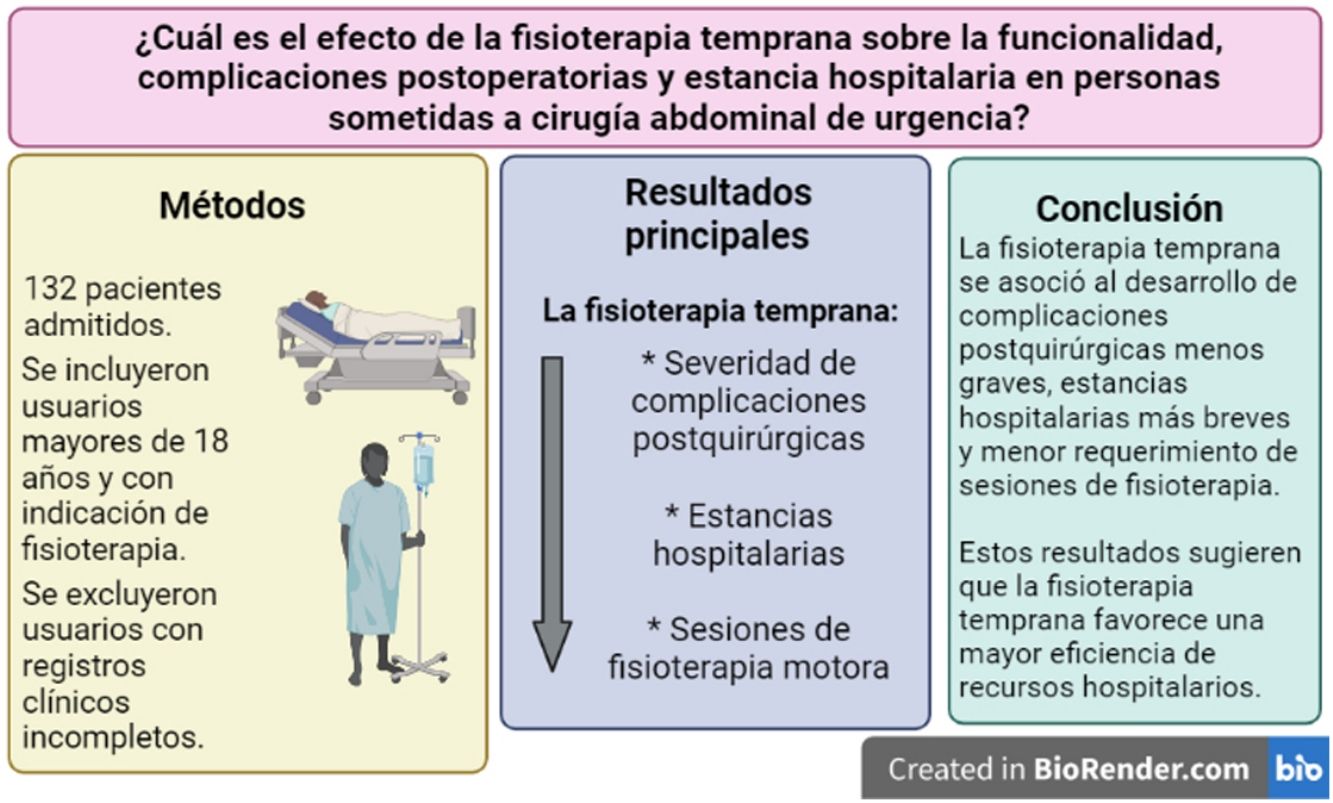
Se desconoce la importancia del acceso temprano a la fisioterapia (FT) en personas sometidas a cirugía abdominal de urgencia, por lo tanto este estudio se enfocó en determinar la efectividad de la FT temprana versus tardía en la mejora de niveles funcionales y reducción de complicaciones postoperatorias (CP) en adultos sometidos a este procedimiento.
MetodologíaEstudio retrospectivo que incluyó a 132 pacientes ingresados por cirugía abdominal de urgencia. Se registró el inicio de FT (temprana vs. tardía), se evaluó la funcionalidad mediante índice de Barthel y la puntuación acumulada de deambulación (CAS), las CP y la duración de la estancia hospitalaria.
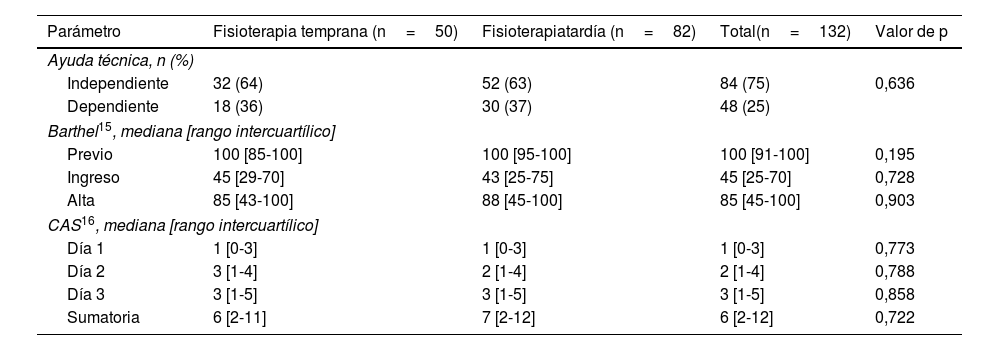
ResultadosLas personas que recibieron FT temprana exhibieron CP de menor gravedad (p=0,012). Asimismo, el grupo con FT temprana tuvo estancias hospitalarias más cortas (mediana=10 vs. 17 días; p=0,0001). Adicionalmente, se observó que la funcionalidad intrahospitalaria disminuyó respecto a valores prehospitalarios (índice de Barthel y CAS), mientras que al alta se observaron incrementos parciales, sin diferencias entre los grupos que recibieron FT temprana o tardía. Sin embargo, el grupo con FT temprana requirió un menor número de sesiones de FT motora (p=0,04).
ConclusiónEn el presente estudio el desarrollo de CP de menor gravedad, menores estancias hospitalarias y una menor necesidad de FT motora fue observada en pacientes sometidos a cirugía abdominal de urgencia que recibieron FT temprana respecto a tardía. Esto sugiere que la FT temprana en este contexto optimizaría los recursos asociados a la atención en salud, mejorando además el proceso posquirúrgico en estos pacientes.
Given that the relevancy of early physiotherapy (PT) in persons undergoing emergency abdominal surgery is unknown, this study aimed to determine the effectiveness of early versus late physiotherapy in improving functional levels and reducing postoperative complications (PC) in adults undergoing this procedure.
MethodologyLongitudinal retrospective study which included a sample of 132 patients admitted for emergency abdominal surgery. Functionality was evaluated using the Barthel index and the cumulated ambulation score (CAS). In addition, the type of PT (early vs. late) and the date of its onset were recorded, the PC during the hospital stay and the length of stay were recorded.
ResultsPatients that received early PT exhibited less severe postoperative complications (p=0.012). Moreover, this group had a shorter length of stay (median=10 vs. 17 days; p=0.0001). In addition, in terms of functionality, decreases were observed during hospitalization compared with baseline levels (Barthel index and CAS), whereas a partial increase was observed at discharge, without differences between the patients that received early PT or not. Nevertheless, the early PT group required a lower number of PT sessions (p=0.04).
ConclusionIn this study, a less severe postoperative complications rate, shorter length of stay, and lower necessity of PT sessions were observed in adults undergoing emergency abdominal surgery that received early PT versus late PT. This suggests that early PT in this context would optimize health care resources, improving the postoperative process in these patients.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".