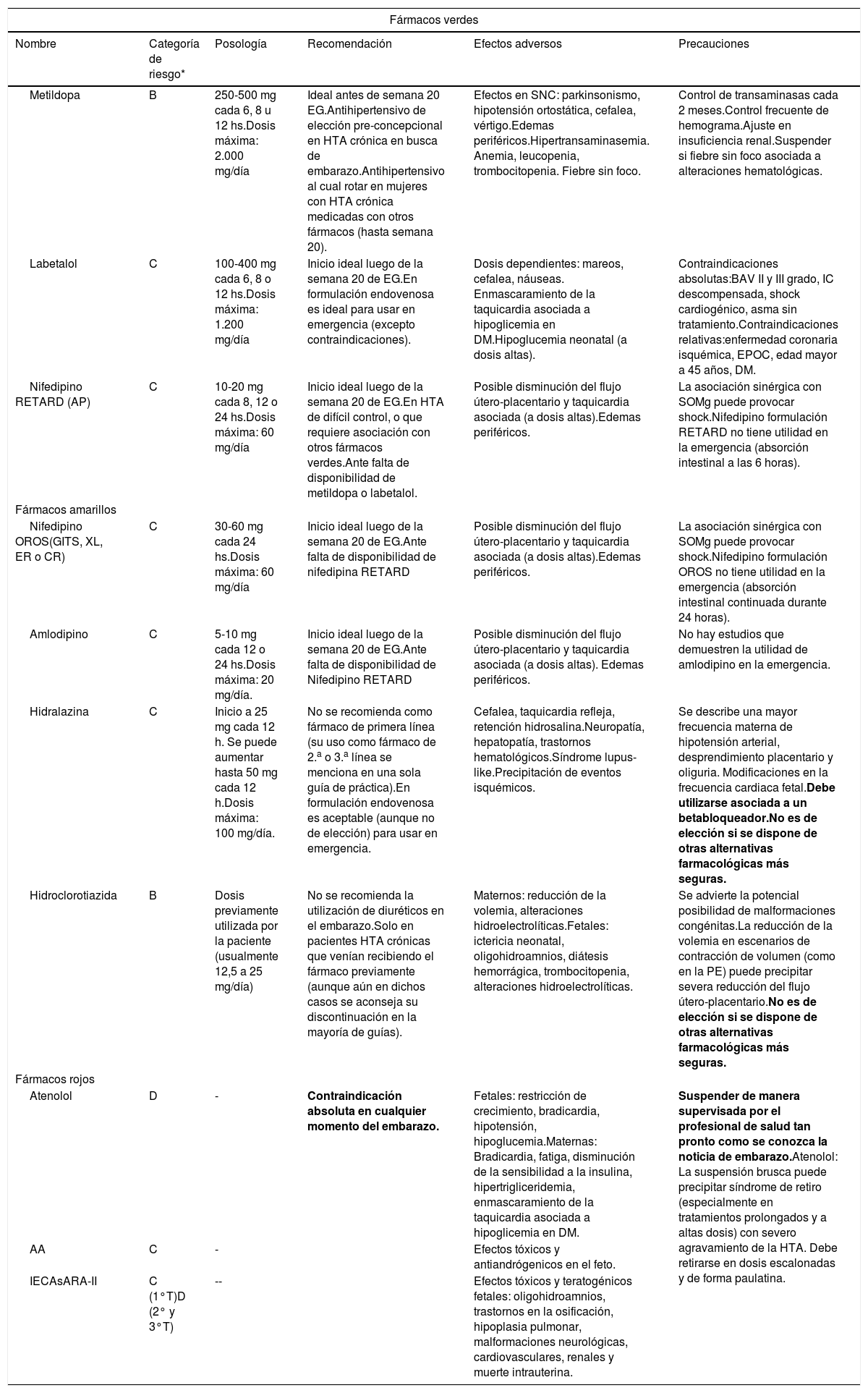
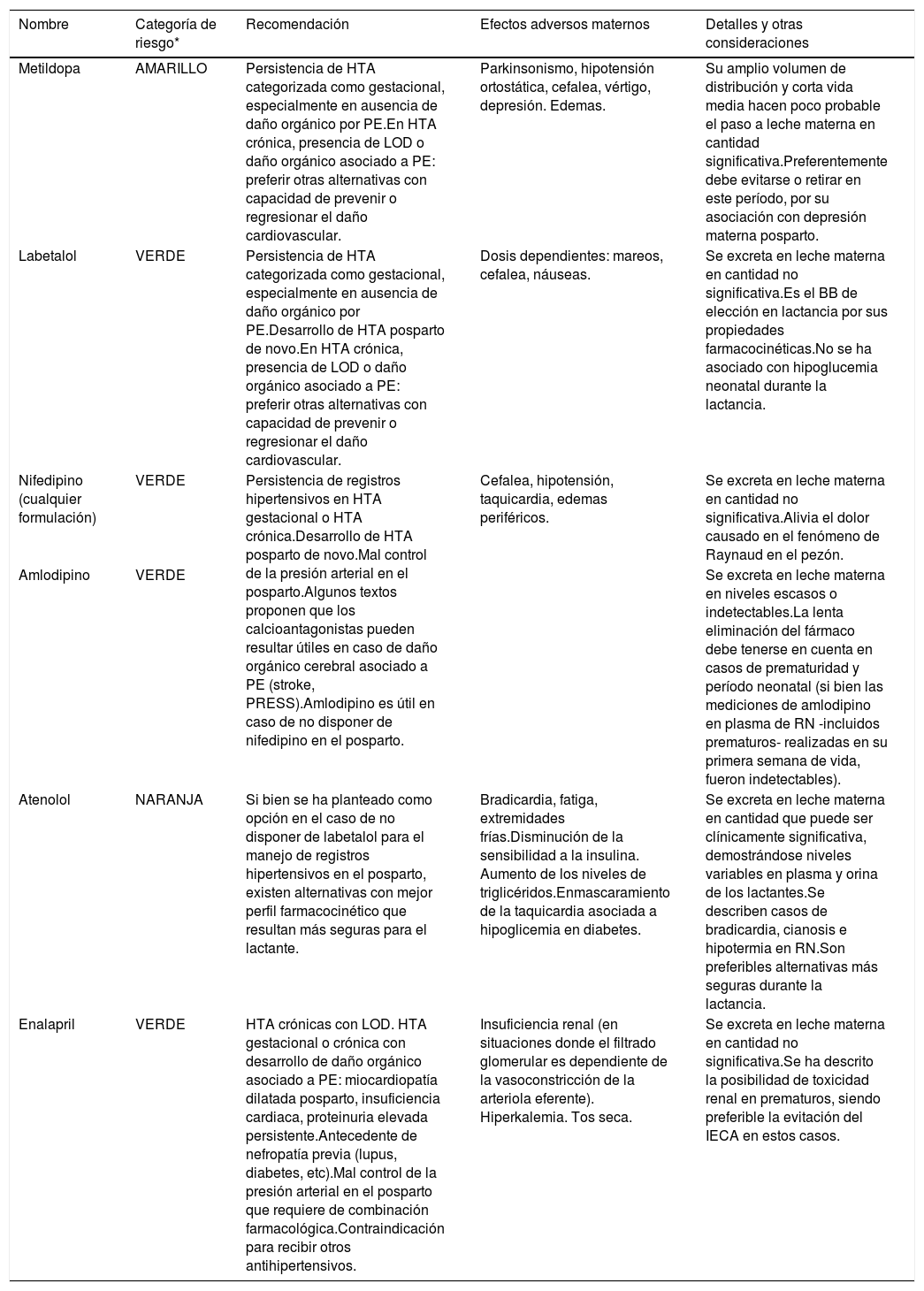
La hipertensión arterial (HTA) en el embarazo se define como una presión arterial sistólica ≥ 140 y/o diastólica ≥ 90 mmHg. Con base en las cifras, se clasifica en no severa (< 160/110 mmHg) y severa (≥ 160/110 mmHg). Previamente a iniciar tratamiento en HTA no severa, se debe descartar HTA de bata blanca. Si es posible el manejo ambulatorio, se sugiere el inicio farmacológico ante valores sostenidamente elevados, evitando cifras < 120/80 mmHg. Los fármacos seguros durante la gestación son metildopa, labetalol y nifedipino-RETARD, pudiendo contemplarse el uso de nifedipino-OROS o amlodipino con menor nivel de evidencia. La utilización de diuréticos, atenolol y otros betabloqueadores con fines antihipertensivos no está recomendada en esta etapa. Los inhibidores del sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona están terminantemente contraindicados. En posparto y lactancia, puede mantenerse el mismo esquema terapéutico empleado durante el embarazo, intentando retirar la metildopa precozmente. Durante el puerperio, amlodipino y enalapril resultan seguros, con ínfima excreción por leche materna.
Hypertension (HTN) in pregnancy is defined as systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg. Based on the values, it is classified as non-severe (< 160/110 mmHg) and severe (≥ 160/110 mmHg). Before starting treatment in non-severe HTN, white- coat HTN should be ruled out. If outpatient management is possible, pharmacological initiation is suggested with sustained high values, avoiding < 120/80 mmHg. Safe drugs during pregnancy are methyldopa, labetalol, and nifedipine-retard. The use of nifedipine-XL or amlodipine can be considered with a lower level of evidence of safety. Diuretics, atenolol, and other beta-blockers for antihypertensive purposes is not recommended in this period. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors are strictly contraindicated. In postpartum and breastfeeding, the same therapeutic regimen used during pregnancy can be maintained, trying early withdrawal of methyldopa. During puerperium, amlodipine and enalapril are safe, with minimal excretion in breast milk.