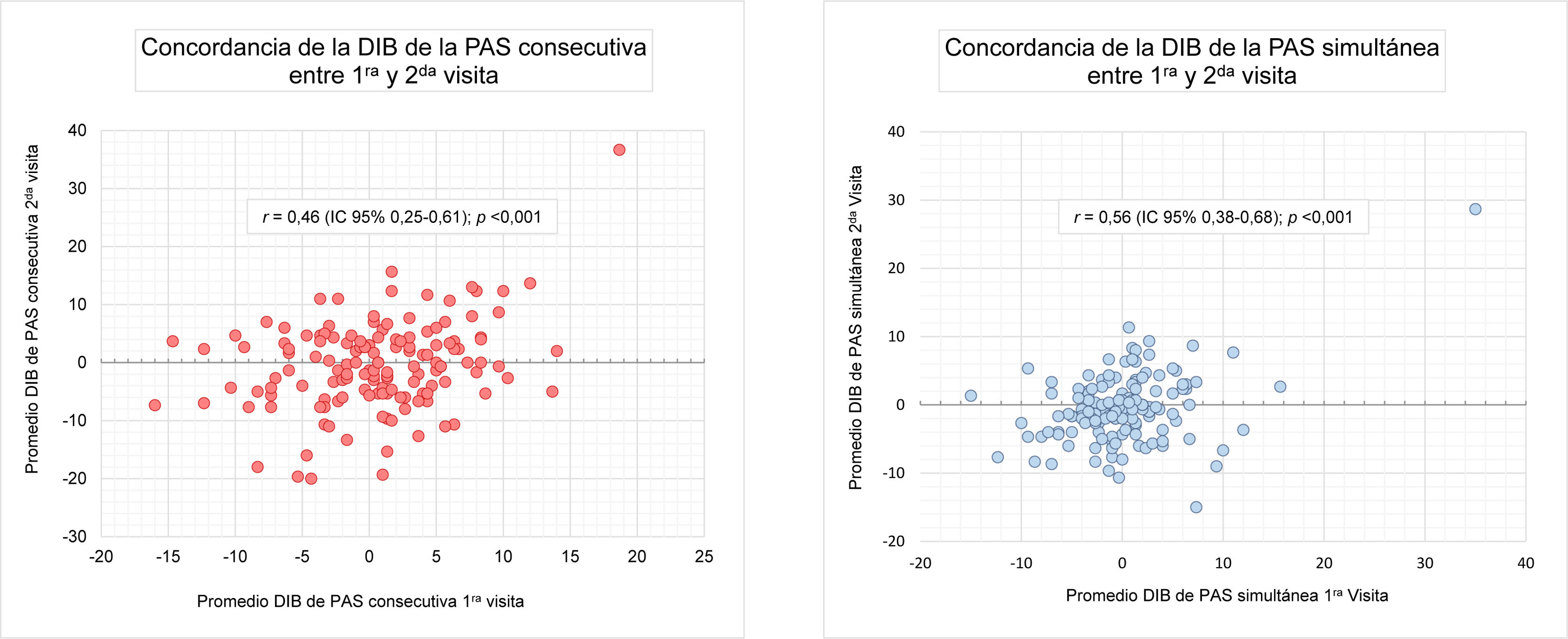
La diferencia interbraquial (DIB) de la presión arterial sistólica (PAS) se asocia a un mayor riesgo cardiovascular. Comparamos los registros simultáneos y consecutivos en la medición de la DIB de la PAS, y evaluamos la reproducibilidad entre visitas. Fueron incluidos 143 pacientes (63,8±9,5 años, 51,7% mujeres) hipertensos tratados y controlados con medicación antihipertensiva estable por un período ≥3meses. La presión arterial (PA) en ambos brazos se midió simultánea y consecutivamente con un dispositivo automático oscilométrico, en dos visitas. La DIB de la PAS simultánea fue significativamente menor respecto a la consecutiva tanto en la primera (3,51±4,1 vs. 4,40±3,7mmHg; p<0,01) como en la segunda visita (3,62±3,5 vs. 5,69±5,1mmHg; p<0,001). Cuando la DIB de la PAS fue categorizada en ≥10 o <10mmHg, la reproducibilidad entre visitas fue insignificante tanto en las mediciones simultáneas como en las consecutivas. La frecuencia de la dominancia inicial fue similar entre el brazo izquierdo y el derecho en las simultáneas (46,2 vs. 43,3%), y mayor en el brazo derecho en las consecutivas (55,2 vs. 38,5). La persistencia de la dominancia entre ambas visitas fue significativamente superior cuando la PAS fue medida en forma simultánea (54,4% vs. 45,5%; p<0,01). Nuestro estudio muestra que para definir el brazo con la PA más alta son preferibles las mediciones simultáneas. En hipertensos tratados y controlados, la pobre persistencia de la dominancia inicial entre visitas nos exige revisar la recomendación de registrar, en el seguimiento, la PA en el brazo donde fue más elevada en la primera visita.
The inter-arm difference (IAD) of systolic blood pressure (SBP) is associated with higher cardiovascular risk. We compared simultaneous and consecutive recordings in measuring IAD of SBP, and evaluated reproducibility between visits. 143 hypertensive patients (63.8±9.5 years, 51.7% women) treated and controlled with stable antihypertensive medication for a period of ≥3 months were included. Blood pressure (BP) in both arms was measured simultaneously and consecutively with an automatic oscillometric device, in two visits. The IAD of the simultaneous SBP was significantly lower compared to the consecutive one, both in the first (3.51±4.1 vs. 4.40±3.7mmHg; P<.01) and in the second visit (3.62±3.5 vs. 5.69±5.1mmHg; P<.001). When the IAD of SBP was categorized as ≥10 or <10mmHg, the reproducibility between visits was insignificant in both simultaneous measurements and consecutive measurements. The frequency of initial dominance was similar between the left and right arm in simultaneous ones (46.2 vs. 43.3%), and greater in the right arm in consecutive ones (55.2 vs. 38.5). The persistence of dominance between both visits was significantly higher when SBP was measured simultaneously (54.4% vs. 45.5%; P<.01). Our study shows that to define the arm with the highest BP, simultaneous measurements are preferable. In treated and controlled hypertensive patients, the poor persistence of initial dominance between visits requires us to review the recommendation of recording, during follow-up, the BP in the arm where it was highest on the first visit.