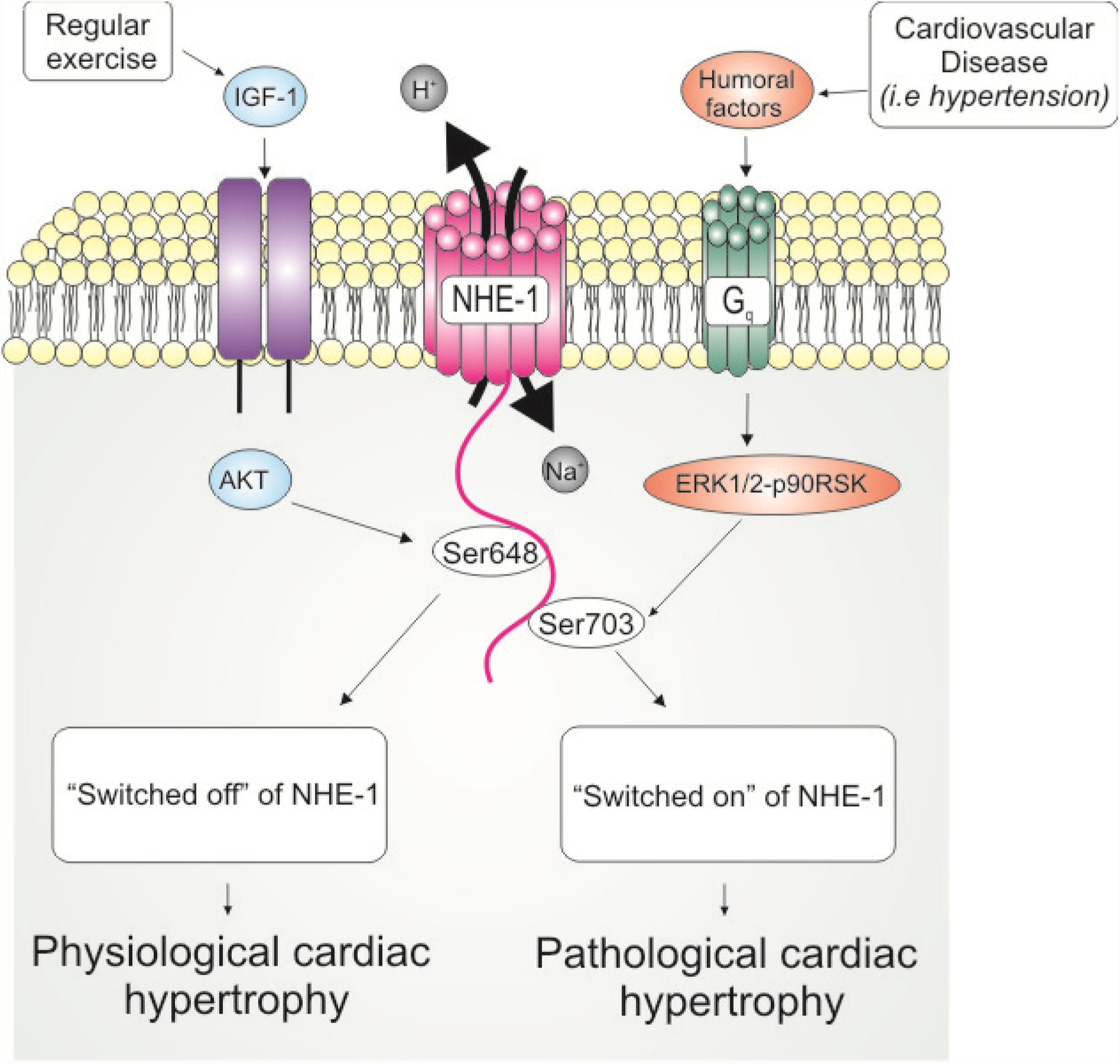
Reactive cardiac hypertrophy (CH) is an increase in heart mass in response to hemodynamic overload. Exercise-induced CH emerges as an adaptive response with improved cardiac function, in contrast to pathological CH that represents a risk factor for cardiovascular health.
The Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE-1) is a membrane transporter that not only regulates intracellular pH but also intracellular Na+ concentration. In the scenario of cardiovascular diseases, myocardial NHE-1 is activated by a variety of stimuli, such as neurohumoral factors and mechanical stress, leading to intracellular Na+ overload and activation of prohypertrophic cascades. NHE-1 hyperactivity is intimately linked to heart diseases, including ischemia-reperfusion injury, maladaptive CH and heart failure.
In this review, we will present evidence to support that the NHE-1 hyperactivity constitutes a “switch on/off” for the pathological phenotype during CH development. We will also discuss some classical and novel strategies to avoid NHE-1 hyperactivity, and that are therefore worthwhile to improve cardiovascular health.
La hipertrofia cardiaca (HC) reactiva es un incremento de la masa cardiaca, como respuesta a la sobrecarga hemodinámica. La HC inducida por ejercicio surge de una respuesta adaptativa con mejora de la función cardiaca, en contraste a la HC patológica, que representa un factor de riesgo para la salud cardiovascular.
El intercambiador Na+/H+ (NHE-1) es un transportador de la membrana que no solo regula el pH intracelular, sino también la concentración de Na+ intracelular. En el escenario de las enfermedades cardiovasculares, el NHE-1 miocárdico se activa por una serie de estímulos, tales como los factores neurohumorales y el estrés mecánico, que origina una sobrecarga intracelular de Na+ y la activación de cascadas pro-hipertróficas. La hiperactividad de NHE-1 está íntimamente ligada a las enfermedades cardiacas, incluyendo lesión por isquemia-reperfusión, HC mal adaptada e insuficiencia cardiaca.
En esta revisión, presentaremos la evidencia que respalda que la hiperactividad de NHE-1 constituye una «conexión/desconexión» para el fenotipo patológico durante el desarrollo de la HC. También trataremos algunas estrategias clásicas y nuevas para evitar la hiperactividad de NHE-1 y, por tanto, mejorar considerablemente la salud cardiovascular.