This study was designed to analyze the influence of age and comprehensive geriatric evaluation on clinical results of pancreaticobiliary disease management in elderly patients.
MethodsA prospective observational study has been undertaken, including 140 elderly patients (over 75 years) with benign pancreaticobiliary disease. Patients were divided according to age in the following groups: group 1: 75–79 years old; group 2: 80–84 years old; group 3: 85 years and older. They underwent a comprehensive geriatric assessment with different scales: Barthel Index, Pfeiffer Index, Charlson Index, and Fragility scale, at admission and had been follow-up 90 days after hospital discharge to analyze its influence on morbidity and mortality.
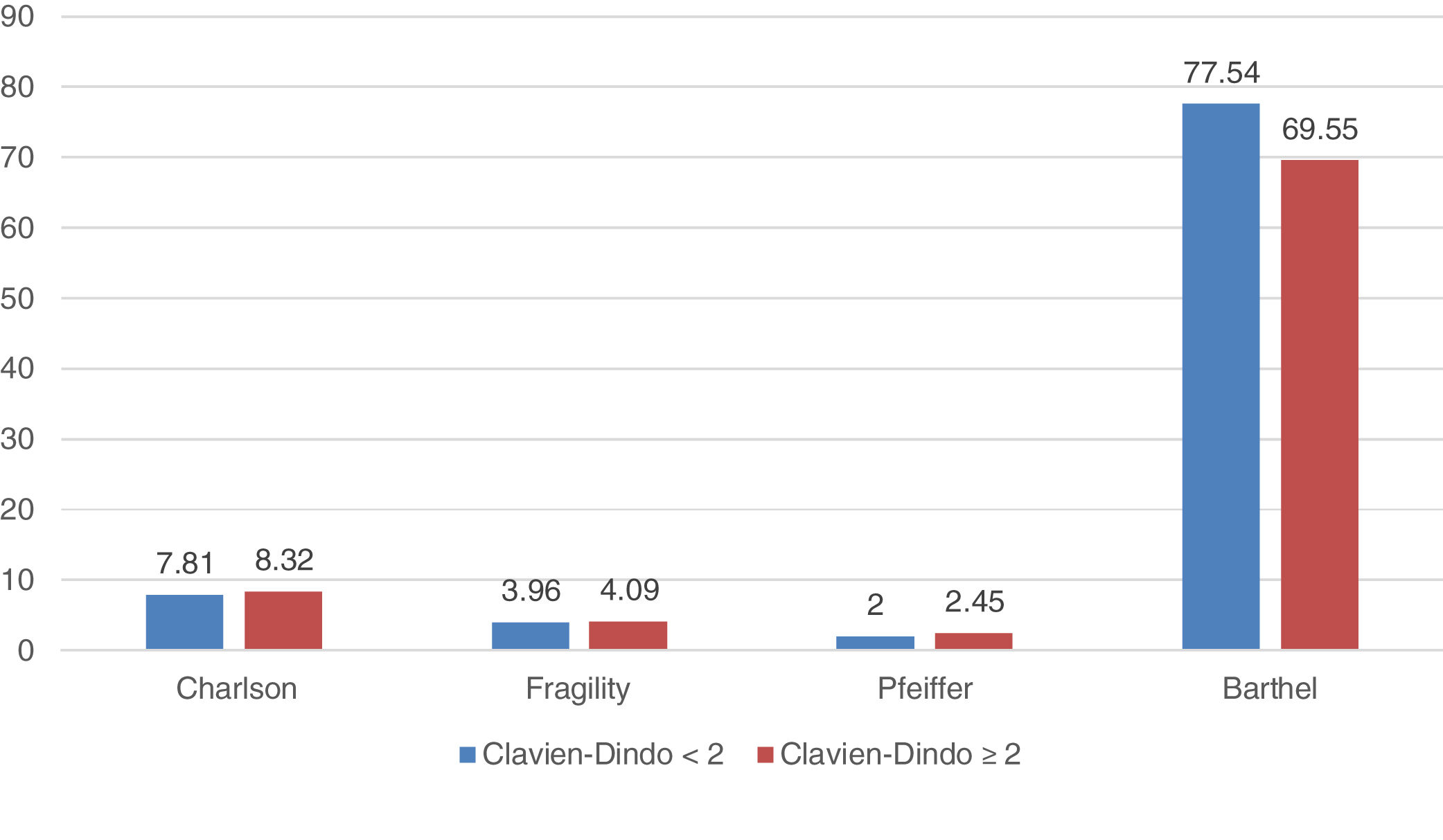
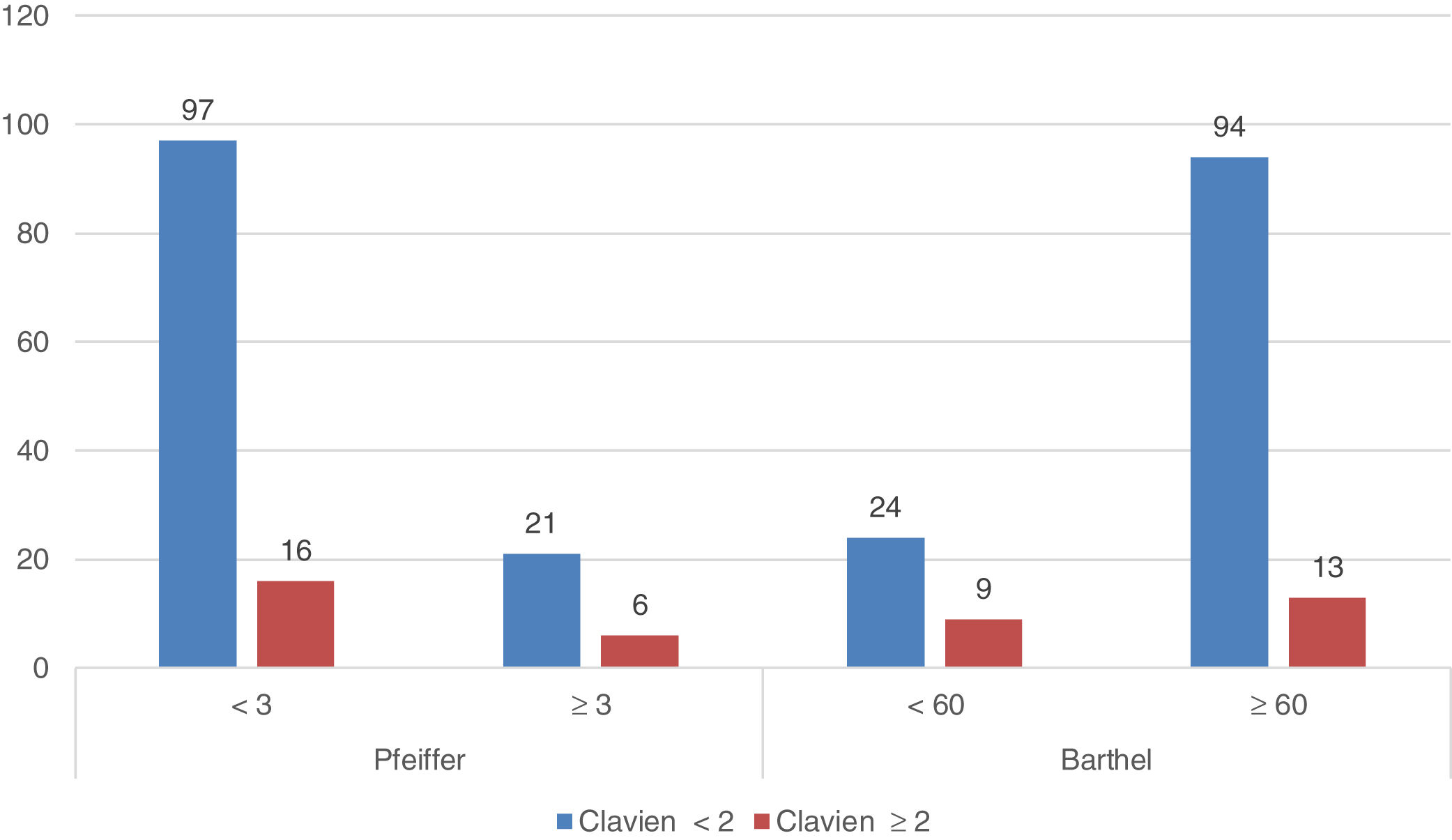
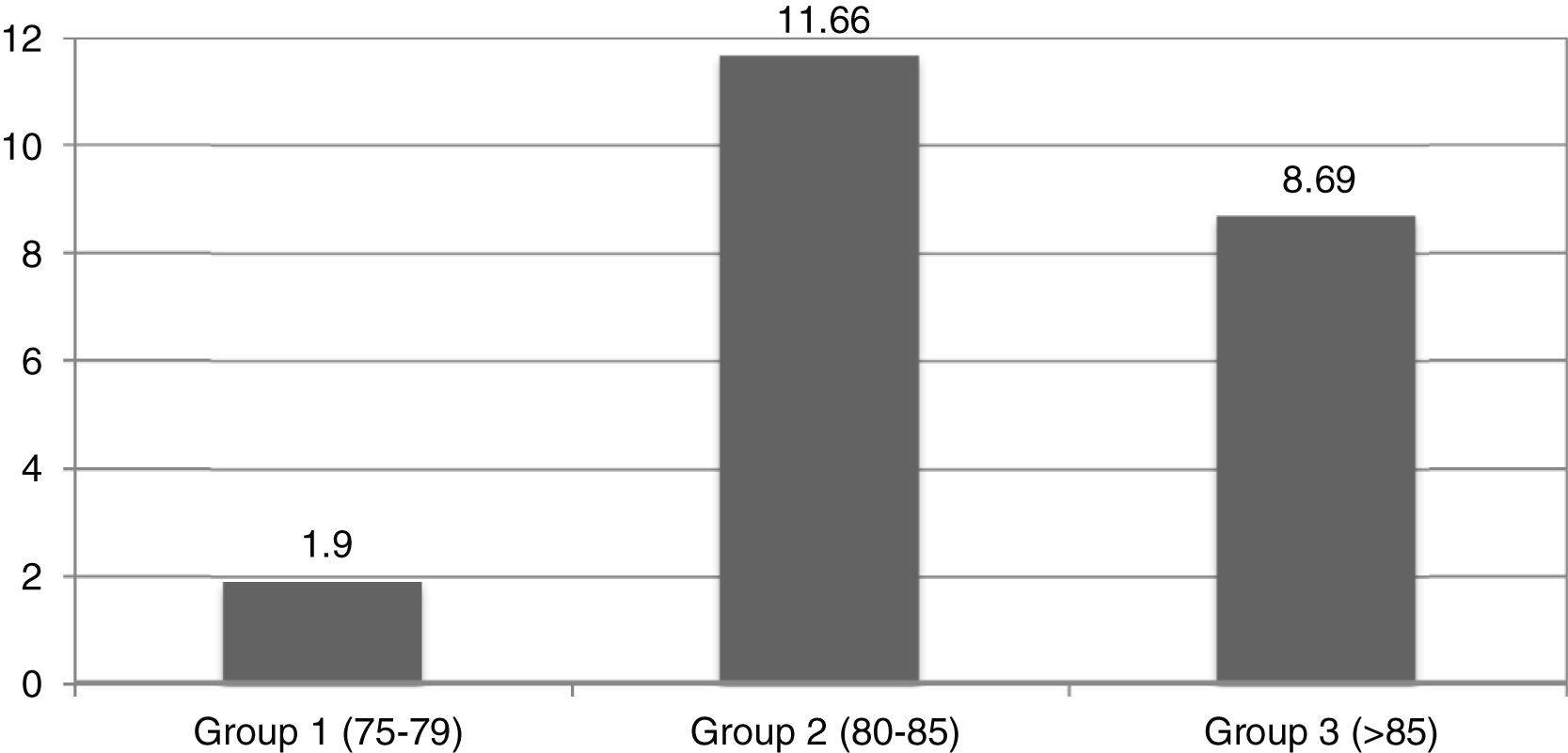
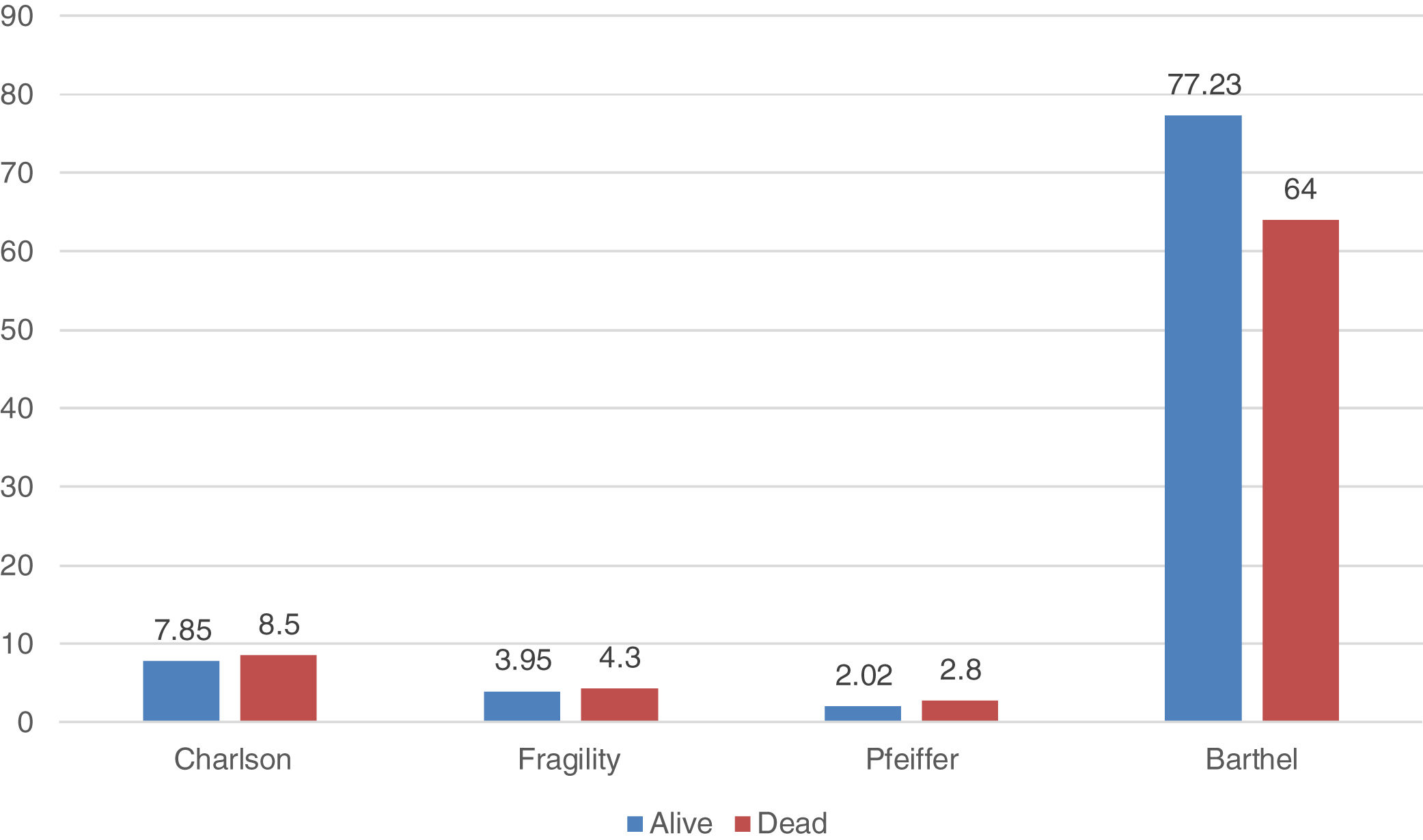
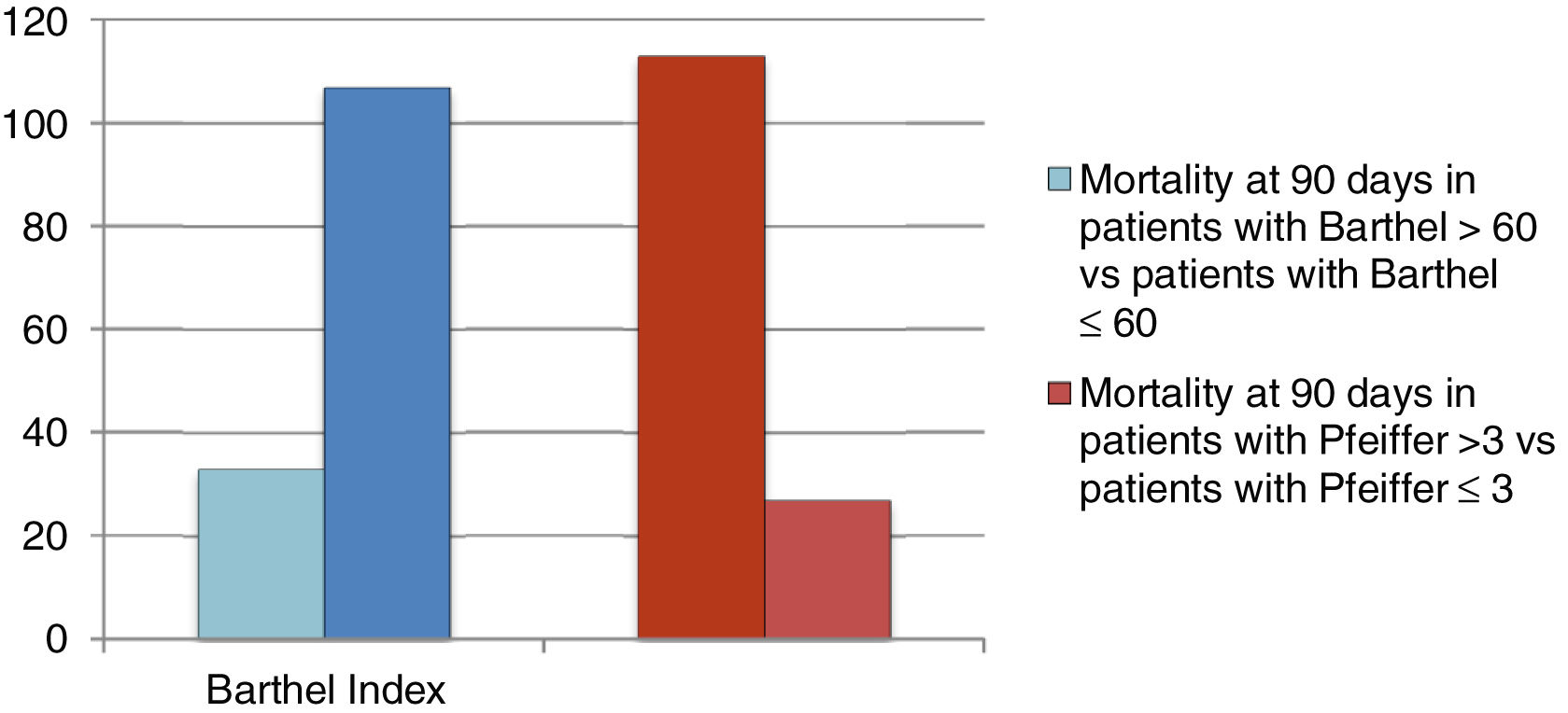
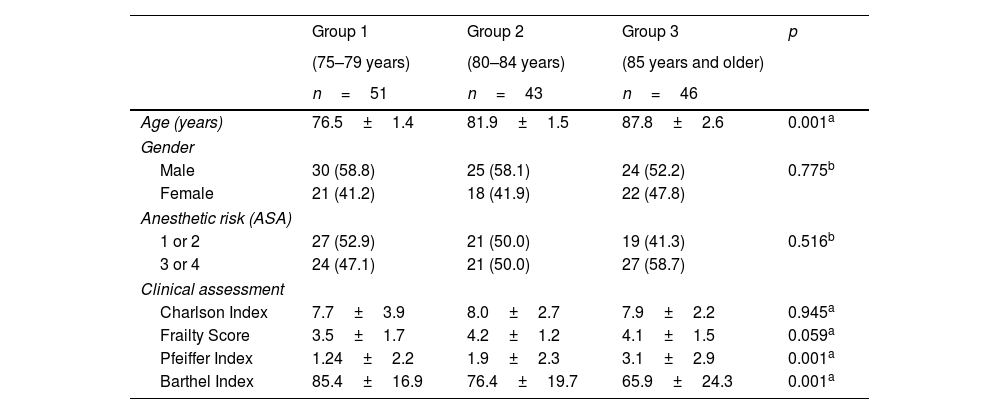
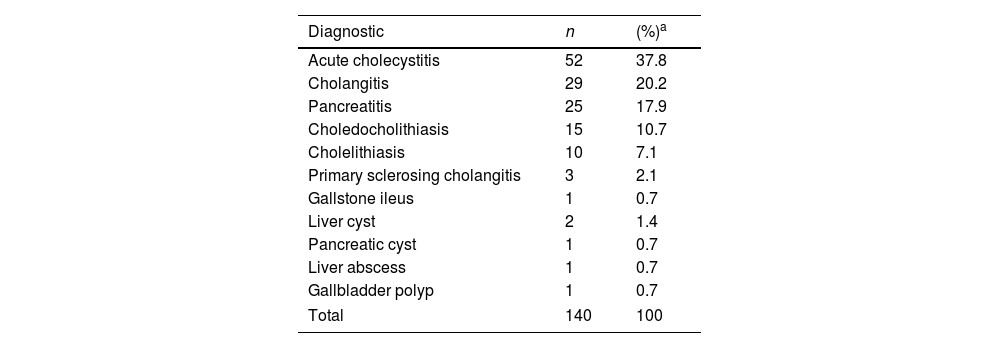
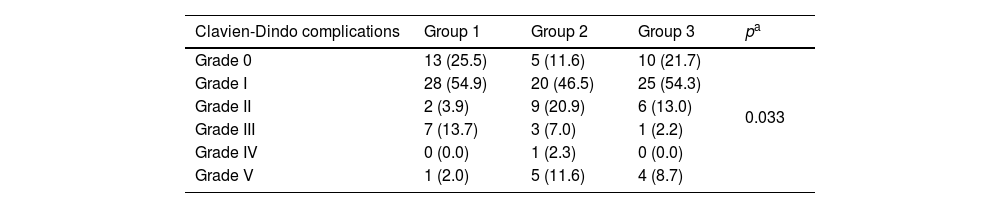
ResultsOverall, 140 patients have been included (group 1=51; group 2=43 and group 3=46). Most of them, 52 cases (37.8%), had acute cholecystitis, followed by 29 cases of acute cholangitis (20.2%) and acute pancreatitis with 25 cases (17.9%). Significant differences has been observed on complications in different age groups (p=0.033). Especially in patients with a Barthel Index result ≤60, which suggests that these less functional patients had more severe complications after their treatment (p=0.037). The mortality rate was 7.1% (10 patients).
ConclusionsNo significant differences were found between age, morbidity and mortality in elderly patients with pancreaticobiliary disease. Comprehensive geriatric scales showed some utility in their association with specific complications.
Este estudio fue diseñado para analizar la influencia de la edad y la evaluación geriátrica integral en los resultados clínicos del manejo de la enfermedad pancreatobiliar en pacientes de edad avanzada.
MétodosSe ha realizado un estudio observacional prospectivo en el que se incluyeron 140 pacientes de edad avanzada (mayores de 75 años) con enfermedad pancreatobiliar benigna. Los pacientes se dividieron según la edad en los siguientes grupos: Grupo 1: 75-79 años; Grupo 2: 80-84 años; Grupo 3: 85 años y más. Se les realizó una valoración geriátrica integral con diferentes escalas: Barthel Index, Pfeiffer Index, Charlson Index y Fragility scale, al ingreso y seguimiento 90 días después del alta hospitalaria para analizar su influencia en la morbimortalidad.
ResultadosEn total, se incluyeron 140 pacientes (Grupo 1=51; Grupo 2=43 y Grupo 3=46). La mayoría de ellos, 52 casos (37,8%), presentaron colecistitis aguda, seguido de colangitis aguda con 29 casos (20,2%) y pancreatitis aguda con 25 casos (17,9%). Se han observado diferencias significativas en las complicaciones en diferentes grupos de edad (p=0,033). Especialmente en pacientes con un índice de Barthel ≤60, lo que sugiere que estos pacientes menos funcionales tuvieron complicaciones más severas después de su tratamiento (p=0,037). La tasa de mortalidad fue de 7,1% (10 pacientes).
ConclusionesNo se encontraron diferencias significativas entre la edad, la morbilidad y la mortalidad en pacientes ancianos con enfermedad pancreatobiliar. Las escalas geriátricas integrales mostraron cierta utilidad en su asociación con complicaciones específicas.