El dolor lumbar crónico es una de las principales causas de incapacidad laboral en el mundo. Requiere un abordaje interdisciplinario para la evolución del paciente. Hasta el momento, no existe consenso en el manejo del dolor lumbar crónico, lo que generó la inquietud de esta revisión sistemática.
ObjetivoIdentificar la efectividad de los protocolos de fisioterapia en el manejo del dolor lumbar crónico.
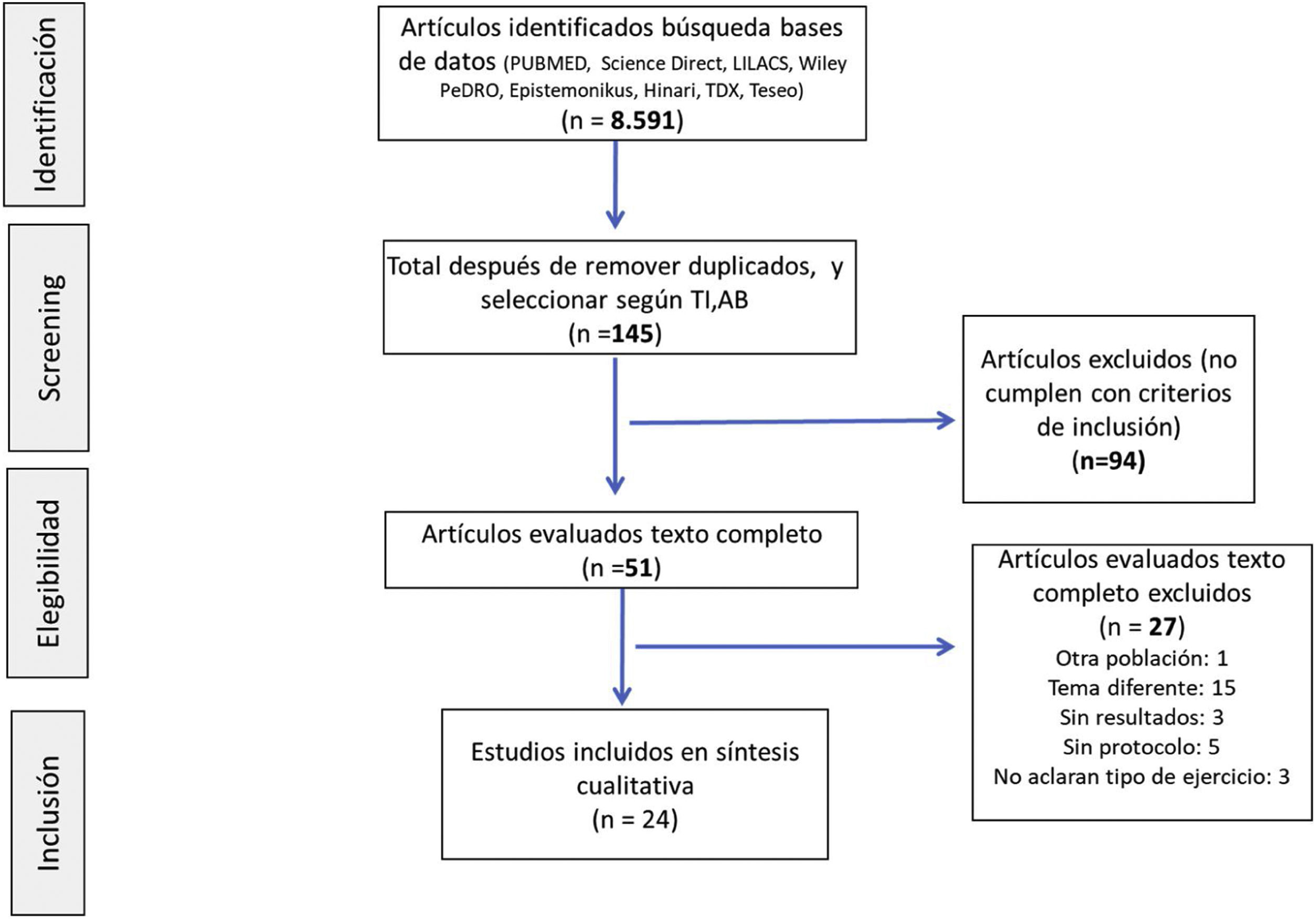
MetodologíaSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en las bases de datos Pubmed, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Oxford, Wiley, Cochrane Library Plus, PEDro, Epistemonikos, Hinari y LILACS, Google Scholar, Teseo y PROSPERO, desde el inicio de las bases hasta agosto de 2021. Los criterios de selección se definieron según la intervención y el tema del artículo.
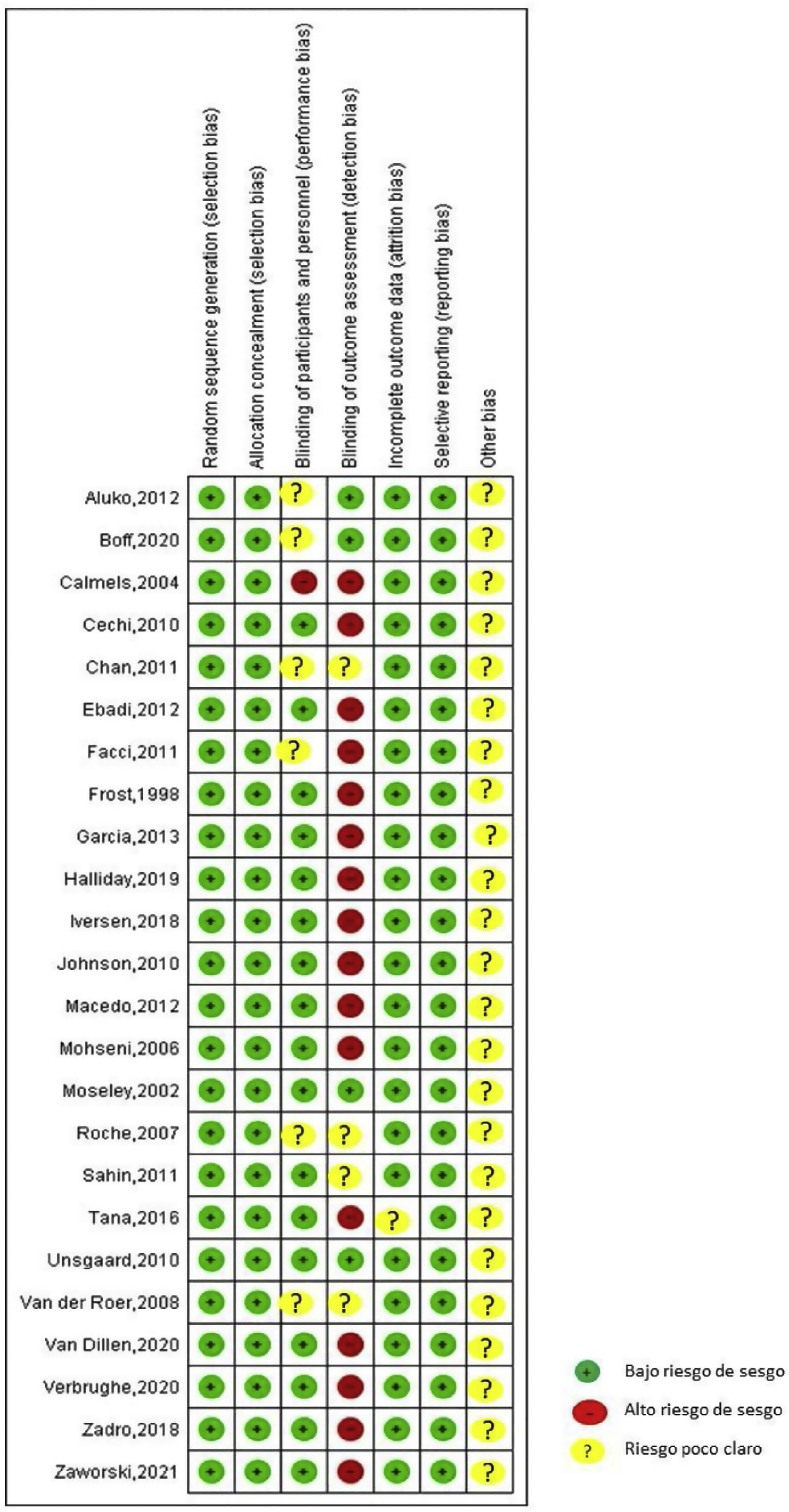
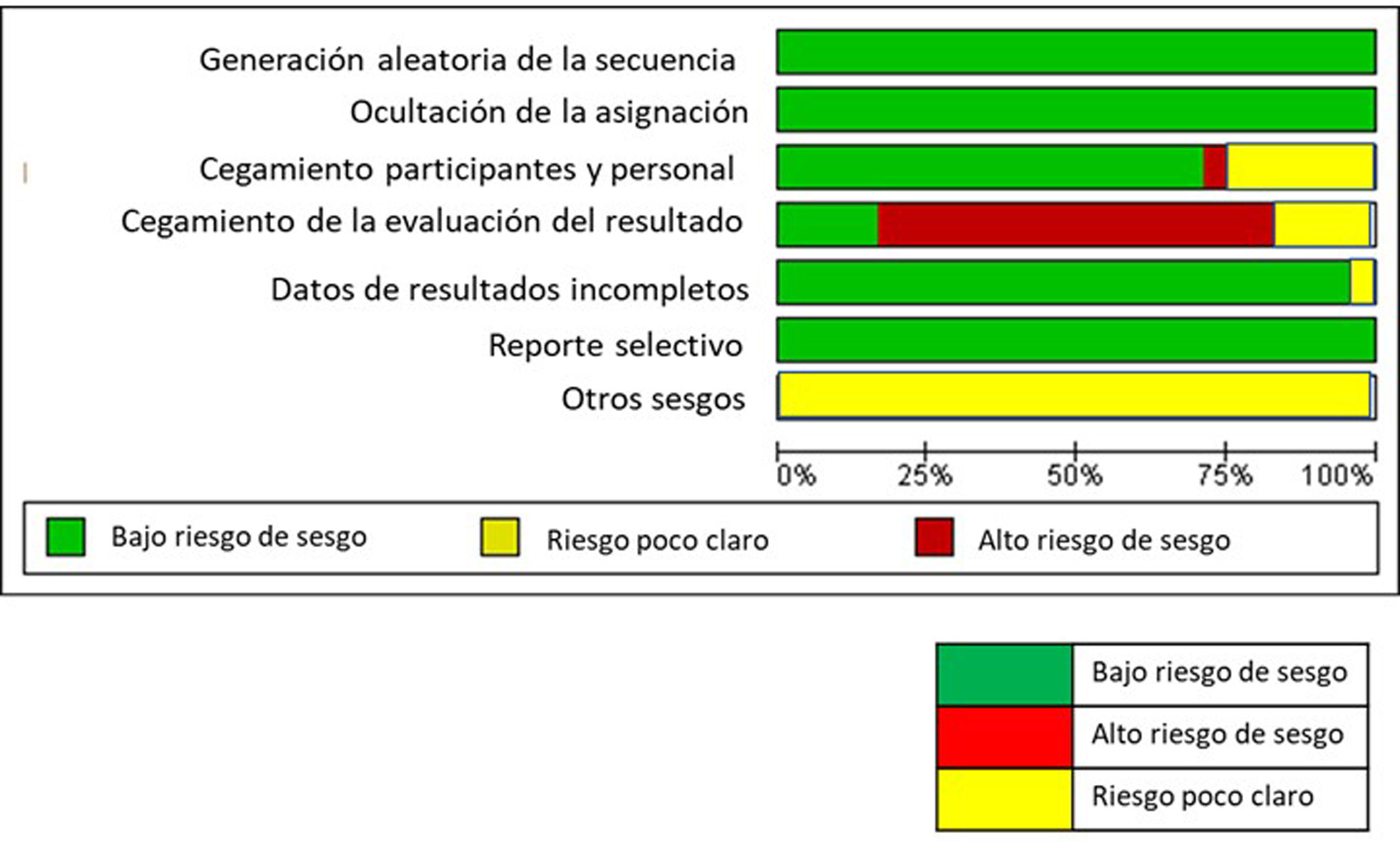
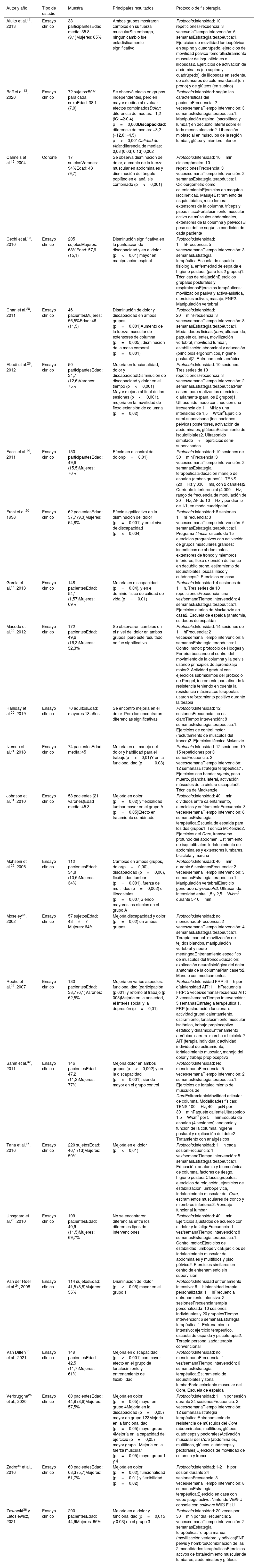
ResultadosSe incluyeron 26 estudios en la síntesis cualitativa, se excluyeron artículos que no cumplieran con los criterios de inclusión. Se encontró efecto en el control del dolor y la disminución de la discapacidad y las principales intervenciones son: fortalecimiento muscular del Core y miembros inferiores, estiramiento de miembros inferiores, movilidad lumbopélvica y educación o escuela de espalda. La frecuencia en el tratamiento osciló entre 2 y 3 veces por semana durante 5 semanas.
ConclusionesSe encontró mayor efectividad en el tiempo de control del dolor y la disminución de la discapacidad, relacionados principalmente con el fortalecimiento muscular del Core y las estrategias educativas. Registro PROSPERO CRD42021269287.
Chronic low back pain is one of the main causes of incapacity for work in the world. It requires an interdisciplinary approach for the evolution of the patient. Until now, there is no consensus on the management of chronic low back pain, which generated the concern of this systematic review.
AimTo identify the effectiveness of physiotherapy protocols in the management of chronic low back pain.
MethodologyA systematic search was carried out in the Pubmed, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Oxford, Wiley, Cochrane Library Plus, PEDro, Epistemonikos, Hinari and LILACS, Google Scholar, Teseo and PROSPERO databases, from the beginning of the databases until August, 2021. The selection criteria were defined according to the intervention and topic of the article.
ResultsTwenty-six studies were included in the qualitative synthesis, articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. An effect was found in the control of pain and the reduction of disability and the main interventions are: muscular strengthening of the core and lower limbs, stretching of the lower limbs, lumbopelvic mobility and education or back school. The treatment frequency ranged from 2 to 3 times per week for 5 weeks.
ConclusionsGreater effectiveness was found in pain control time and disability reduction, mainly related to core muscle strengthening and educational strategies.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".