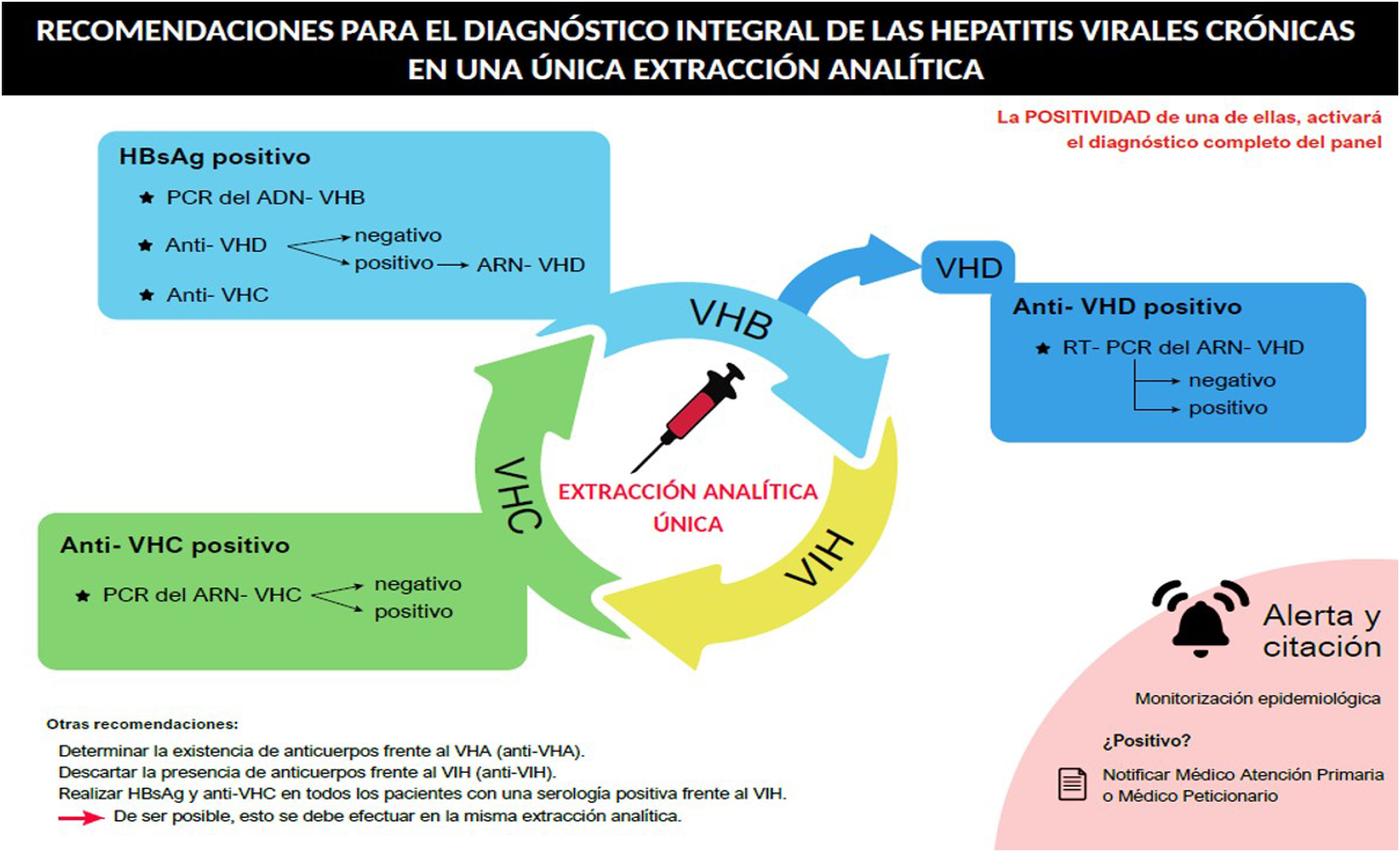
La Sociedad Española de Patología Digestiva (SEPD), la Asociación Española para el Estudio del Hígado (AEEH), la Sociedad Española de Infecciones y Microbiología Clínica (SEIMC) y su Grupo de Estudio de Hepatitis Víricas (GEHEP), y con el aval de la Alianza para la Eliminación de las Hepatitis Víricas en España (AEHVE), han consensuado un documento para realizar un diagnóstico integral de las hepatitis virales (B, C y D), a partir de una única extracción analítica; es decir diagnóstico integral, en el centro hospitalario y/o en el punto de atención del paciente. Proponemos un algoritmo, de manera que el resultado positivo en serología frente a los virus de las hepatitis (B, C y D), así como el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH), activaría el análisis del resto de virus, incluyendo la carga viral cuando sea preciso, a partir de la misma extracción sanguínea. Además, hacemos dos recomendaciones adicionales. Por un lado, la necesidad de descartar una infección previa por el virus de la hepatitis A (VHA), para proceder a la vacunación en los casos en que los anticuerpos de tipo IgG frente a este virus sean negativos y la vacuna esté indicada. Y, por otro lado, la determinación de la serología del VIH. En caso de un resultado positivo para cualquiera de los virus analizados se deben emitir alertas automatizadas y activar la monitorización epidemiológica.
The Spanish Society of Digestive Pathology (SEPD), the Spanish Association for the Study of the Liver (AEEH), the Spanish Society of Infections and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC) and its Viral Hepatitis Study Group (GEHEP), and with the endorsement of the Alliance for the Elimination of Viral Hepatitis in Spain (AEHVE), have agreed on a document to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of viral hepatitis (B, C and D), from a single blood sample; that is, a comprehensive diagnosis, in the hospital and/or at the point of care of the patient. We propose an algorithm, so that the positive result in a viral hepatitis serology (B, C and D), as well as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), would trigger the analysis of the rest of the virus, including the viral load when necessary, in the same blood draw. In addition, we make two additional recommendations.
First, the need to rule out a previous hepatitis A virus (VHA) infection, to proceed with its vaccination in cases where IgG-type studies against this virus are negative and the vaccine is indicated. Second, the determination of the HIV serology. Finally, in case of a positive result for any of the viruses analyzed, there must be an automated alerts and initiate epidemiological monitoring.