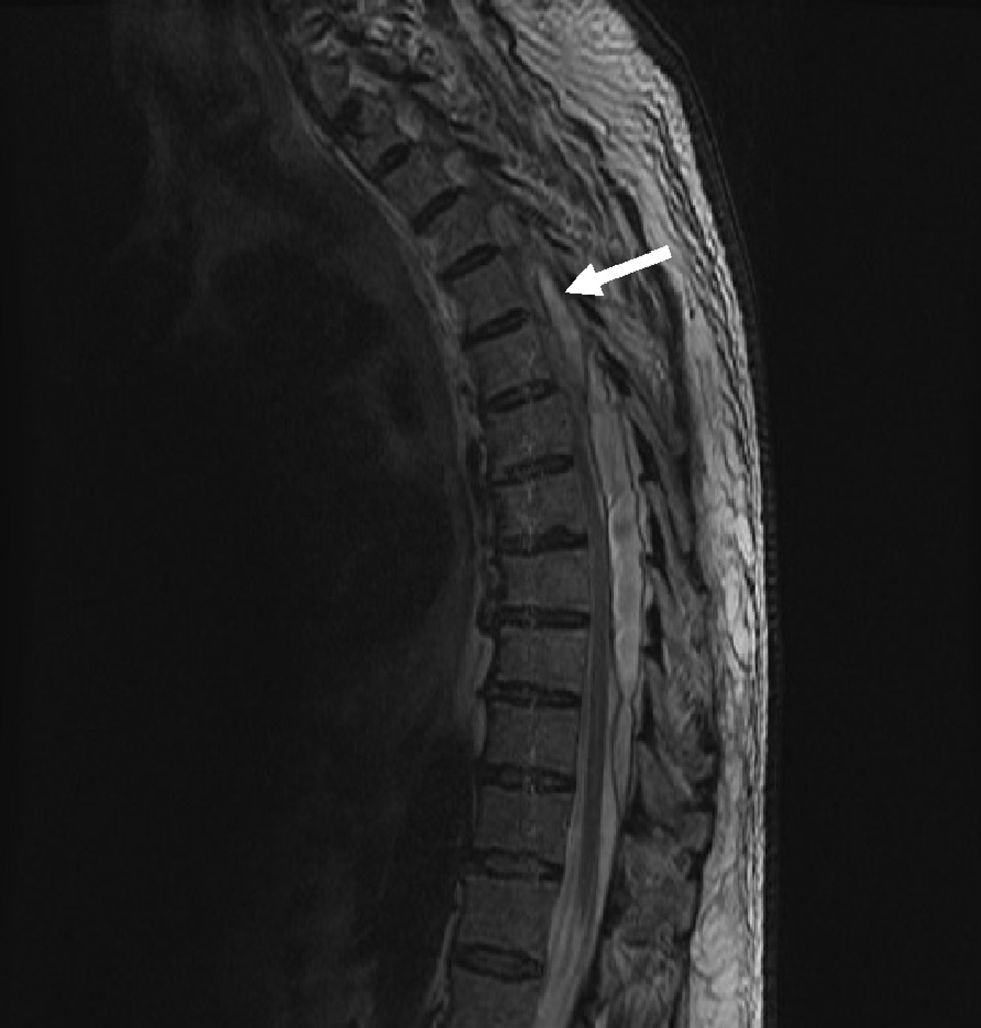
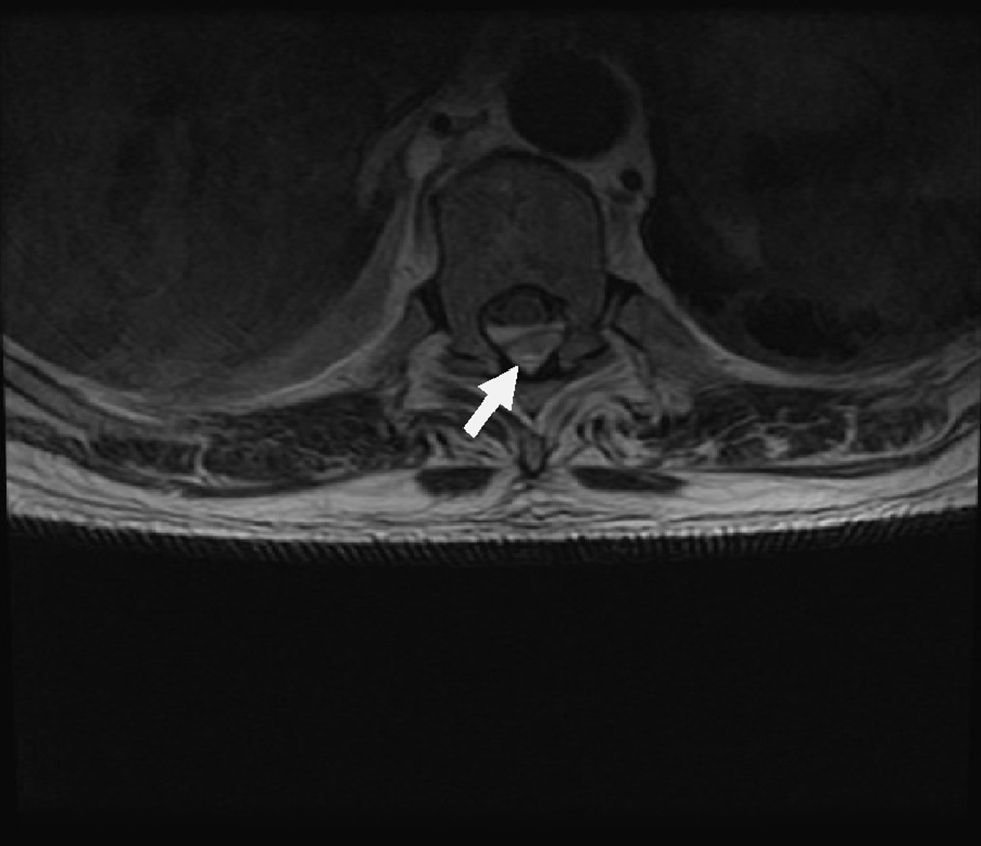
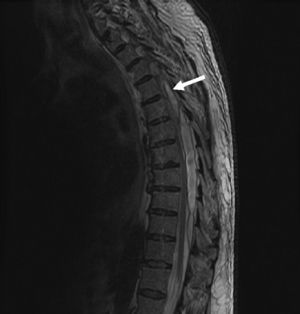
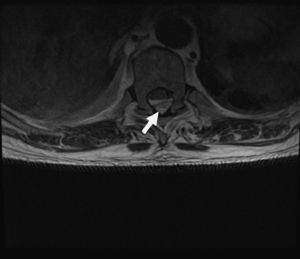
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the thoracic spine (Figs. 1 and 2) revealed a posterior collection between the thoracic vertebrae T5 and T10–11 suggesting epidural hematoma which caused medullary compression, but no clear edema. Because of these findings, the neurology department was consulted, and a T7–T8 laminectomy was performed, as well as evacuation of the epidural abscess and surgical debridement of the sacral ulcer.
During admission, empirical antibiotic therapy was started with intravenous vancomycin, as well as rehabilitation therapy leading to progressive total recovery from neurological signs and symptoms.
SEA is an uncommon condition. The incidence of bacterial SEA has increased in the past two decades because of population aging, intravenous drug abuse, the increased use of epidural instrumentation, and greater diagnostic capabilities due to the routine use of MRI. The reported incidence of epidural abscess after epidural anesthetic block ranges from 0.5% to 3%, but no data are currently available on the incidence of SEA in diabetic patients.1
The mean age at the presentation of SEA is 50 years, with a prevalence peak between 50 and 70 years of age.2
The most significant predisposing factor is the use of epidural catheters for gynecological anesthesia.3 Other risk factors include diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, the human immunodeficiency virus, trauma, acupuncture, contiguous bone and soft tissue infection or bacteremia, and intravenous drug use.4
The most common pathogen involved (found in up to 60% of cases) is S. aureus, mainly acquired at the hospital. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus, which is found in more than 40% of patients, involves a poorer prognosis as compared to epidural infections caused by methicillin-sensitive S. aureus. Other less commonly involved pathogens include Gram-negative bacilli (16%), streptococci (9%), anaerobic pathogens (2%) and, less frequently, fungi and parasites.5
The clinical signs and symptoms are highly nonspecific. Initially only fever and malaise may occur, followed by symptom progression in a typical sequence: backache, paresthesia in the distribution of the affected nerve, motor weakness, and bladder dysfunction. The classical triad consists of backache, fever, and neurological deficits, but this only occurs in 10–15% of patients at diagnosis.6
Laboratory tests show, as in any infectious process, an increase in acute phase reactants. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is increased in both vertebral osteomyelitis and SEA. Ninety-four percent of patients with SEA have elevated ESR levels at the baseline visit. An increase in CRP levels is, however, less marked, and leukocytosis may be absent in 40% of patients.7
Imaging studies of the spine are indispensable for diagnosis. MRI is preferred over tomography as the first option because it is usually positive early in the course of infection and allows the localization and extent of the inflammatory changes to be determined. Once SEA is located, it is important to try and determine the etiological agent using blood, abscess, and/or CSF cultures.6
A differential diagnosis from degenerative bone diseases, tumor metastases, vertebral osteomyelitis, meningitis, and herpes zoster should be performed before skin lesions appear.8
Treatment consists of a combination of systemic antibiotic therapy and/or surgical drainage by laminectomy if appropriate. The success of medical treatment depends on age at diagnosis, abscess size, and neurological abnormalities at presentation. Prior studies reported that patients given medical treatment alone had poorer long-term results than those immediately given combined treatment.
To sum up, we report an uncommon case of SEA in a patient with type 2 diabetes with poor chronic metabolic control, which caused backache and a neurological deficit and in which the probable origin of epidural infection was a soft tissue infection in the sacral eschar, as no bacteremia was found, and there was no possibility of iatrogenic inoculation. We believe, therefore, that priority consideration should be given to early empirical antibiotic therapy for infections in diabetic patients in order to prevent the occurrence of potentially fatal complications, and that SEA should be considered in differential diagnosis.
Please cite this article as: Zubillaga I, Nicolau J, Francés C, Estremera A, Masmiquel L. Absceso epidural espinal en un paciente diabético. Endocrinol Nutr. 2014;61:224–226.