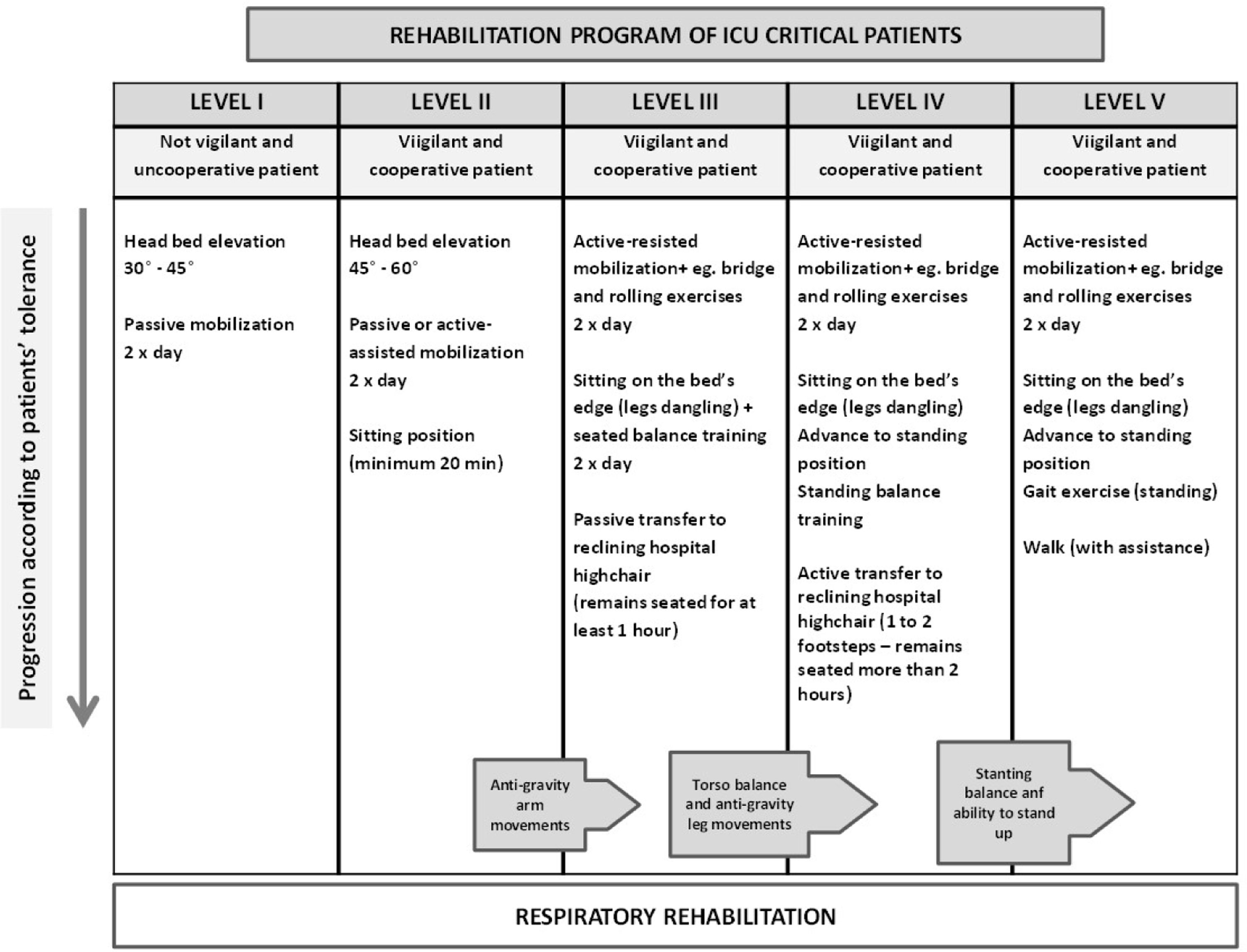
Intensive care unit-acquired muscle weakness (ICUAW) in critically ill patients is frequent and associated with negative outcomes. Early rehabilitation is a strategy to improve outcomes. The aim was to assess the effects of a rehabilitation nursing programme at discharge from intensive care unit.
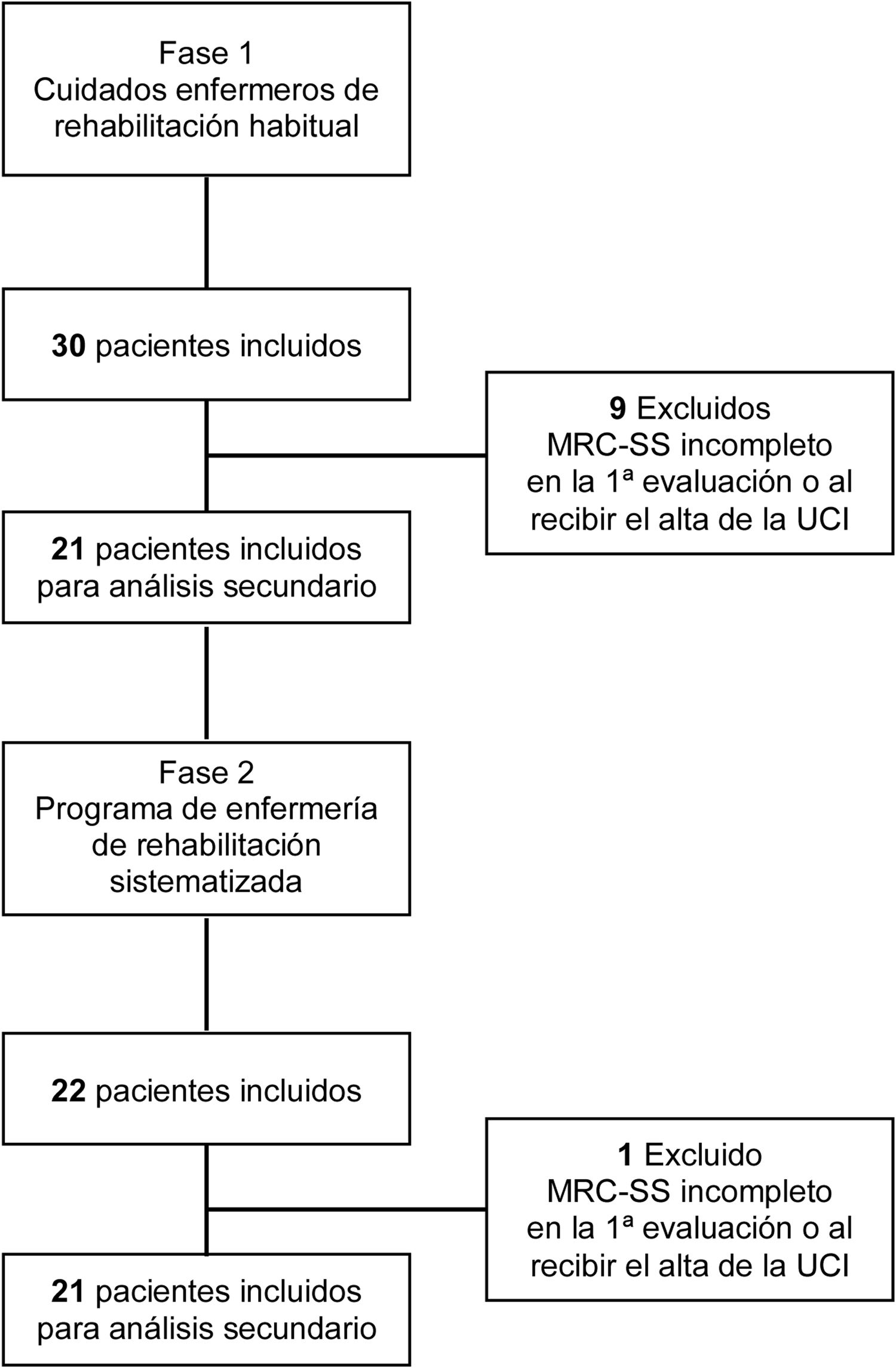
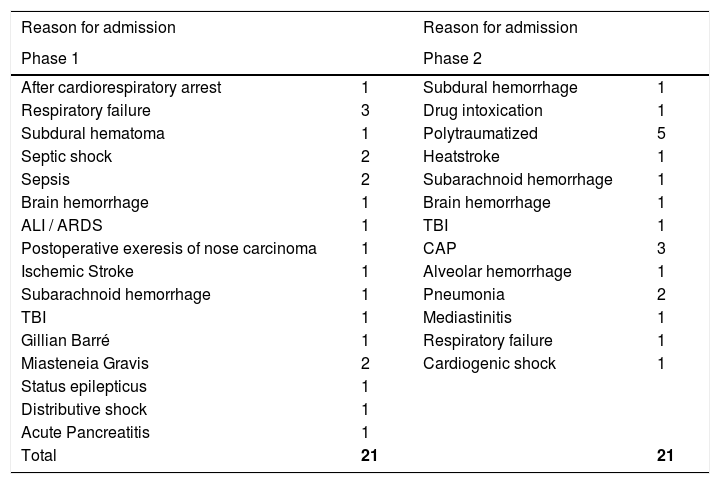
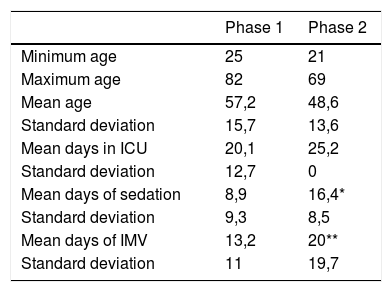
MethodsQuasi-experimental study with the comparison between two groups: one enrolled in a systematized nursing rehabilitation program and the other with usual nursing rehabilitation care. A non-probabilistic sample, sequential, of 42 critically ill ventilated patients, 21 patients in the control group and 21 patients the intervention group (June 2017 to June 2019), in three intensive care units of one large Portuguese teaching hospital. Mann-Whitney test was performed to compare Medical Research Council Sum Score (MRC-SS) values between groups.
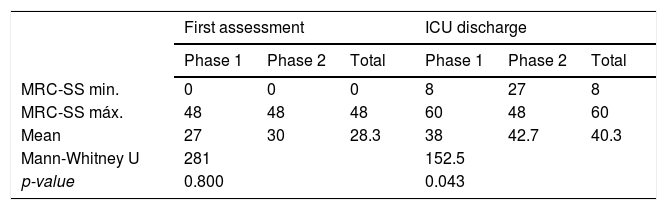
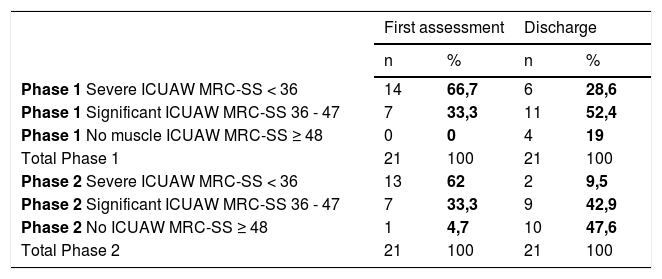
ResultsPatients undergoing the rehabilitation program had a decrease in ICUAW (at ICU discharge mean MRC-SS = 38 vs. mean MRC-SS = 42.7, p = 0.043, U = 152,5). There was a decrease in severe muscle weakness (9.5% vs. 28.6%) and significant muscle weakness (42.9% vs. 52.4%) and an increase without muscle weakness (47,6% vs. 19%).
ConclusionsThe systematic rehabilitation nursing program can improve muscle strength and reduce functional disability at the time of discharge from intensive care.
La debilidad adquirida en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (DAUCI) en pacientes críticos es frecuente y se asocia a resultados negativos. La rehabilitación es una estrategia para mejorar los resultados. El propósito fue evaluar los efectos de un programa de enfermería de rehabilitación al alta de la unidad de cuidados intensivos.
MétodosEstudio cuasi-experimental. Comparación entre pacientes que se sometieron a cuidados habituales de rehabilitación de enfermería con pacientes que se sometieron a un programa de enfermería de rehabilitación sistematizado. Una muestra no probabilística, secuencial de 42 pacientes críticos ventilados, 21 pacientes en el grupo de control y 21 pacientes en el grupo de intervención (de junio 2017 a junio 2019), en tres unidades de cuidados intensivos de un gran hospital universitario portugués. Se realizó la prueba de Mann-Whitney para comparar los valores de la puntuación total del Medical Research Council Sum Score (MRC-SS) entre los grupos.
ResultadosLos pacientes sometidos al programa de rehabilitación sistematizado, presentaran una disminución de la DAUCI (en el momento del alta de la UCI media de MRC-SS = 38 vs. media de MRC-SS = 42.7, p = 0.043, U = 152,5). Hubo una disminución de la debilidad muscular severa (9,5% vs 28,6%) y debilidad muscular significativo (42,9% vs 52,4%) y aumento de pacientes sin debilidad muscular (47,6% vs 19%).
ConclusionesEl programa de enfermería de rehabilitación sistemática puede mejorar la fuerza muscular y reducir la incapacidad funcional al momento del alta de cuidados intensivos.