Helicobacter pylori infections affect almost 50% of the world population, constituting a risk factor for benign and malignant gastrointestinal diseases. The increased resistance to antibiotic treatment against this infection represents a dilemma in the search of other therapeutic alternatives.
ObjectiveTo determine the efficacy of the use of vitamin C and E supplements concomitantly to antibiotic treatment against H. pylori infections.
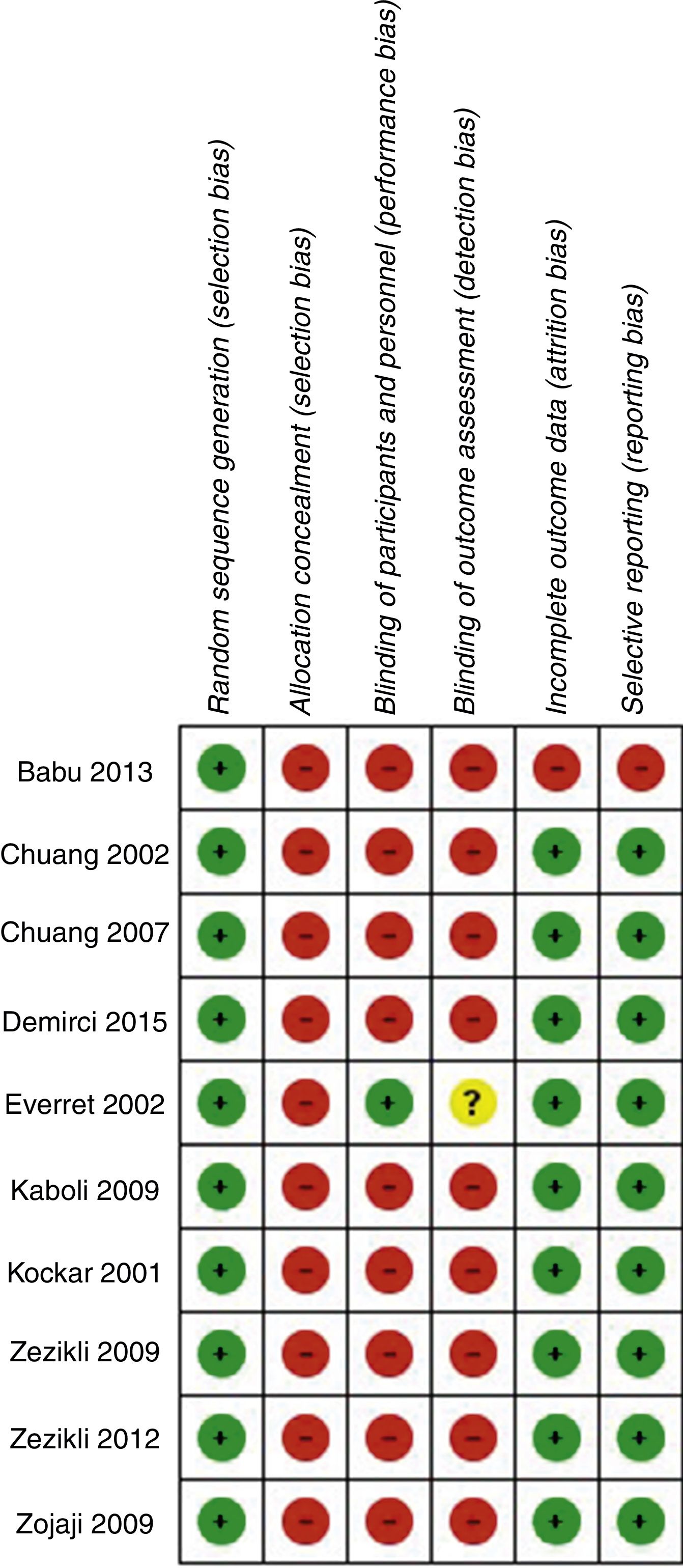
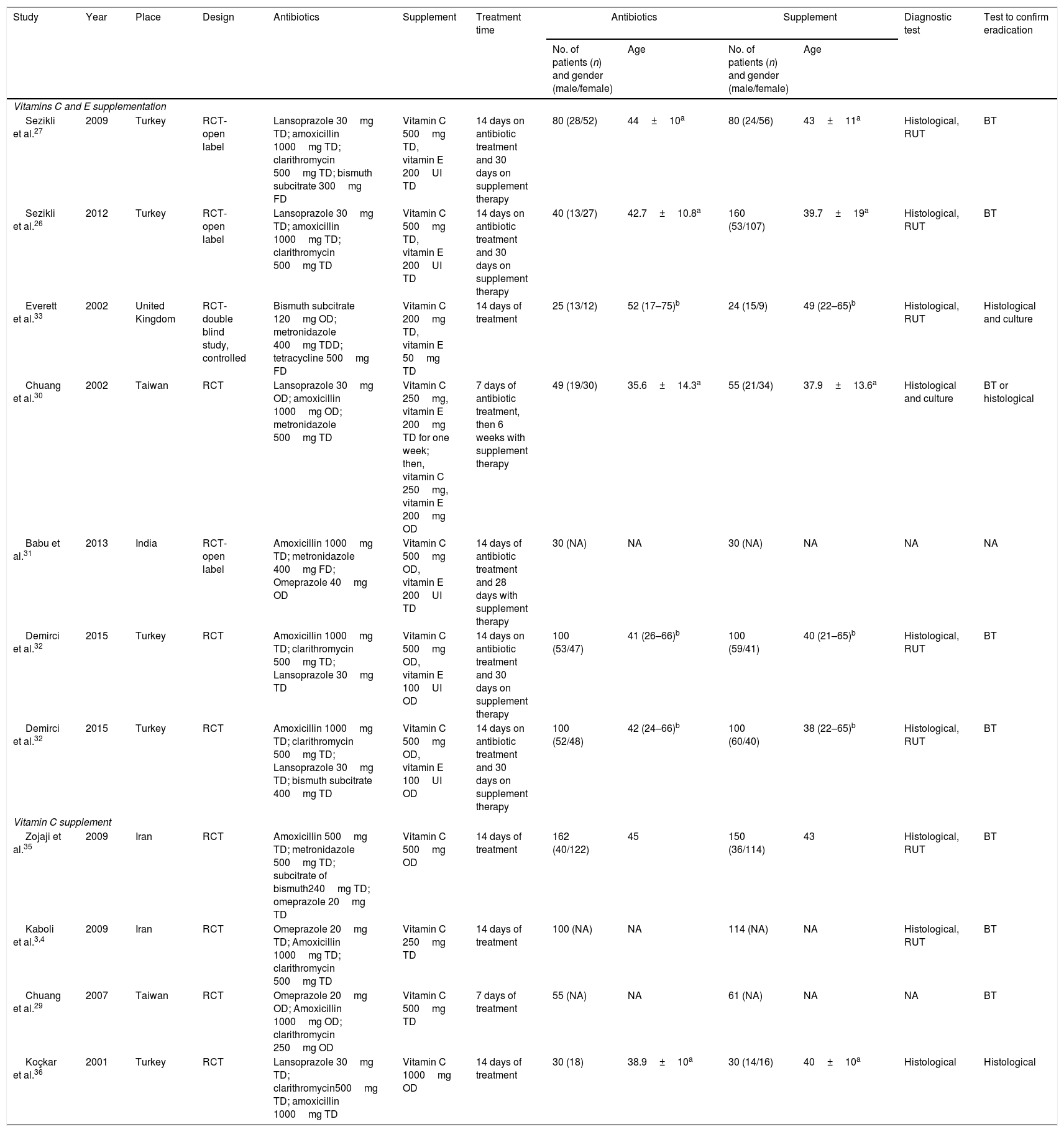
MethodsWe performed a systematic review on the MedLine (PubMed), Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Clinical Trials (CENTRAL) databases, searching for studies evaluating the efficacy of vitamin C and/or E supplements in the antibiotic treatment of H. pylori infections. The primary outcome was eradication of the infection. The secondary outcome was the adverse effects. The meta-analysis was conducted using the random effects method.
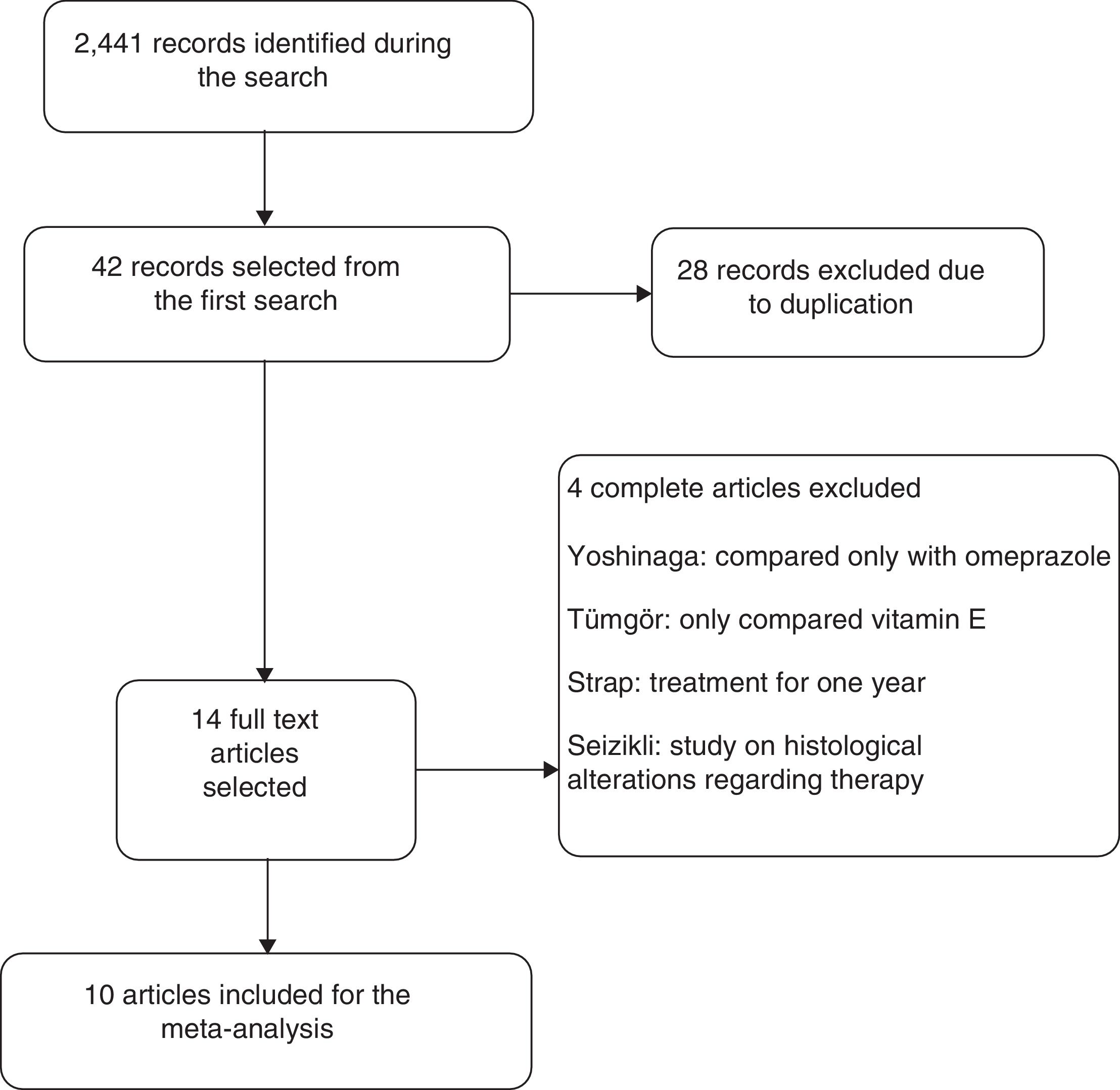
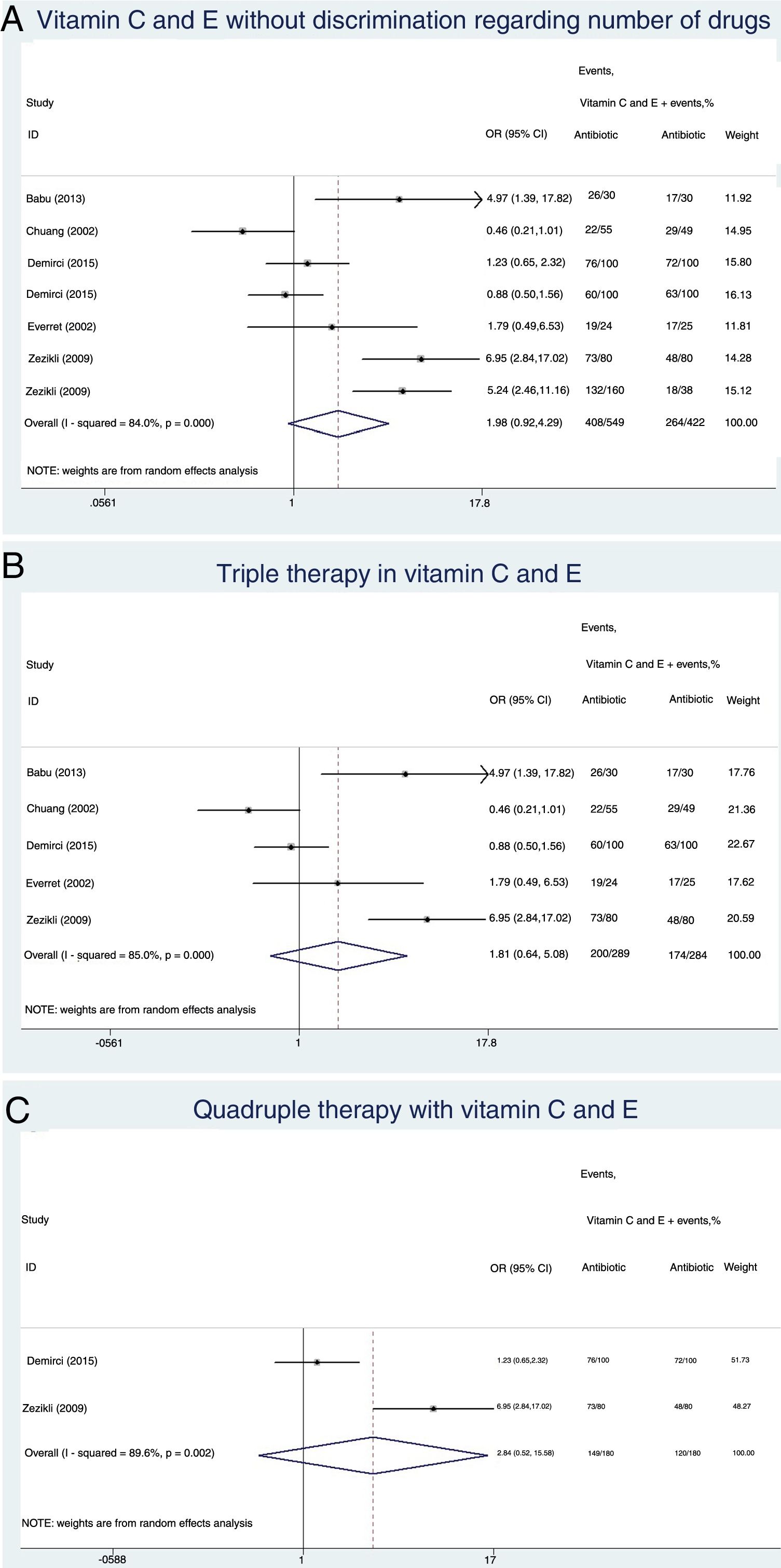
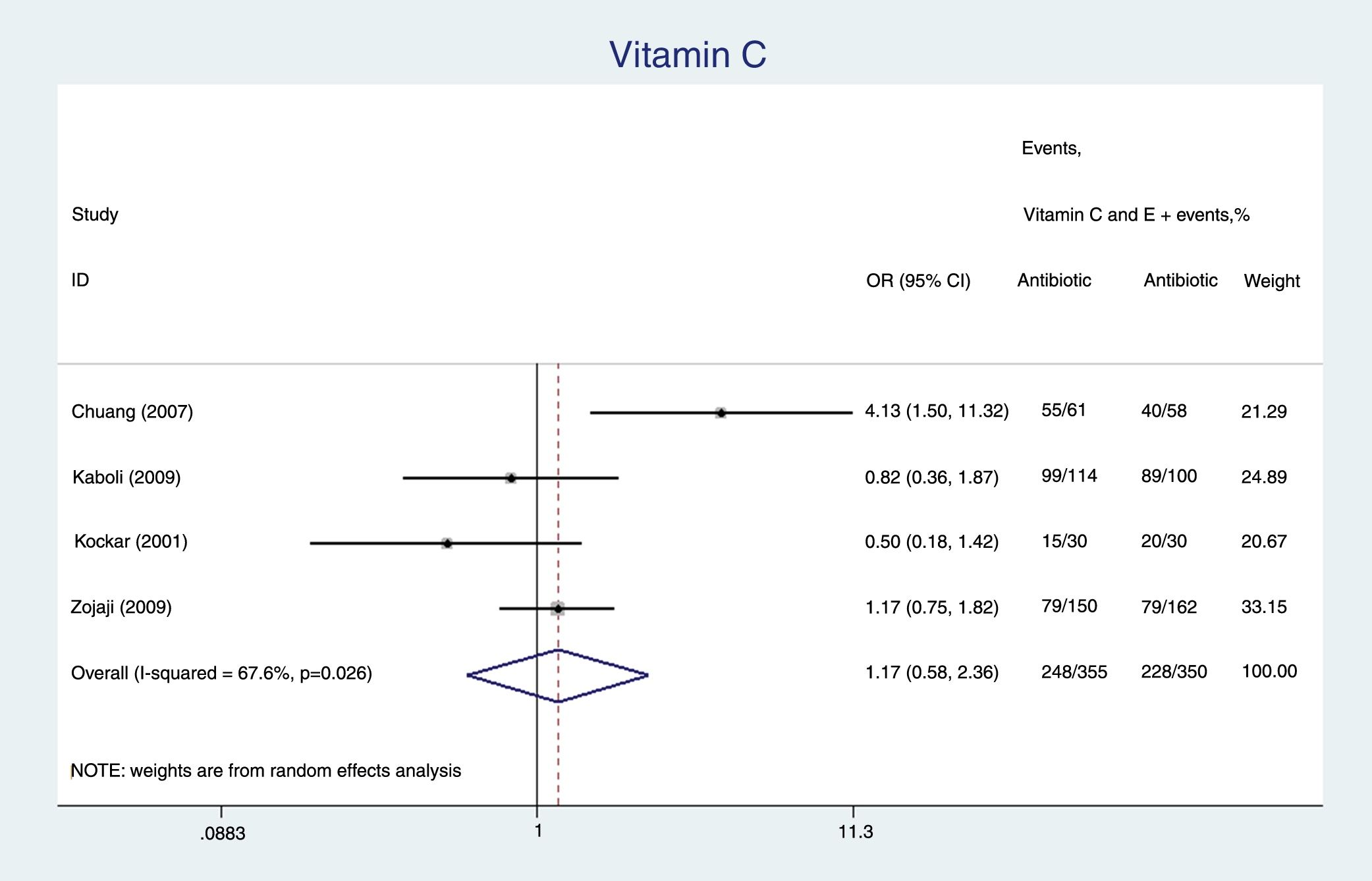
ResultsTen studies were included and analyzed in two groups. The first group, which was comprised by 973 patients, compared the use of supplementation with vitamin C and E, showing that, without discriminating the number of antibiotics used, there was no relationship with the eradication of the infection (OR: 1.98 [95% CI: 0.92–4.29], p=0.08). The triple or quadruple antibiotic therapy had no effect on eradication rates either (OR 1.80 [95% CI: 0.64–5.08], p=0.26 and OR: 2.84 [95% CI: 0.51–15.56], p=0.22, respectively). No effect on the eradication rates was observed either in the group that only assessed the use of vitamin C, comprised by 702 patients (OR: 1.17 [95% CI: 0.58–2.31], p=0.65). Only four studies reported adverse effects, the most common one being nausea.
ConclusionsSupplementation with vitamin C and E in the antibiotic treatment against H. pylori has no effect. However, the reviewed studies had several biases and differences in the dosage of the supplements and antibiotics administered.
La prevalencia de la infección por Helicobacter pylori afecta casi al 50% de la población mundial, siendo un factor de riesgo para enfermedades benignas y malignas gastrointestinales. El aumento de la resistencia al tratamiento antibiótico contra esta infección ha presentado un dilema en el abordaje de otras alternativas en la terapéutica.
ObjetivoDeterminar la eficacia del suplemento de vitaminas C y E añadido al tratamiento antibiótico en la erradicación de la infección por H. pylori.
MétodosSe realizó una revisión sistemática en las bases de datos de MedLine, Embase y Cochrane Central Register of Clinical Trials (CENTRAL), para estudios que evaluaran la eficacia del suplemento de vitaminas C y/o E en el tratamiento antibiótico de infección por H. pylori. El resultado principal fue erradicación de la infección y el secundario fueron efectos adversos. El metaanálisis fue elaborado mediante el método de efectos aleatorios.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 10 estudios y se hicieron 2 grupos. El primero comparó el uso de suplemento de vitaminas C y E incluyendo 973 pacientes, en el cual sin discriminar el número de antibióticos no se obtuvo una relación con la erradicación de la infección (OR: 1,98 [IC95%: 0,92-4,29], p=0,08). La terapia triple o cuádruple antibiótica no tuvo un efecto sobre la erradicación (OR: 1,80 [IC95%: 0,64-5,08], p=0,26, y OR: 2,84 [IC95%: 0,51-15,56], p=0,22, respectivamente). En el grupo en que solo se evaluó el uso de vitaminaC se incluyeron 702pacientes, pero no se obtuvo un efecto sobre la erradicación (OR: 1,17 [IC95%: 0,58-2,31], p=0,65). Los efectos adversos solo fueron reportados en 4 estudios, siendo el más frecuente las náuseas.
ConclusionesEl suplemento de vitaminas C y E en la terapia antibiótica contra H. pylori no tuvo ningún efecto. Sin embargo, los estudios presentaron bastantes sesgos y diferencias en la posología de los suplementos y antibióticos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora