Determinar las variables y los factores predictivos asociados a la transfusión sanguínea alogénica (TSA) y a su frecuencia en pacientes con diagnóstico de fractura de fémur y con indicación de intervención quirúrgica. El objetivo secundario fue describir la frecuencia y cantidad de TSA en estos pacientes.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio observacional transversal retrospectivo sobre pacientes ingresados en el Hospital Sagrat Cor de Barcelona con diagnóstico de fractura de fémur en el año 2016 que requirieron intervención quirúrgica. Se recogieron variables demográficas y clínicas de los pacientes transfundidos, así como también de los no transfundidos, incluyendo el tipo de fractura.
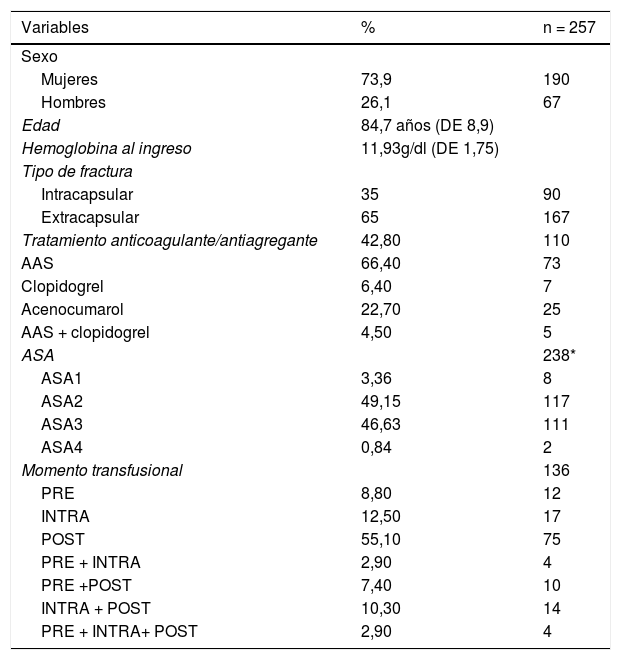
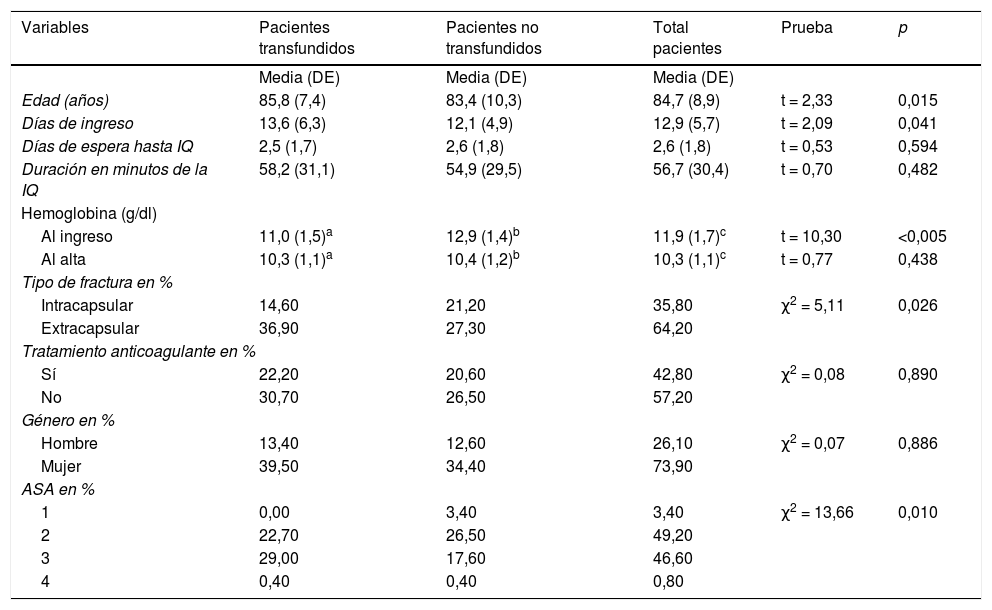
ResultadosLa muestra de pacientes incluidos en el estudio fue de 257. El 52,9% de los pacientes estudiados requirió soporte transfusional; presentaban una hemoglobina media al ingreso de 11,01 g/dl, frente a los que no requirieron transfusión, que tenían un valor de 12,97 g/dl. El 42,80% de los pacientes recibía tratamiento con anticoagulantes o antiagregantes antes de producirse la fractura.
ConclusionesMás de la mitad de los pacientes que presentaron fractura de fémur precisaron transfusión sanguínea durante su estancia en el hospital. Los factores asociados a la necesidad de TSA en pacientes con fractura de fémur fueron el nivel de hemoglobina al ingreso y el tipo de fractura, así como la edad y clasificación ASA (sistema de clasificación de la Sociedad Americana de Anestesiología). Esta información se podría tener en cuenta en los protocolos de ahorro de sangre. Por último, consideramos que es importante que para todos los pacientes que ingresen en el hospital con el diagnóstico de fractura de fémur y que requieran de intervención quirúrgica se haga una petición de reserva de sangre, puesto que un alto porcentaje de ellos en algún momento de su estancia hospitalaria será transfundido.
To determine the variables and predictive factors associated with the administration and frequency of the allogenic blood transfusion (ABT) on patients diagnosed with fracture of femur requiring surgical intervention. The secondary objective was to describe the frequency and quantity of ABT on those patients.
MethodA retrospective transversal observational study was performed on patients admitted to the Sagrat Cor hospital of Barcelona with a diagnosis of fractured femur that required surgical intervention in 2016. Several demographic variables were gathered along with the clinical data and outcome of transfused and non-transfused patients, including the type of fracture.
ResultsThe overall sample was 257 patients. Of the patients studied, 52.9% required blood transfusion support. Patients who required ABT had haemoglobin values on admission of 11.01 gdl while those that did not require transfusion had an average value of 12.97 g/dl.
Of the patients, 42.8% were on anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet therapy before the fracture occurred.
ConclusionsMore than half the patients admitted for fracture of femur received blood transfusion. The data collected showed that the hospital transfusion policy offered satisfactory results. Factors associated with the need for ABT were haemoglobin levels on admission and the type of fracture. Age and ASA risk (classification system of the American Society of Anesthesiologists) were also risk factors for ABT. This information could be useful for blood saving protocols. Finally, we think that it is important that all patients that are hospitalised with a diagnosis of fracture of femur and require surgery have a blood reserve request made, given that a high percentage of them, at any time during their stay, will be transfused.