Virtual reality (VR) is a neurosensory experience in which simulated spaces a person has the sensation of being able to function within them. Some patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) receive intravenous biological treatments in an Adult Day Hospital (ADH) regime. VR has been used in some fields of medicine, demonstrating its usefulness in reducing negative symptoms. However, we do not have any literature showing the applicability in real clinical practice of VR in IBD.
MethodsDescriptive observational pilot study based on an initial cohort of 87 patients that were obtained from the ADH of the IBD Unit. Satisfaction and acceptance of VR through the use of 3D glasses and the reduction of negative symptoms during intravenous biological treatment in patients with IBD in ADH have been assessed.
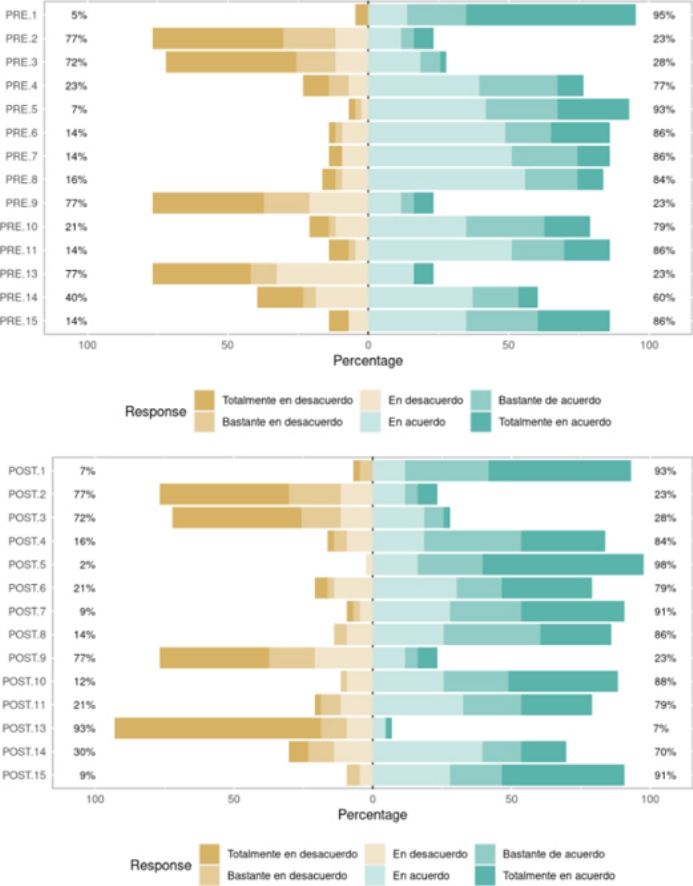
Results43 patients (52.4%) used VR and completed the study. In the comparative analysis of the results of the questionnaires before and after the use of VR, a statistically significant improvement was observed in the patients’ view on the ability of VR to achieve a reduction in stress (65% patients improve; p: 0.0021) and pain (VAS, 54% p. improve; p<0.05) during treatment. Likewise, with the applicability of VR in other areas of medicine (53%; p: 0.05) and with the possibility of improving well-being during the stay in the ADH (56%; p: 0.0014). No side effects were reported with the use of the 3D glasses.
ConclusionsVR is a useful complementary tool to improve the stay of patients with IBD on ADH during intravenous treatment.
La realidad virtual (RV) es una experiencia neurosensorial en la que se crean imágenes y espacios simulados donde una persona tiene la sensación de estar y poder desenvolverse dentro de ellos. Un porcentaje elevado de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) reciben tratamientos biológicos intravenosos en régimen de hospital de día (HDD). La RV ha sido empleada en diversos campos de la medicina, como la oncología, demostrando su utilidad en la reducción de síntomas crónicos como el dolor o la ansiedad. Sin embargo, no disponemos de bibliografía que demuestre la aplicabilidad en la práctica clínica real de la RV en la EII.
MétodosEstudio piloto observacional descriptivo a partir de una cohorte inicial de 87 pacientes obtenida de la unidad de EII del HDD. Se ha valorado la satisfacción y la aceptación de la RV mediante la utilización de gafas 3D y la reducción de síntomas negativos durante el tratamiento biológico intravenoso en los pacientes con EII en HDD.
ResultadosCuarenta y tres pacientes (52,4%) utilizaron la RV y completaron el estudio. La edad promedio fue de 45,3 años. Del cuestionario validado IBDQ-32 sobre calidad de vida en EII se obtuvo una puntuación media de 169 puntos (intervalo: 32-224). En el análisis comparativo de los resultados de los cuestionarios previo y posterior al uso de la RV, se observó una mejoría estadísticamente significativa en la visión de los pacientes de la capacidad de la RV para lograr una reducción del estrés (65% de mejoría; p: 0,0021) y del dolor (escala EVA; 54% de mejoría; p<0,05) durante el tratamiento. Asimismo, también con la aplicabilidad de la RV en otros ámbitos de la medicina (53% de mejoría; p: 0,05) y con la posibilidad de mejoría del bienestar durante la estancia en el HDDA (56% de mejoría; p: 0,0014). No se notificaron efectos secundarios con el uso de las gafas 3D.
ConclusionesLa utilización de la RV ha demostrado ser una herramienta complementaria útil para mejorar la estancia de los pacientes con EII en HDD durante el tratamiento con fármacos biológicos intravenosos.