Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct intervention (EUS-PDI) is one of the most technically challenging procedures. There remains a knowledge gap due to its rarity. The aim is to report the accumulated EUS-PDI experience in a tertiary center.
MethodsSingle tertiary center, retrospective cohort study of prospectively collected data during the study period, from January 2013 to June 2021.
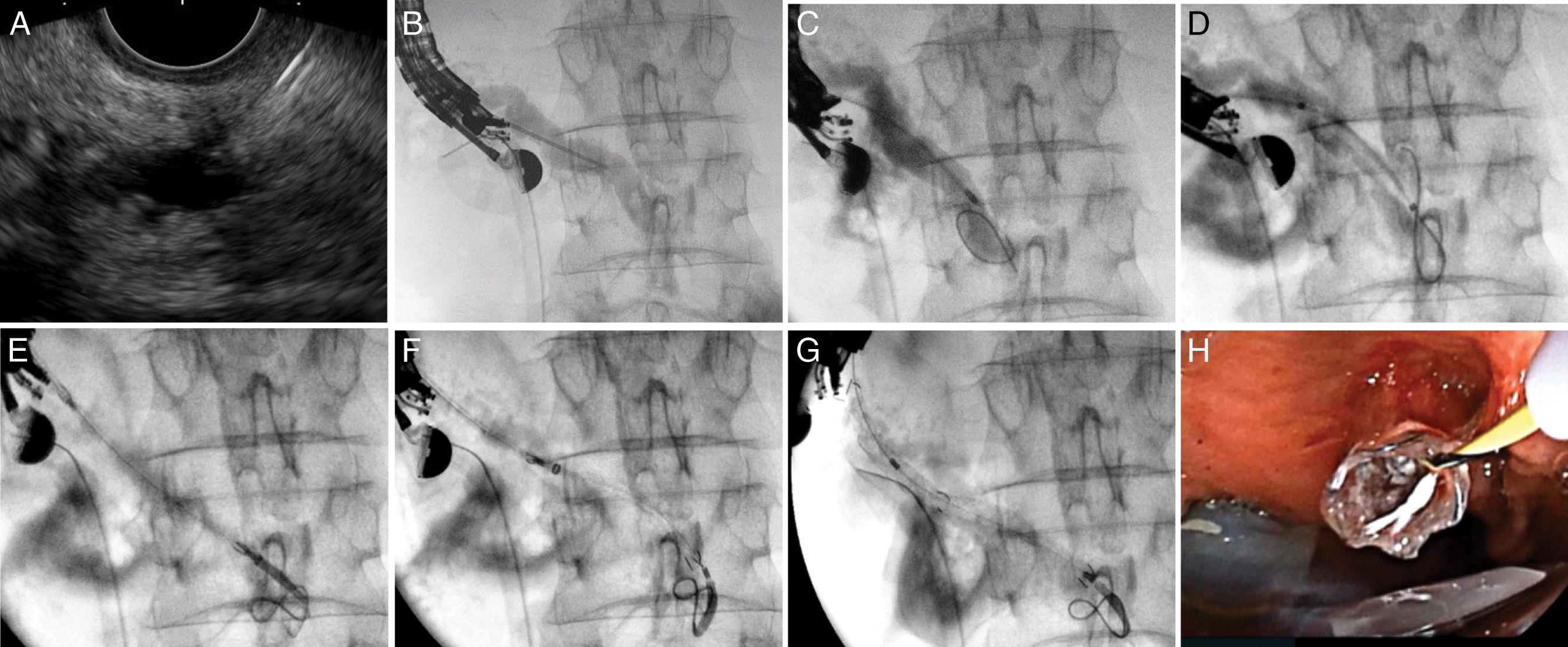
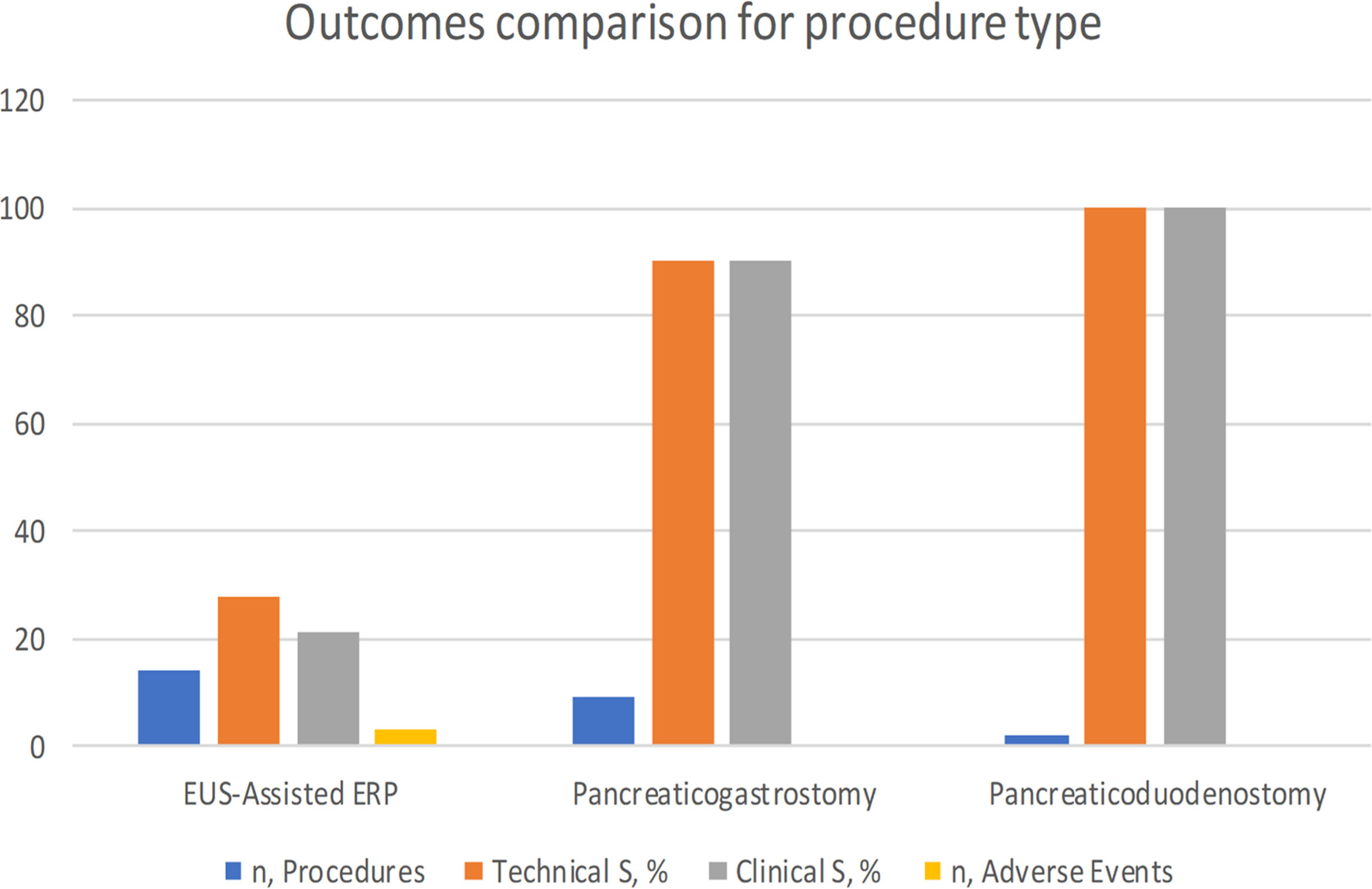
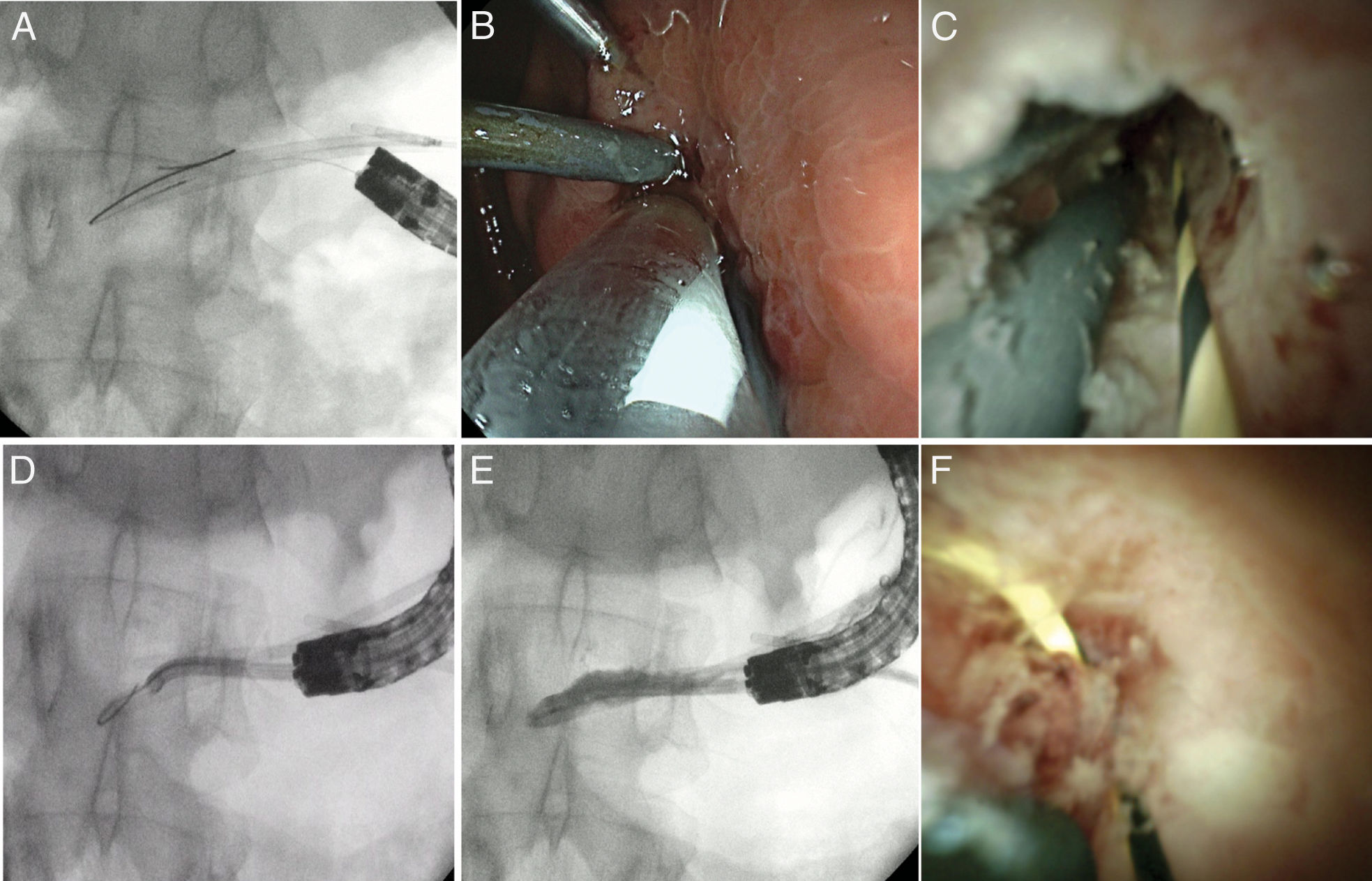
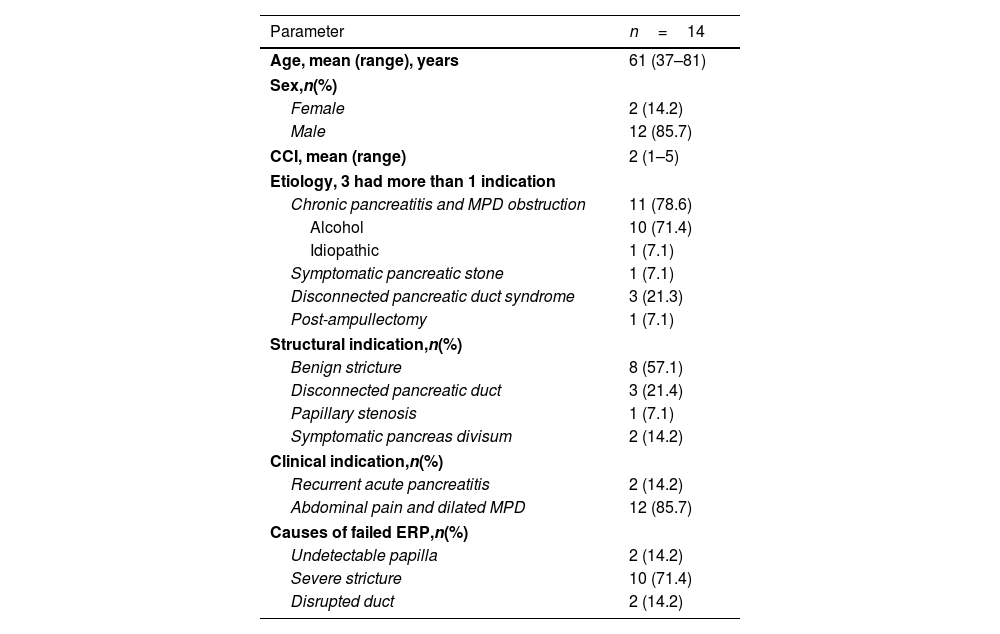
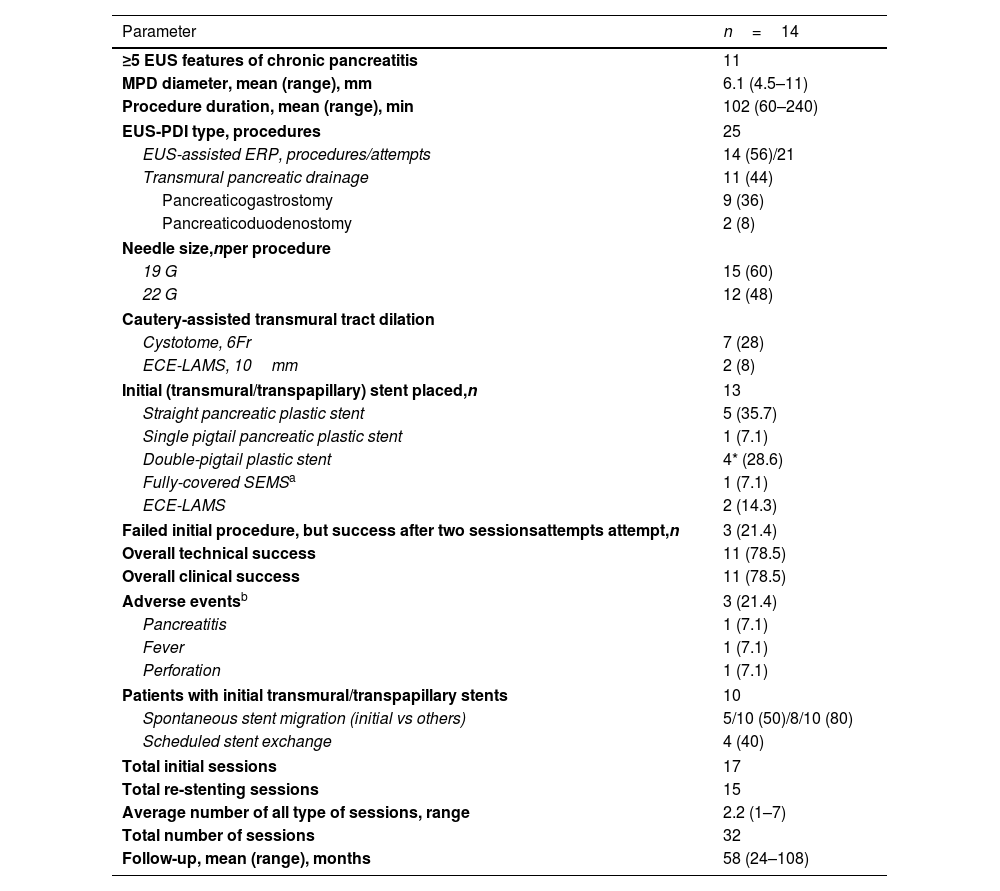
ResultsIn total, 14 patients (85% male; mean age, 61 years, range 37–81) and 25 EUS-PDI procedures for unsuccessful endoscopic retrograde pancreatography (ERP) were included. Principal etiology was chronic pancreatitis with pancreatic duct obstruction (78%). EUS-guided assisted (colorant and/or guidewire, rendezvous) ERP was performed in 14/25 (56%); and transmural drainage in 11 procedures, including pancreaticogastrosmy in 9/25 (36%) and pancreaticoduodenostomy in 2/25 (8%). Overall technical and clinical success was 78.5% (11/14). Three (21%) patients required a second procedure with success in all cases. Two failed cases required surgery. Three (21%) adverse events (AEs) were noted (fever, n=1; perforation, n=1; pancreatitis, n=1). Patients underwent a median of 58 months (range 24–108) follow-up procedures for re-stenting. Spontaneous stent migration was detected in 50% of cases.
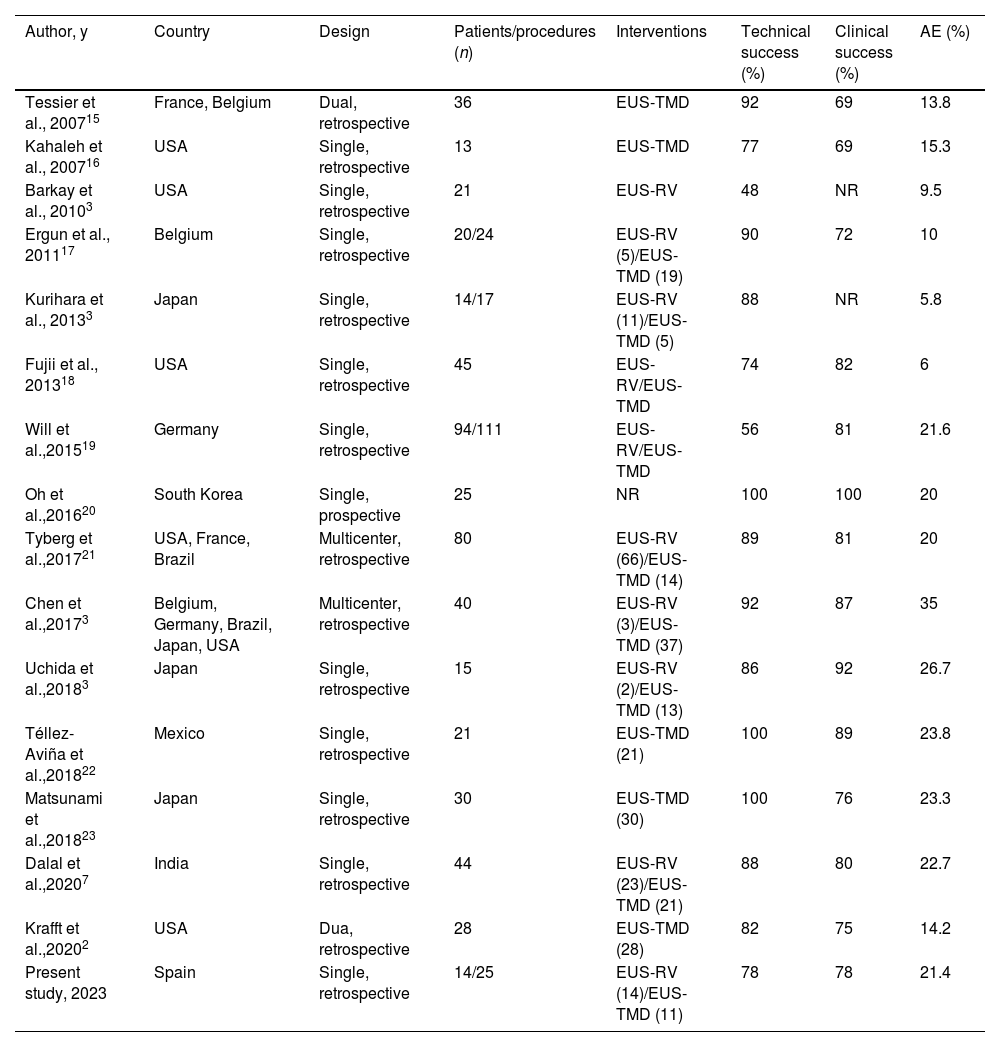
ConclusionsEUS-PDI is an effective salvage therapy for unsuccessful ERP, although 21% of patients may still experience AEs. In case of EUS-guided rendezvous failure, it can cross over to a transmural drainage.
La intervención terapéutica del conducto pancreático guiada por ecoendoscopia (EUS-PDI) es una de las técnicas endoscópicas más exigentes. Actualmente su conocimiento es limitado, al ser un procedimiento poco frecuente en la rutina asistencial. El objetivo del estudio es reportar la experiencia acumulada de la EUS-PDI en un centro terciario.
MétodosEstudio unicéntrico observacional, de cohorte retrospectiva, durante el período entre enero de 2013 y junio de 2021.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 14 pacientes (85% hombres; media de edad, 61años, rango: 37-81) y 25 procedimientos EUS-PDI realizados por pancreatografía retrógrada endoscópica (ERP) fallida. La etiología principal fue pancreatitis crónica con obstrucción ductal pancreática (78%). La ERP asistida por EUS (colorante y/o guía, rendezvous) fue realizada en 14/25 (56%), y drenaje transmural, en 11 procedimientos, incluyendo pancreaticogastrostomía en 9/25 (36%) y pancreaticoduodenostomía en 2/25 (8%). El éxito técnico y clínico global fue del 78,5% (11/14). Tres (21%) pacientes requirieron un segundo procedimiento, con éxito en los 3casos. Dos casos fallidos precisaron cirugía. Se identificaron tres (21%) acontecimientos adversos (fiebre, n=1; perforación n=1, y pancreatitis n=1). Seguimiento clínico por re-stenting, mediana de 58 meses (rango: 24-108). Detección de migración espontánea en el 50% de los casos.
ConclusionesEUS-PDI es una terapéutica endoscópica efectiva como rescate de ERP fallidas. Así y todo, el 21% pueden presentar acontecimientos adversos. En caso de una EUS-rendezvous fallida, se puede rescatar con un drenaje transmural.