The 4th Udayana International Nursing Conference (4th INC)
More infoThe COVID-19 pandemic has impacted breastfeeding self-efficacy directly or indirectly. This is likely due to the adverse effect of movement and community activity restrictions to prevent virus transmission. This study aims to measure how breastfeeding self-efficacy has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
MethodThis study uses a cross-sectional design with participants consisting of mothers giving birth from June to July 2021 in Bekasi, Indonesia. The recruitment used a consecutive sampling method. The data were collected using the breastfeeding self-efficacy scale-short form, the postpartum bonding questionnaire, the Zung self-rating anxiety scale, and the multidimensional scale of perceived social support. The COVID-19-related factors, i.e., anxiety, bonding and social support on breastfeeding self-efficacy, were measured using the Path Analysis.
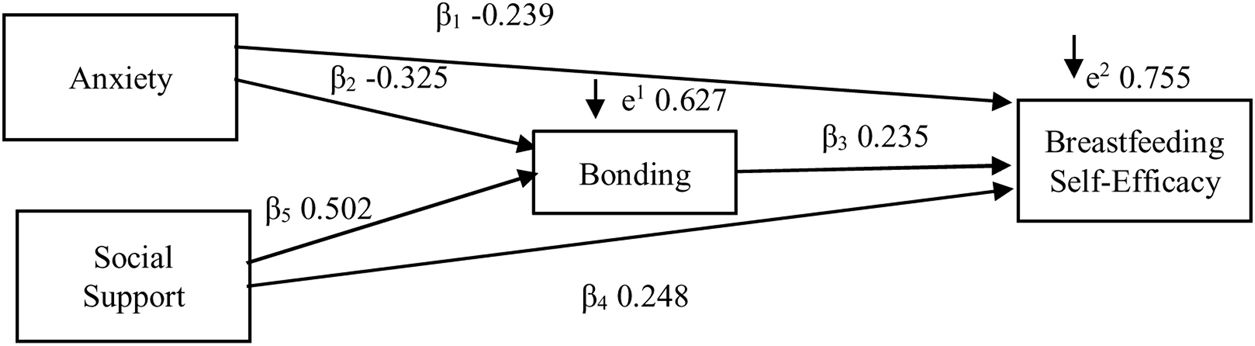
ResultsThe results showed that anxiety, bonding, and social support affected breastfeeding self-efficacy among the 118 respondents. While anxiety had a negative effect on breastfeeding self-efficacy, bonding and social support had a positive effect. The effect of anxiety was more direct (β −0.239; p 0.00) than indirect (β −0.076; p 0.04). Social support also had a more direct (β 0.248; p 0.00) than indirect effect (β 0.118; p 0.046). Likewise, bonding had a significant impact on breastfeeding self-efficacy (β 0.235; p 0.039). However, the effect of anxiety and social support indirectly on breastfeeding self-efficacy via bonding was less significant than their direct impacts.
ConclusionThe factors related to breastfeeding self-efficacy affected by the COVID-19 pandemic are anxiety, bonding, and social support. Interventions during a crisis such as the pandemic could aim to reduce anxiety and improve social support. Health education and counselling are essential to enhance competence and self-efficacy in breastfeeding their babies and build more positive interactions with their children.