To identify the relationship between use of alcohol, number of sexual partners and age of sexual initiation.
MethodDescriptive-correlational study. A random sample of 319 young women (age 18–25) from Nuevo Laredo, Mexico was recruited. A sociodemographic data sheet and the AUDIT questionnaire were used. Non-parametric Spearman's rank correlation coefficient and Kruskal–Wallis H test were selected.
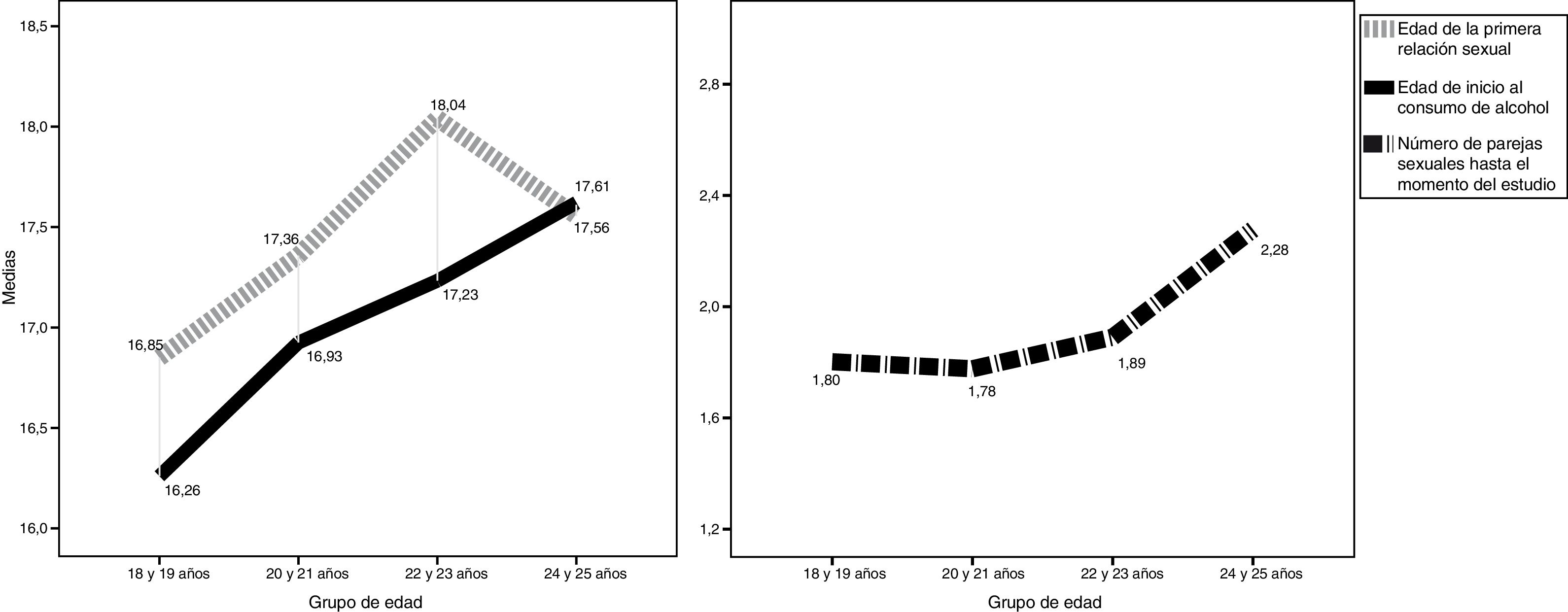
ResultsOn average the participants were 20.70 years old (±2.1), had 1.86 sexual partners (±1.27), started drinking alcohol at the age of 16.82 (±1.79), and their first sexual intercourse was at the age of 17.38 (±1.65). There was a decrease in the age of onset of alcohol use (H=16.646, p<.001) and the age at first sexual intercourse (H=26.749, p<.001) on the lower their current age. The overall AUDIT score negatively correlated with the age of the participants on their first sexual intercourse (rs=−.168, p<.001) and positively correlated with the number of sexual partners (rs=.243, p<.001). The aforementioned correlations were more intense among the younger participants (18- and 19-year olds; p<.01).
ConclusionsThere was an association between higher use of alcohol, early age of sexual initiation and number of sexual partners. Nursing professionals may address such variables simultaneously through preventive strategies directed specifically at young women.
Identificar la relación del consumo de alcohol con la edad de la primera relación sexual y el número de parejas sexuales.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo-correlacional. Se seleccionó una muestra aleatoria de 319 mujeres jóvenes (18 a 25 años) de Nuevo Laredo, México. Se utilizó una cédula de datos y el cuestionario AUDIT. Se empleó el coeficiente de correlación de Spearman y la prueba H de Kruskal–Wallis.
ResultadosEn promedio, las participantes tuvieron 20,70 ± 2,1 años de edad, 1,86 ± 1,27 parejas sexuales, iniciaron a beber alcohol a los 16,82 ± 1,79 años y su primera relación sexual fue a los 17,38 ± 1,65 años. Se apreció un decremento de la edad de inicio en el consumo de alcohol (H=16,646, p <0,001) y de la primera relación sexual (H=26,749, p <0,001) en función de tener menor edad. La puntuación del AUDIT correlacionó de forma negativa con la edad de la primera relación sexual (rs=–0,168, p <0,001) y de manera positiva con el número de parejas sexuales (rs=0,243, p <0,001). Las anteriores correlaciones fueron más intensas entre las participantes de menor edad (18 y 19 años; p <0,01).
ConclusionesEl elevado consumo de alcohol, el inicio temprano de la actividad sexual y el mayor número de parejas sexuales se asociaron de forma significativa. Tales variables podrían ser abordadas conjuntamente por las enfermeras durante las acciones preventivas dirigidas específicamente al segmento de las mujeres jóvenes.