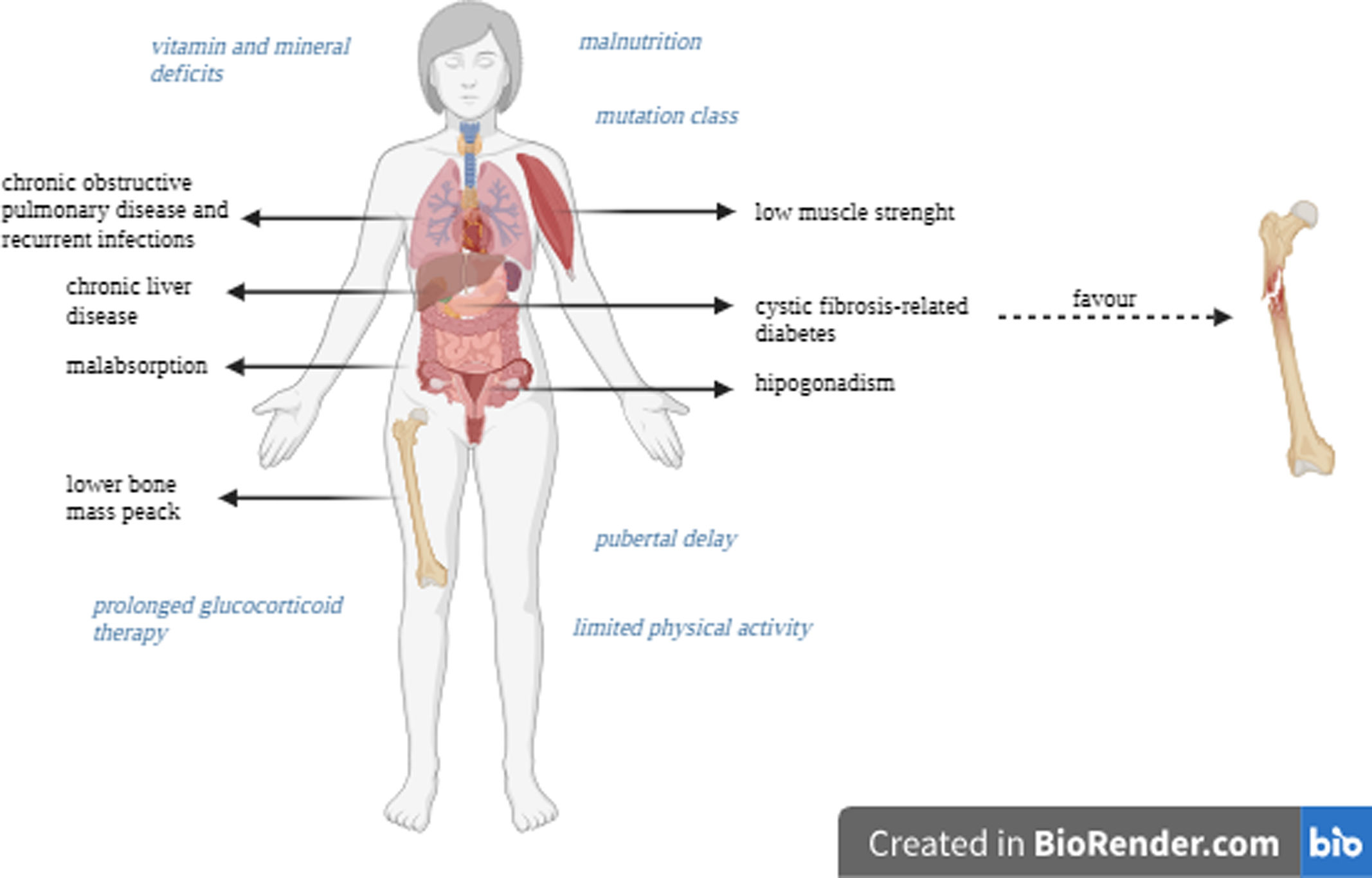
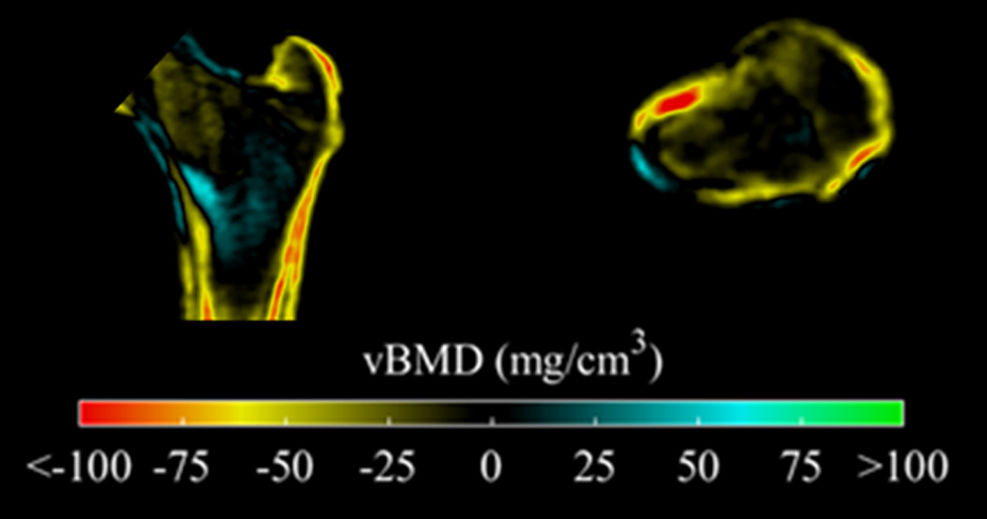
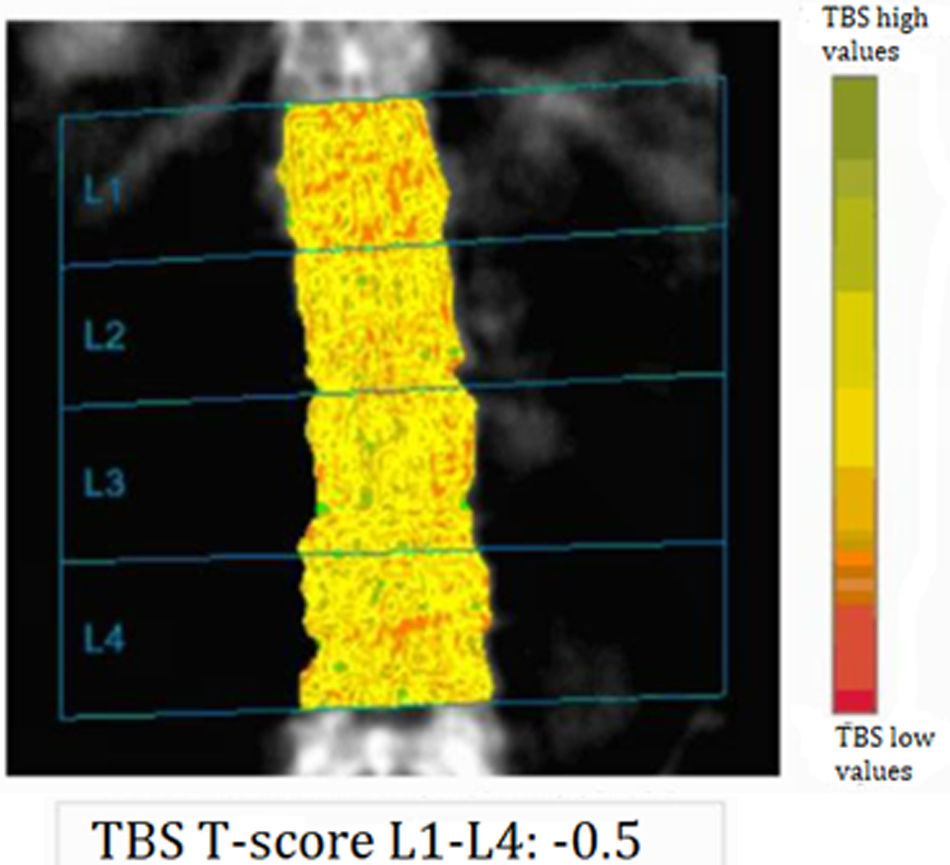
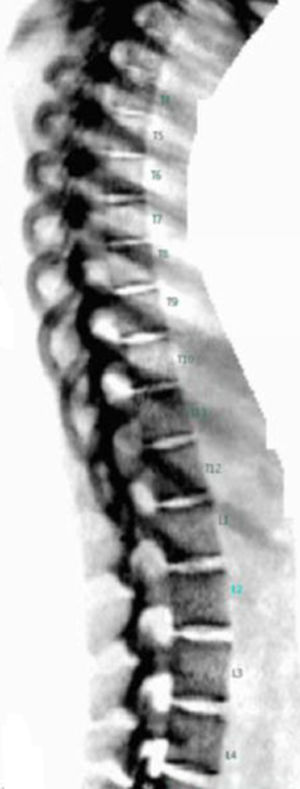
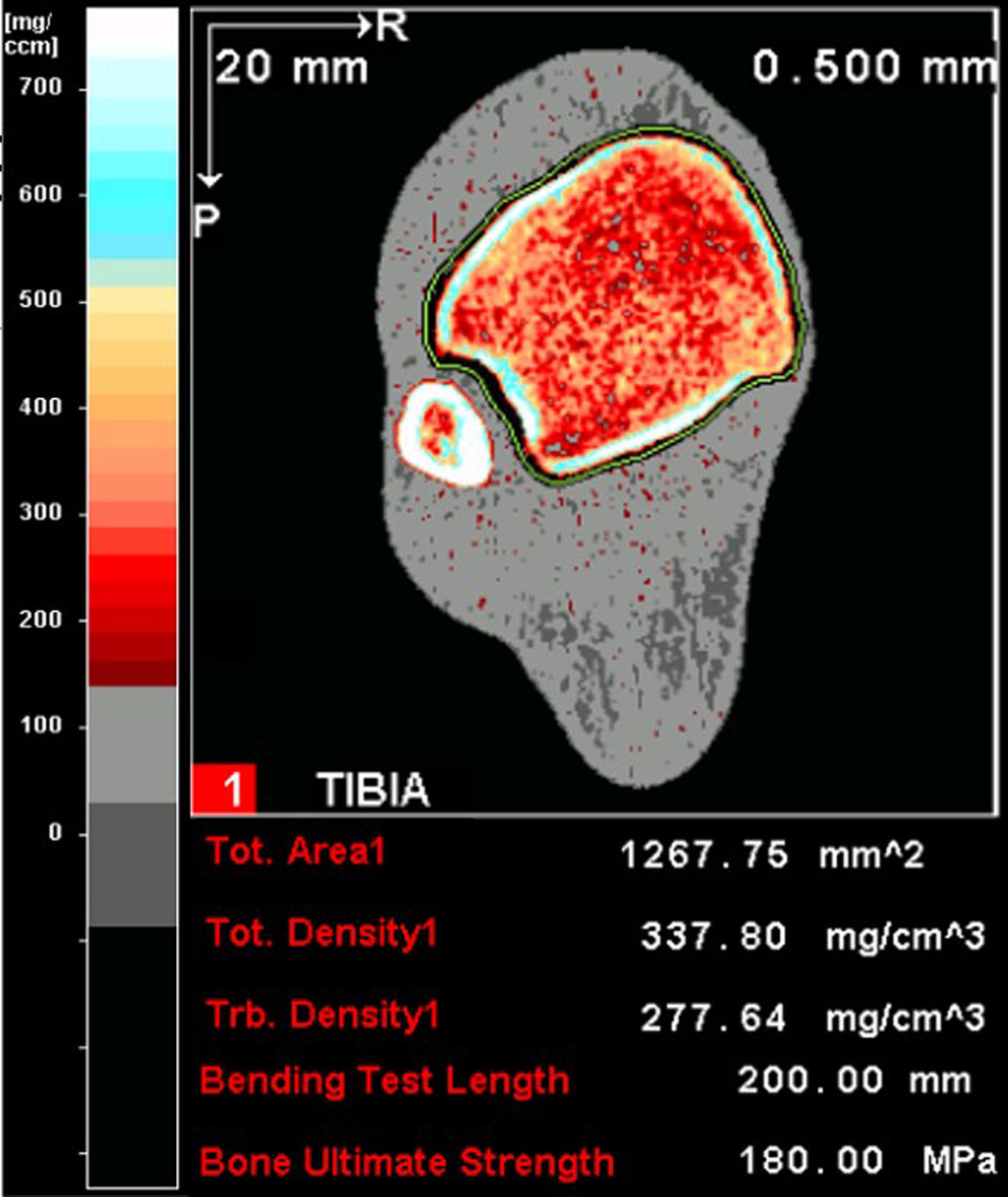
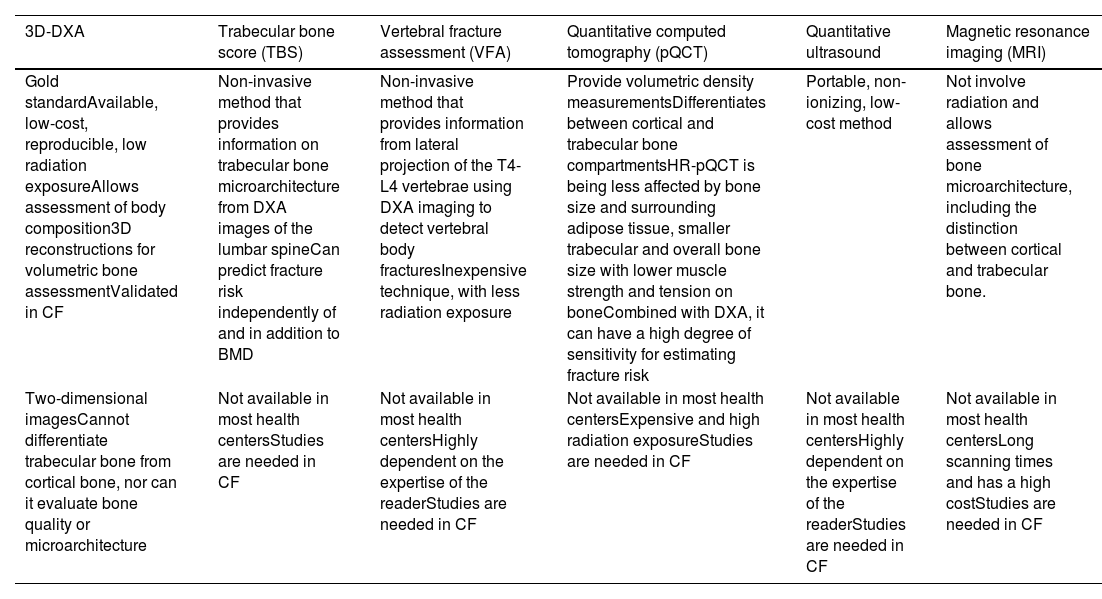
With the increased life expectancy of people with cystic fibrosis (CF), clinical attention has focused on prevention and treatment of non-pulmonary comorbidities. CF-related bone disease (CFBD) is a common complication and leads to increased fracture rates. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the recommended and gold standard technique to identify and monitor bone health. However, DXA has limitations because of its two-dimensional nature. Complementary tools to DXA are available, such as trabecular bone score (TBS) and vertebral fracture assessment (VFA). Quantitative computed tomography (QCT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and quantitative ultrasound (QUS) may also be useful.
Con el aumento de la esperanza de vida de las personas con fibrosis quística (FQ), la atención clínica se ha centrado en la prevención y el tratamiento de las comorbilidades no pulmonares. La enfermedad ósea relacionada con la FQ es una complicación frecuente y provoca un aumento de las tasas de fractura. La absorciometría de rayosX de energía dual (DXA) es la técnica recomendada y de referencia para identificar y monitorizar la salud ósea. Sin embargo, presenta limitaciones debido a su naturaleza bidimensional. Por ello, se están implementando herramientas complementarias a la DXA, como la puntuación ósea trabecular (trabecular bone score [TBS]) y la morfometría vertebral mediante DXA (VFA). También la tomografía computarizada cuantitativa (QCT), la resonancia magnética (RM) y la ecografía cuantitativa (QUS) pueden resultar útiles. Estas herramientas proporcionan información sobre la densidad ósea volumétrica real y la microestructura ósea, lo que puede contribuir a la evaluación y minimizar el riesgo de fracturas, e incluso prevenirlas, para evitar la elevada morbilidad y mortalidad asociada a las fracturas.