Loss-of-response and adverse events (AE) to biologics have been linked to HLA-DQA1*05 allele. However, the clinical factors or biologic used may influence treatment duration. Our objective was to evaluate the influence of clinical and therapeutic factors, along with HLA, in biological treatment discontinuation.
MethodsA retrospective study of consecutive IBD patients treated with biologics between 2007 and 2011 was performed. Main outcome was treatment discontinuation due to primary non-response (PNR), secondary loss of response (SLR) or AE. HLA-DQA1 genotyping was done in all patients. Regression analyses were used to assess risk factors of treatment discontinuation.
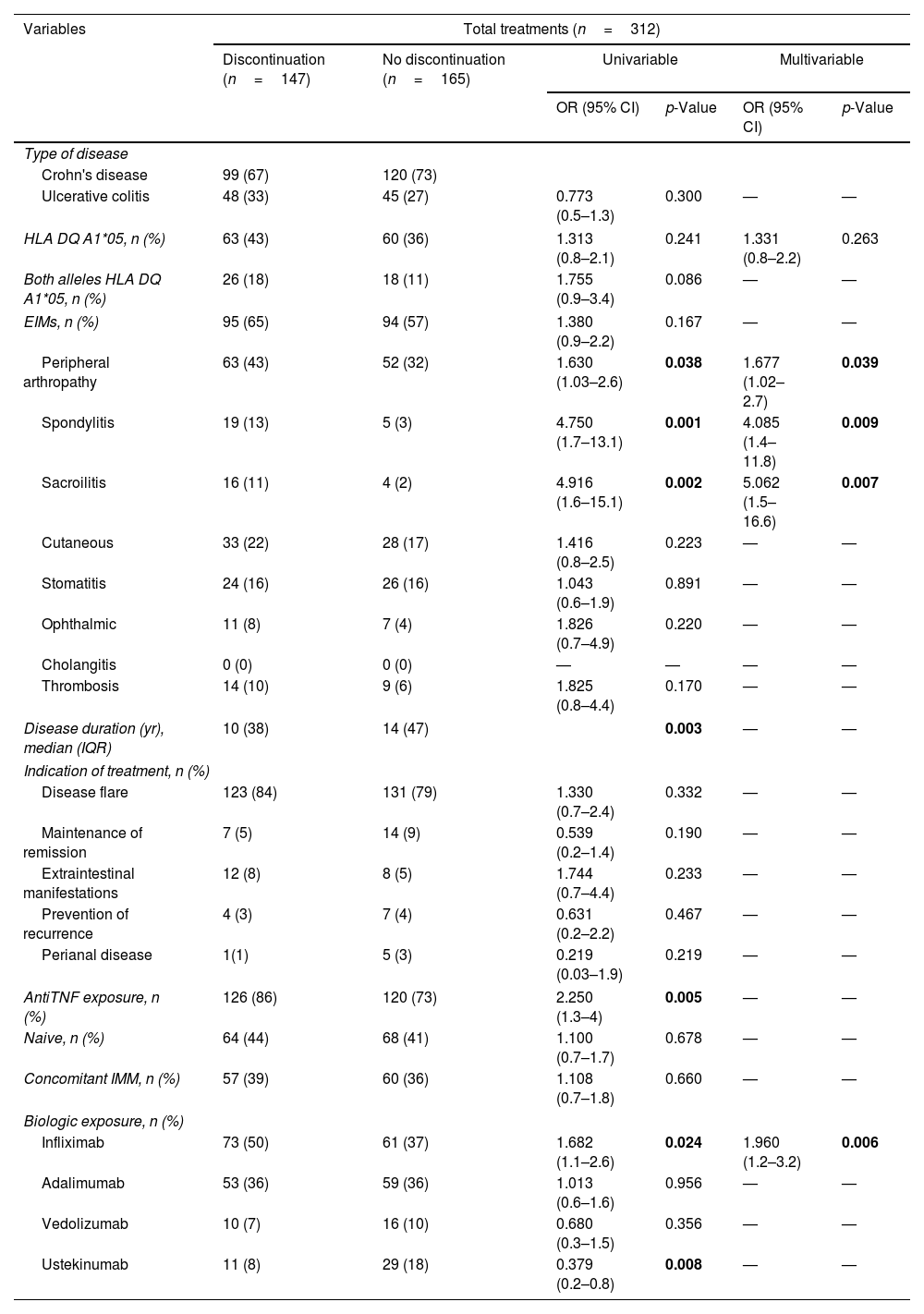
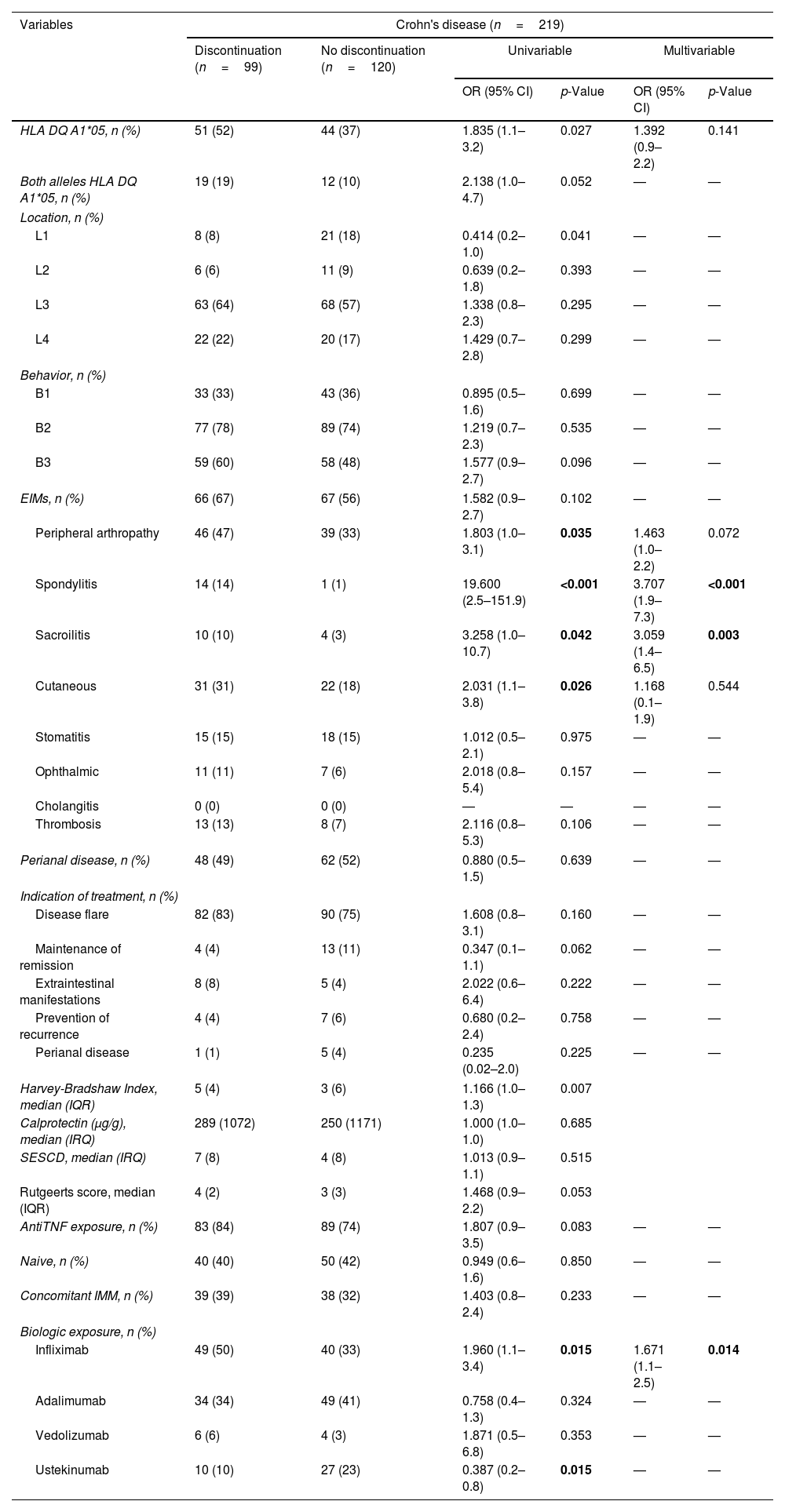
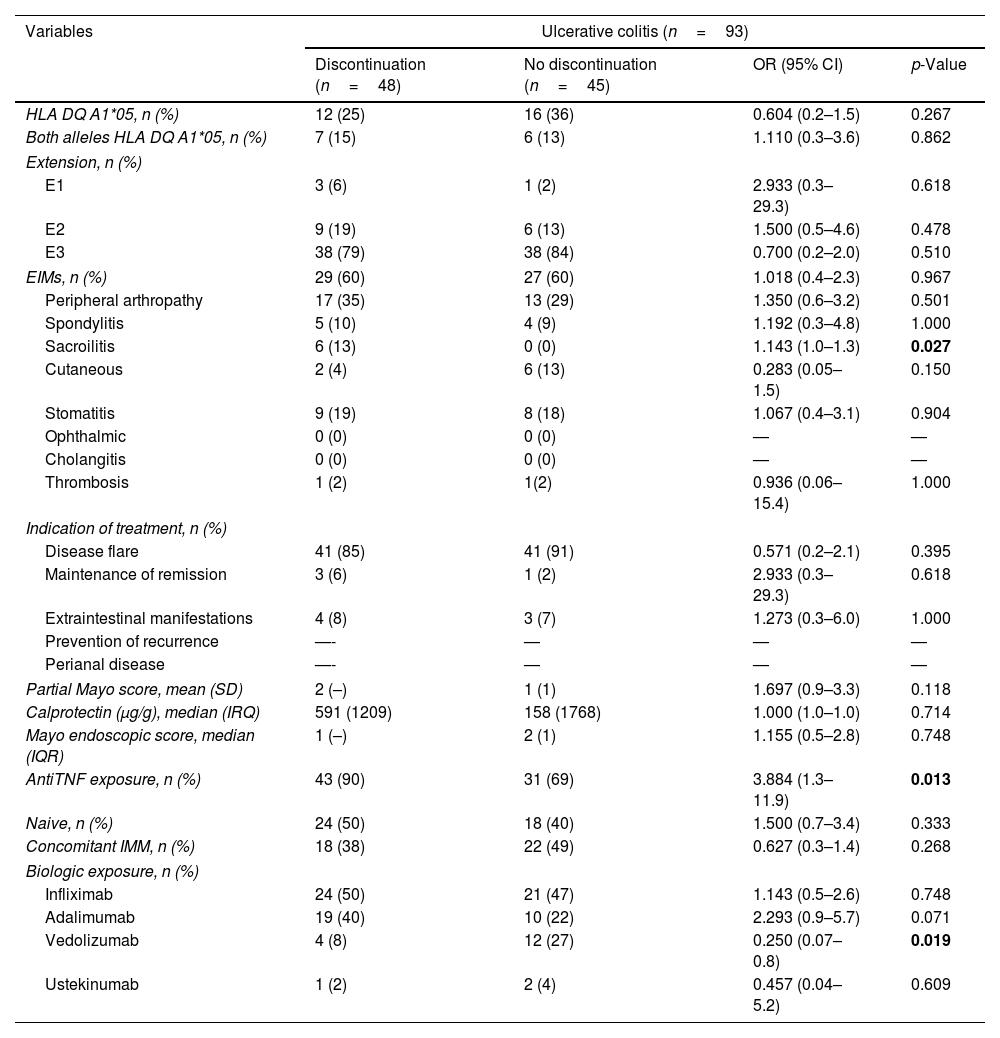
ResultsOne hundred fifty patients (61% male) with 312 biologic treatments were included. 147 (47%) were discontinued with a cumulative probability of 30%, 41% and 56% at 1, 2 and 5 years. The use of infliximab (p=0.006) and articular manifestations (p<0.05) were associated with treatment discontinuation. Considering cause of withdrawal, Ulcerative Colitis (UC) had a higher proportion of PNR (HR=4.99; 95% CI=1.71–14.63; p=0.003), SLR was higher if biologics had been indicated due to disease flare (HR=2.32; 95% CI=1.05–5.09; p=0.037) while AE were greater with infliximab (HR=2.46; 95% CI=1.48–4.08; p<0.001) or spondylitis (HR=2.46; 95% CI=1.78–6.89; p<0.001). According to the biological drug, HLA-DQA1*05 with adalimumab showed more SLR in cases with Crohn's disease (HR=3.49; 95% CI=1.39–8,78; p=0.008) or without concomitant immunomodulator (HR=2.8; 95% CI=1.1–6.93; p=0.026).
ConclusionsHLA-DQ A1*05 was relevant in SLR of IBD patients treated with adalimumab without immunosupression. In patients treated with other biologics, clinical factors were more important for treatment interruption, mainly extensive UC or extraintestinal manifestations and having indicated the biologic for flare.
Estudios previos han observado una asociación entre el HLA-DQA1*05 y la pérdida de respuesta a biológicos y el desarrollo de efectos adversos (EA). Hay factores clínicos y biológicos que podrían influir en la duración del tratamiento. El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar la influencia del HLA, de factores clínicos y terapéuticos en la interrupción del tratamiento biológico.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) tratados con biológicos entre 2007 y 2011. Los principales eventos analizados fueron la suspensión del tratamiento por fallo de respuesta primaria (PRP), secundaria (PRS) o EA. Se realizó un tipaje del HLA-DQA1*05 y se evaluaron los factores de riesgo de interrupción del tratamiento mediante un análisis de regresión logística.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 150 pacientes y 312 tratamientos, de los cuales se suspendieron 147 (47%) en el seguimiento. El infliximab (p=0,006) y las manifestaciones articulares (p<0,05) se relacionaron con la interrupción del tratamiento. La colitis ulcerosa (CU) presentó mayor PRP (HR: 4,99; IC 95%: 1,71-14,63; p=0,003), el brote como indicación de tratamiento se asoció a más PRS (HR: 2,32; IC 95%: 1,05-5,09; p=0,037); el uso de infliximab (HR: 2,46; IC 95%: 1,48-4,08; p<0,001) y la espondilitis (HR: 2,46; IC 95%: 1,78-6,89; p<0,001) a la suspensión por EA. El HLA-DQA1*05 fue un factor de riesgo de PRS en los pacientes tratados con adalimumab (ADA) con enfermedad de Crohn (HR: 3,49; IC 95%: 1,39-8,78; p=0,008) o con EII sin inmunosupresor asociado (HR: 2,8; IC 95%: 1,1-6,93; p=0,026).
ConclusionesEl HLA-DQA1*05 se asoció al cese del tratamiento con ADA por PRS en los pacientes con EII sin inmunosupresor asociado. Respecto a otros biológicos, la suspensión se debió más a factores como la CU, las manifestaciones articulares y la indicación para remisión de brote intestinal.