The issue of quality of life and its relationship with learning motivation is very important in different sections of the society, especially people who have special physical, mental and psychological conditions. The aim of this study was to determine the status of the health-related quality of life and its relationship with students' learning motivation during the Covid-19 era.
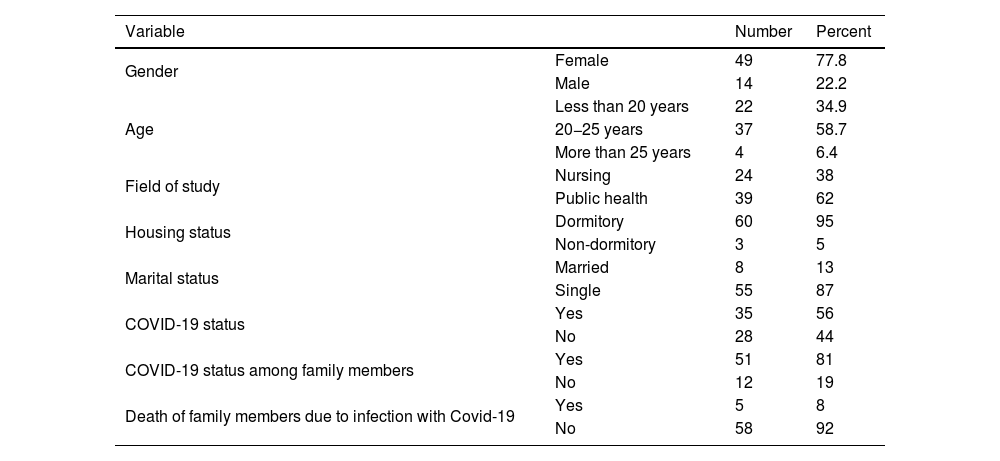
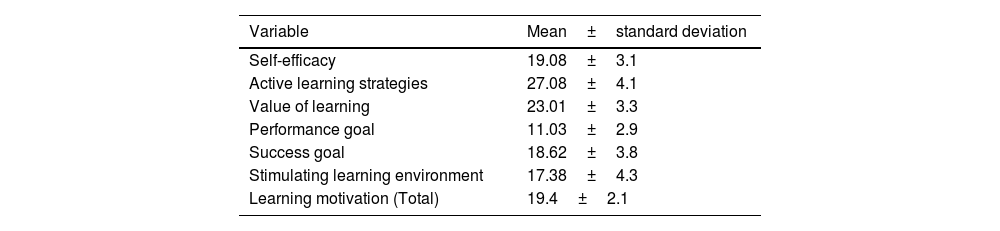
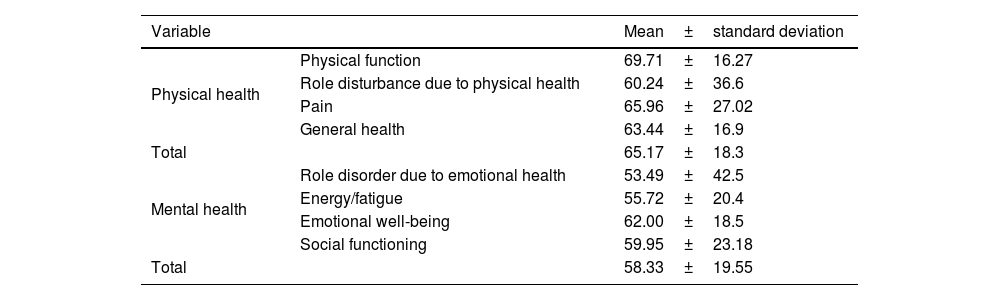
MethodsIn this cross-sectional descriptive analytical study, 63 students of Chabahar nursing faculty participated in the study. Data collection tools were demographic information, SF-36 health related quality of life questionnaire and learning motivation questionnaire. Data analysis was done in SPSS version 16 statistical software. Descriptive (mean, standard deviation, and percentage) and analytical (Spearman, Mann-Whitney, and Kruskal-Wallis tests) tests were used to analyze the data.
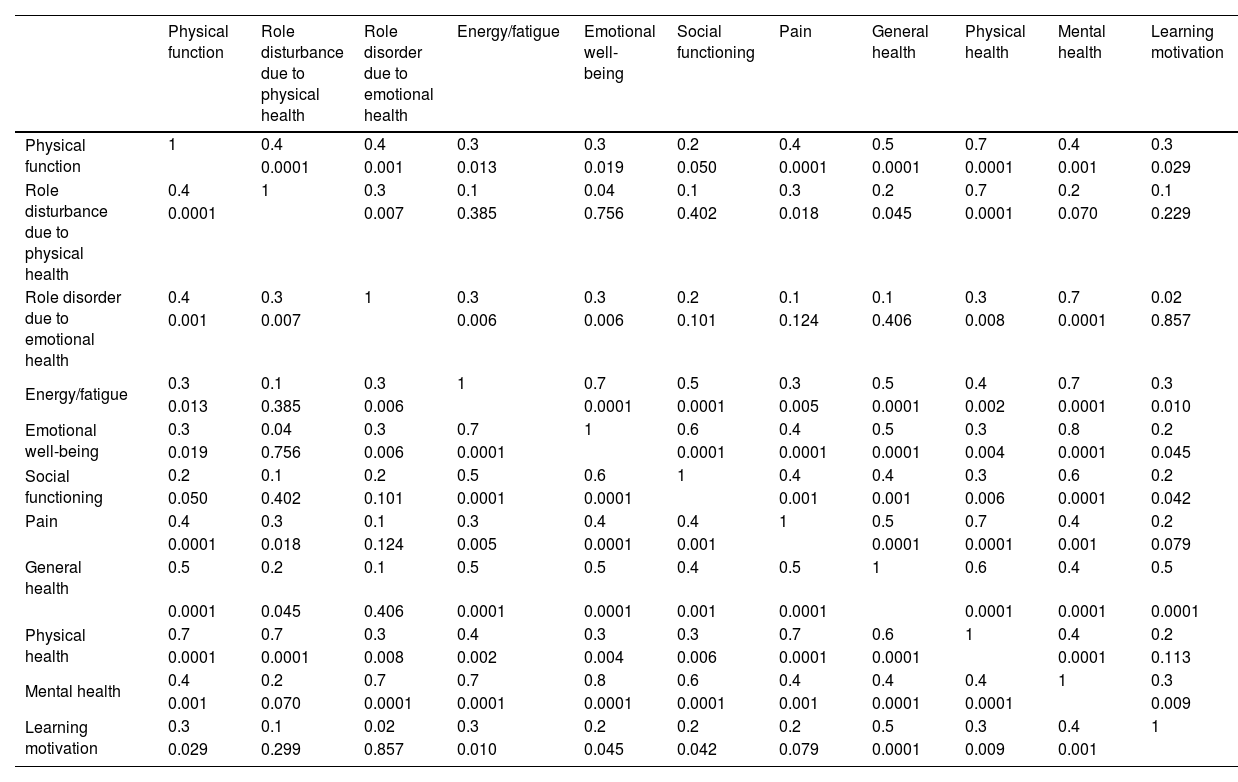
ResultsThe physical function subscale related to physical health had a significant relationship with all the mental health subscales (role disruption due to emotional health (r=0.4, P=.001), energy/fatigue (r=0.3, P=.013), emotional well-being (r=0.3, P=.019), social functioning (r=0.2, P=.05)) and learning motivation (r=0.3, P=.029) in the students participating in the study. There was no significant relationship between learning motivation and general physical health (r=0.2, P=.113).
ConclusionThe findings of the present study showed that there is a strong and significant relationship between students' mental health and their motivation to learn. In this way, increasing students' mental health has a positive effect on their motivation to learn. Therefore, in order to increase the motivation to learn among students, providing special care in the field of mental health can be useful for this group and provide a basis for improving their quality of life.
La cuestión de la calidad de vida y su relación con la motivación para aprender es muy importante en los diferentes sectores de la sociedad, sobre todo en las personas que presentan condiciones físicas, mentales y psicológicas especiales. El objetivo de este estudio fue determinar el estado de la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud y su relación con la motivación de aprender de los alumnos durante la pandemia de Covid-19.
MétodosEn este estudio analítico descriptivo transversal, participaron 63 estudiantes de la facultad de enfermería de Chabahar. Las herramientas de recopilación de datos fueron información demográfica, cuestionario SF-36 sobre calidad de vida relacionada con la salud y cuestionario de motivación para el aprendizaje. El análisis de los datos se realizó utilizando el software estadístico SPSS versión 16. Para analizar los datos se utilizaron pruebas descriptivas (media, desviación estándar y porcentaje) y analíticas (pruebas de Spearman, Mann-Whitney y Kruskal-Wallis).
ResultadosLa subescala de función física relacionada con la salud física tuvo relación significativa con todas las subescalas de salud mental (interrupción de roles por salud emocional (r=0,4, P=,001), energía/fatiga (r=0,3, P=,013), bienestar emocional (r=0,3, P=,019), funcionamiento social (r=0,2, P=,05)) y motivación para el aprendizaje (r=0,3, P=,029) en los estudiantes que participaron en el estudio. No hubo una relación significativa entre la motivación para aprender y la salud física general (r=0,2, P=,113).
ConclusiónLos hallazgos del presente estudio mostraron que existe una relación fuerte y significativa entre la salud mental de los estudiantes y su motivación para aprender. De este modo, mejorar la salud mental de los estudiantes tiene un efecto positivo en su motivación para aprender. Por tanto, para aumentar la motivación para aprender entre los estudiantes, el brindar una atención especial en el campo de la salud mental puede ser útil para este colectivo, proporcionando una base para mejorar su calidad de vida.