Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is an autoimmune disease that affects the small bile ducts. The only treatments currently approved in our country are ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and obeticholic acid. Different indices evaluate the response after 1 year of treatment. The aim of our study was to evaluate the different predictive scores and prognostic factors of response to UDCA.
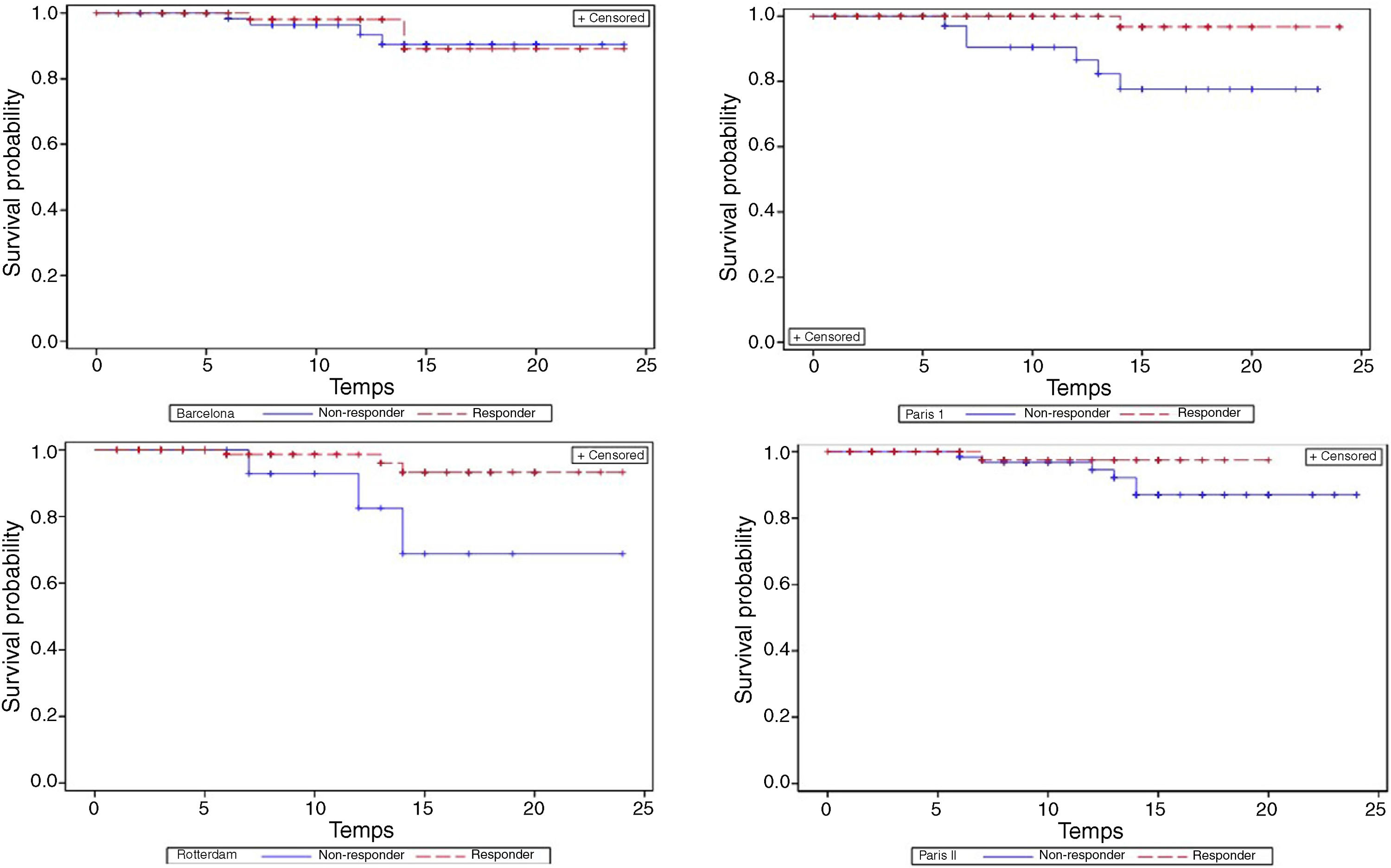
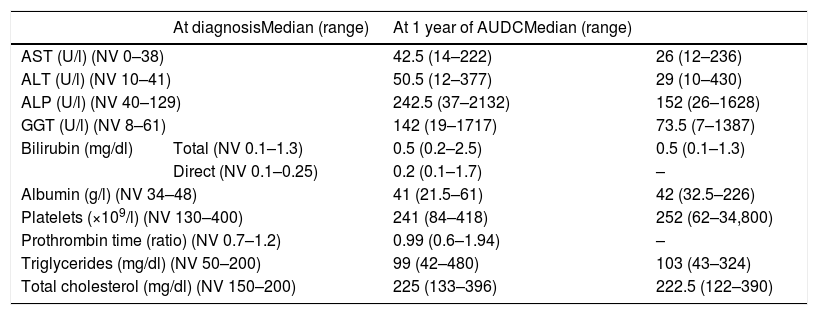
Material and methodsRetrospective single-centre study in which clinical and analytical data of patients diagnosed with PBC were collected from January 1987 to December 2015. The response after 1 year of treatment was evaluated using the different response scores and their concordance degree using the Kappa index. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was calculated to determine the predictive capacity of the scores. Likewise, the prognostic factors of response to treatment were analysed.
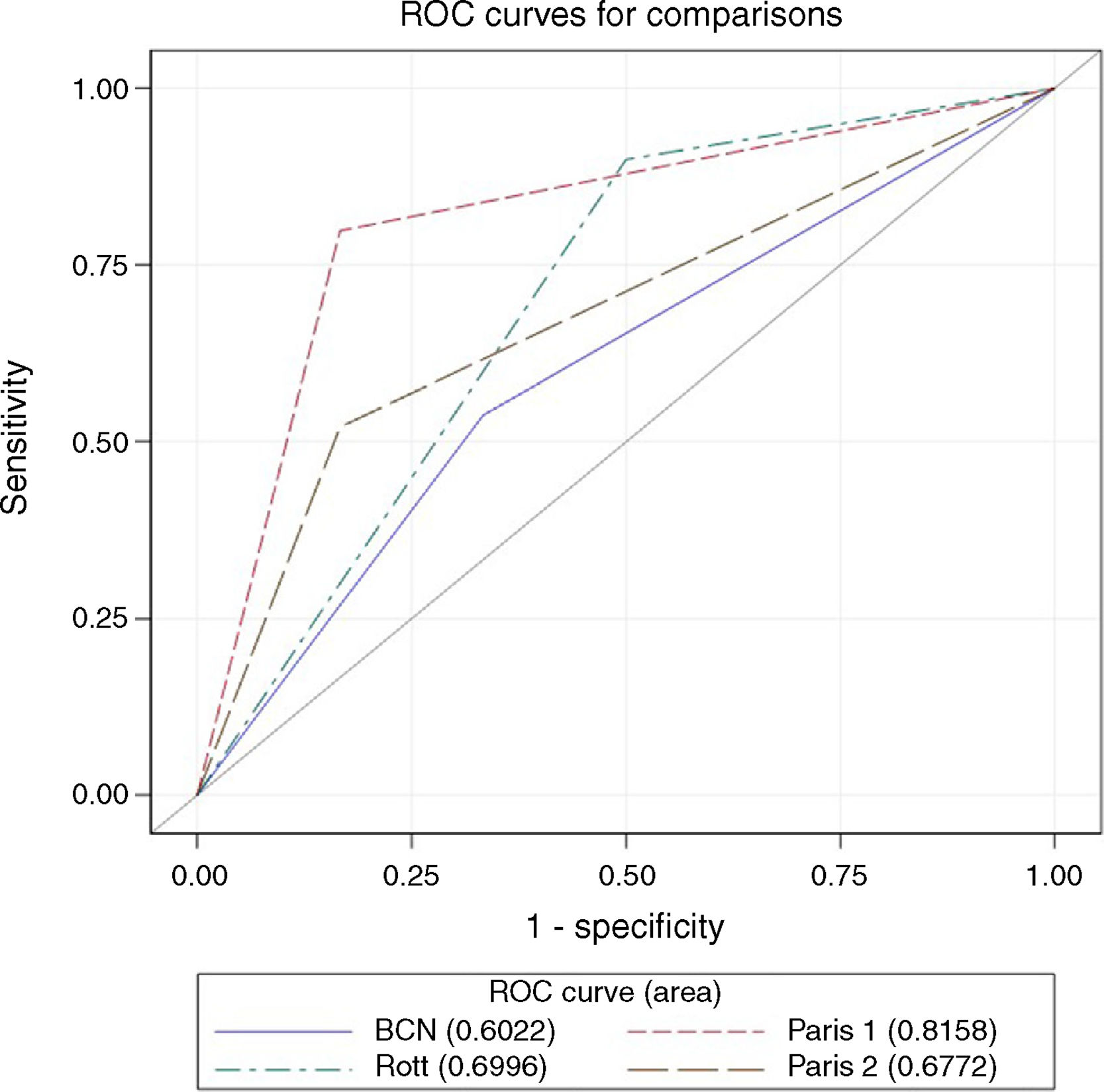
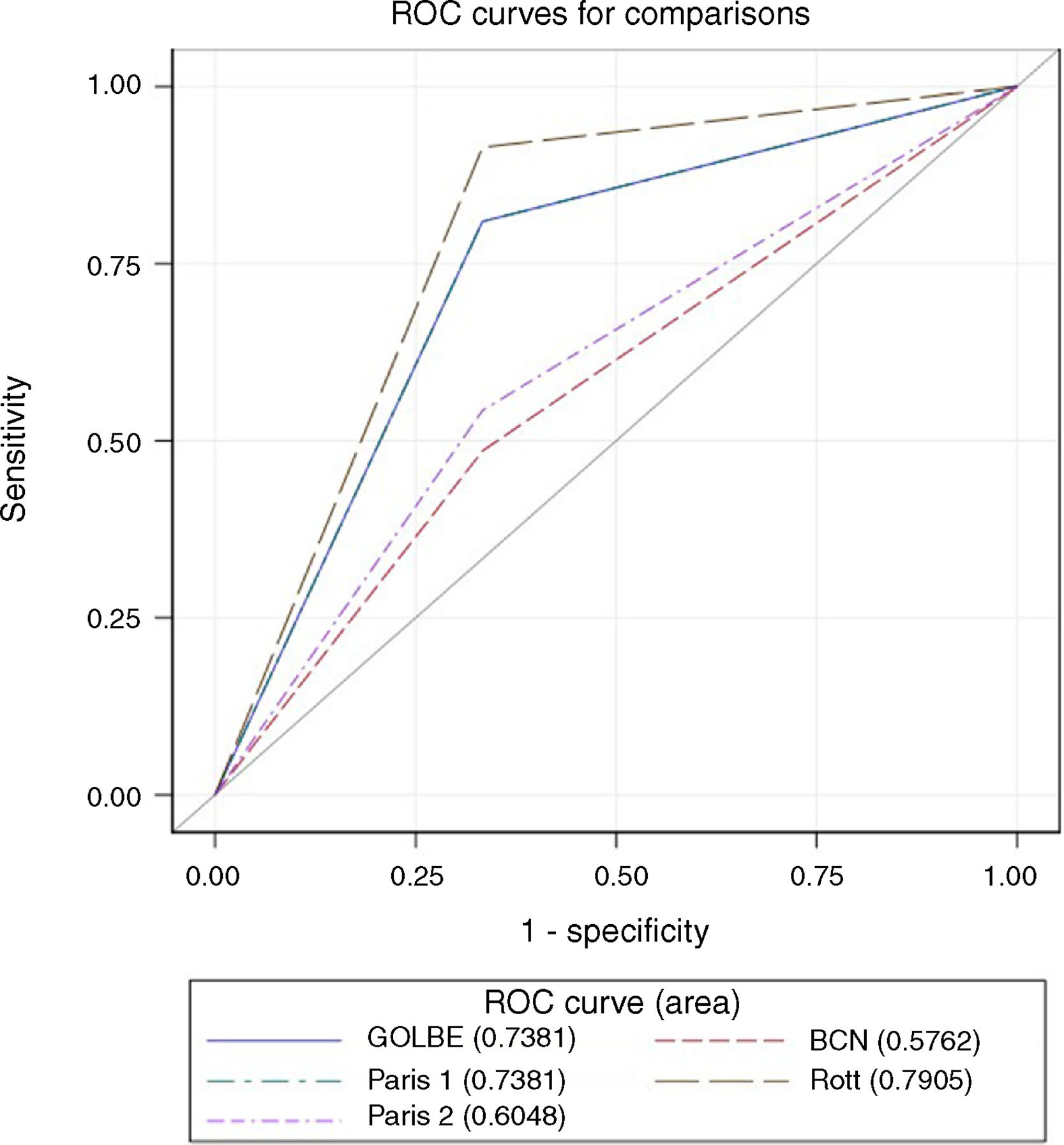
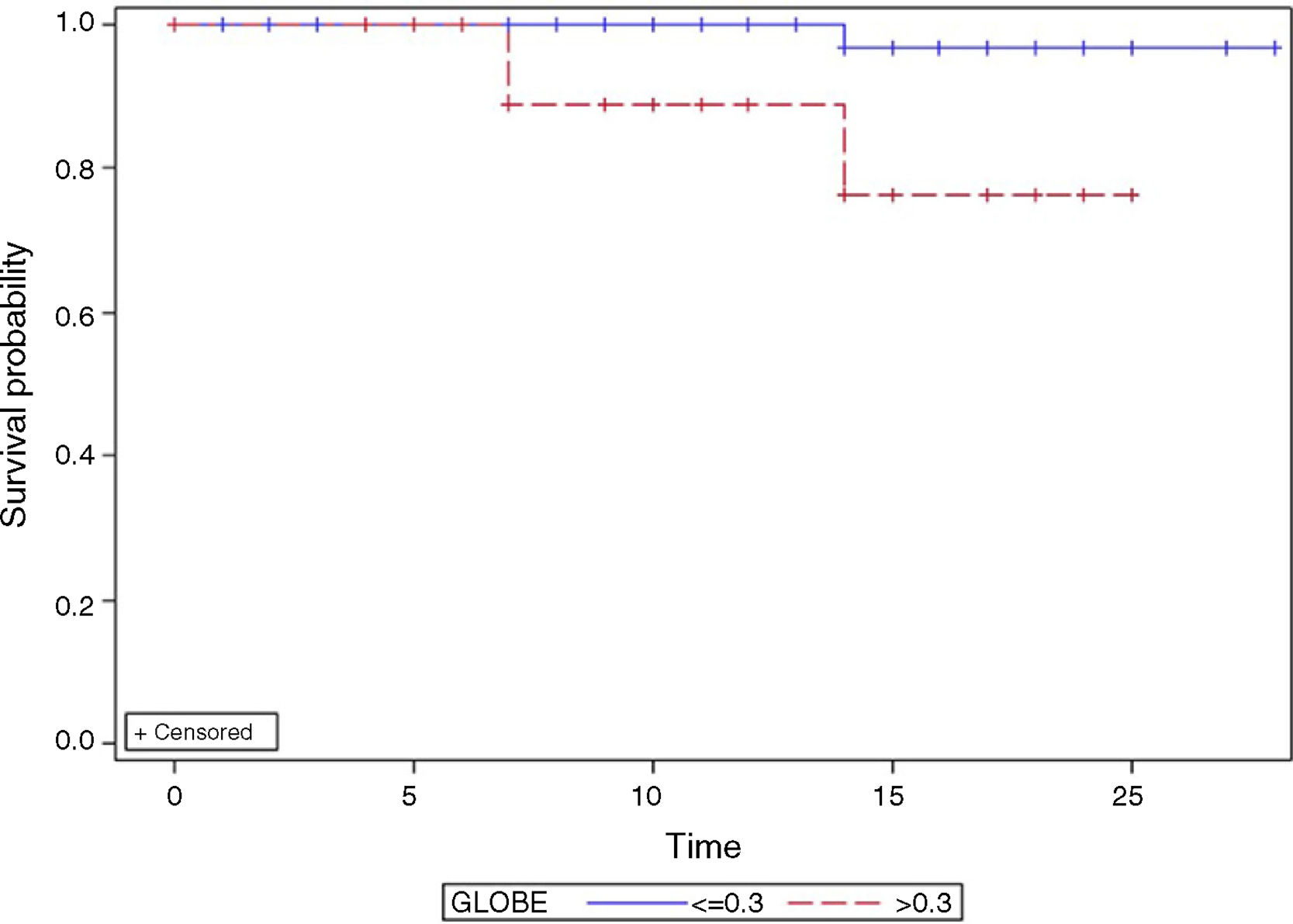
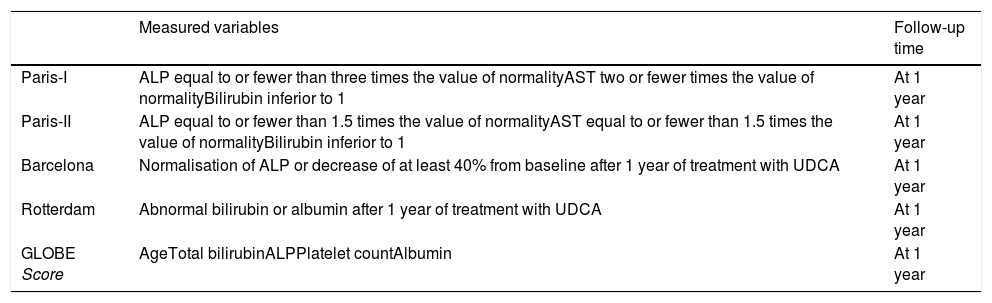
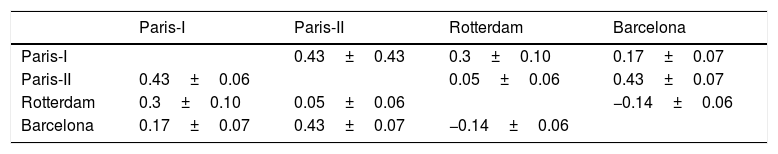
ResultsWe included 153 patients. The bivariate analysis showed a statistically significant relationship between the initial high levels of alkaline phosphatase and cholesterol and the poor response to treatment. The best AUROC was in Paris-I score (0.81). The concordance between the different scores was low. The GLOBE score was valid to evaluate the prognosis.
ConclusionBasal alkaline phosphatase and cholesterol were predictors of poor outcome. The best predictive qualitative score in our cohort patients was Paris-I. There was a poor concordance between the different predictive scores. GLOBE score is valid to evaluate prognosis.
Antecedentes y objetivos La colangitis biliar primaria (CBP) es una enfermedad autoinmunitaria que afecta a los conductos biliares de pequeño y mediano tamaño. Los únicos tratamientos aprobados actualmente en nuestro país son el ácido ursodeoxicólico (AUDC) y el ácido obeticólico. Diversos índices evalúan la respuesta al año de tratamiento. El objetivo de nuestro estudio fue evaluar los diferentes índices predictivos de respuesta al tratamiento con AUDC.
Material y métodosEstudio unicéntrico retrospectivo en el que se recogieron los datos clínicos y analíticos de los pacientes diagnosticados de CBP desde enero de 1987 hasta diciembre de 2015. Se calculó la respuesta al año de inicio del tratamiento utilizando los diferentes índices de respuesta y se evaluó su grado de concordancia mediante el índice Kappa. Se calculó el area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC, «área bajo la curva ROC») para determinar la capacidad predictiva de los índices. Asimismo, se analizaron los factores pronósticos basales.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 153 pacientes. El análisis bivariante demostró una relación estadísticamente significativa entre los niveles altos iniciales de fosfatasa alcalina y colesterol y la mala respuesta al tratamiento. La mejor AUROC fue del índice París-I (0,81). La concordancia entre los diferentes índices fue baja. El índice pronóstico GLOBE fue válido para evaluar el pronóstico.
ConclusiónLa fosfatasa alcalina y el colesterol basales fueron factores predictores de mala evolución. El índice cualitativo que mejor predijo la supervivencia fue el París-I. Se obtuvo una mala concordancia entre los diferentes índices predictivos. El índice GLOBE es válido para evaluar el pronóstico de la CBP.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora