Los profesionales de enfermería que trabajan en unidades de cuidados intensivos (UCI) poseen un alto riesgo de desarrollar respuestas emocionales negativas, así como problemas emocionales y espirituales relacionados con cuestiones éticas. El diseño de estrategias efectivas que mejoren estos aspectos viene determinado por el conocimiento de los niveles de burnout y conflicto ético de dichos profesionales, así como la influencia que el entorno de la práctica puede tener en ellos.
ObjetivoAnalizar la relación existente entre niveles de burnout, exposición a conflicto ético y la percepción del ambiente de la práctica entre sí y con las variables sociodemográficas de los diferentes profesionales de enfermería de cuidados intensivos.
MetodologíaEstudio transversal correlacional en una UCI de un hospital universitario de nivel terciario. Se evaluó el nivel de burnout con la escala Maslach Burnout Inventory-Human-Services Survey; el nivel de conflicto ético, con el cuestionario de conflictividad ética para enfermeros, y la percepción del entorno, con la escala Practice-Environment-Scale of the Nursing-Work-Index. La asociación entre variables categóricas ha sido analizada mediante el test exacto de Fisher de chi-cuadrado (χ2).
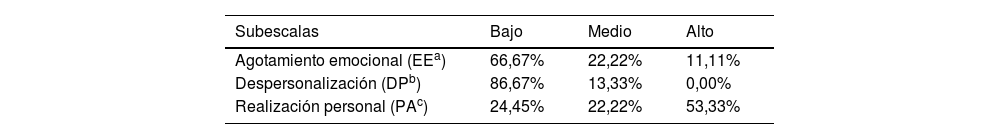
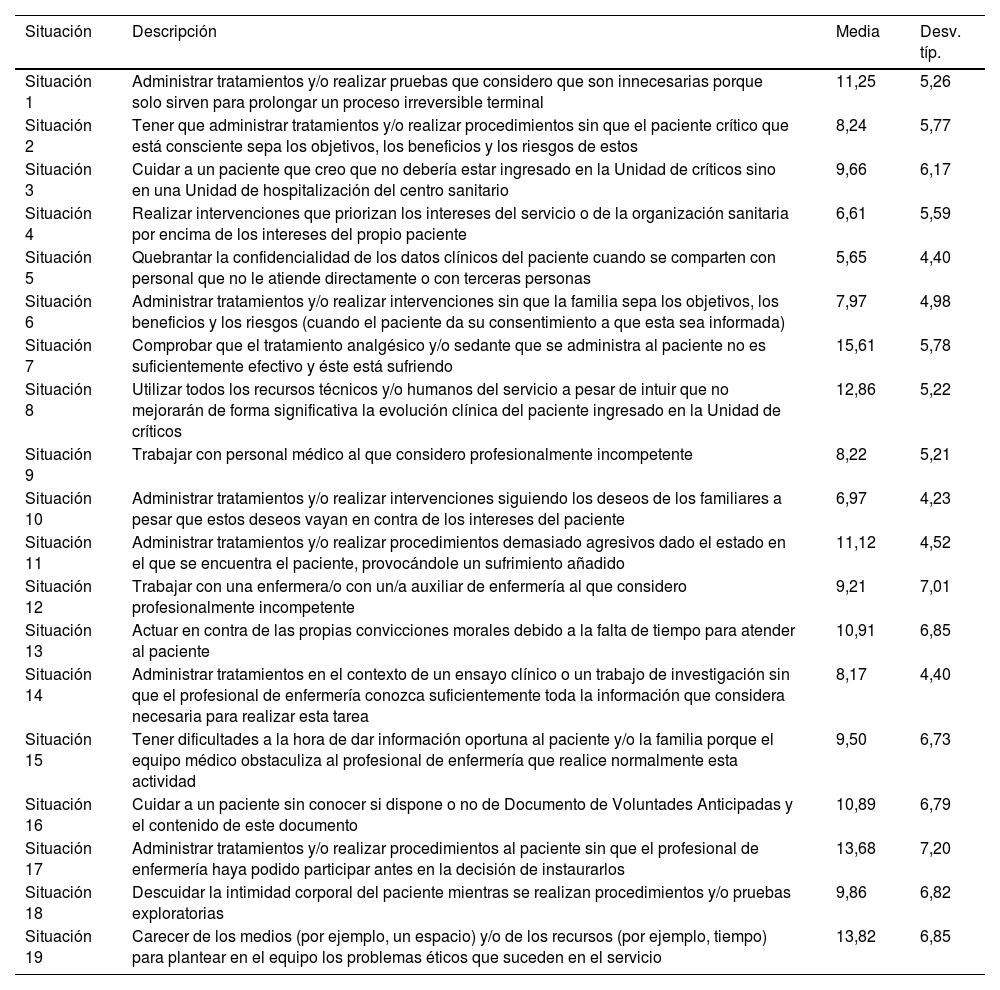
ResultadosSe evaluaron 39 enfermeras y 8 auxiliares, obteniendo una tasa de participación del 82,93%. El 31,10% de los profesionales de enfermería presentaron signos de burnout, el 14,89% consideraron que trabajan en un entorno desfavorable y el 87,23% presentaron un índice de exposición a conflicto ético medio-alto.
El nivel educativo (χ2=11,084, p=0,011) y la categoría profesional (χ2=5,007, p=0,025) influyeron en el nivel de burnout, presentando las auxiliares mayores niveles del mismo.
Al comparar el nivel de burnout con el entorno y el índice de conflicto ético no hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas.
ConclusionesLa ausencia de asociación encontrada en el estudio entre burnout y conflicto ético con la percepción del entorno de la práctica hace pensar que los factores personales pueden influir en su desarrollo.
Nursing professionals working in intensive care units (ICU) are at high risk of developing negative emotional responses as well as emotional and spiritual problems related to ethical issues. The design of effective strategies that improve these aspects is determined by knowing the levels of burnout and ethical conflict of these professionals, as well as the influence that the practice environment might have on them.
ObjectivesTo analyze the relationship between levels of burnout, the exposure to ethical conflicts and the perception of the practice environment among themselves and with sociodemographic variables of the different intensive care nursing professionals.
MethodsDescriptive, correlational, cross-sectional, observational study in an ICU of a tertiary level university hospital. The level of burnout was evaluated with the Maslach Burnout Inventory Human Services Survey scale; the level of ethical conflict with the Ethical Conflict Questionnaire for Nurses; and the perception of the environment with the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index. Descriptive and inferential statistics were performed. The association between categorical variables was analyzed using Fisher's exact chi-square test (χ2)
Results31 nurses and 8 nursing assistants were evaluated, which meant a participation rate of 82.93%. 31.10% of the nursing professionals presented signs of burnout, 14.89% considered that they work in an unfavorable environment and 87.23% presented a medium-high index of exposure to ethical conflict.
The educational level (χ2=11.084, P=.011) and the professional category (χ2=5.007, P=.025) influenced the level of burnout: nursing assistants presented higher levels of this.
When comparing the level of burnout with the environment and the index of ethical conflict, there were no statistically significant differences.
ConclusionsThe absence of association found in the study between burnout and ethical conflict with the perception of the practice environment suggests that personal factors may influence its development.
Article
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.