Persistent post-COVID olfactory dysfunction continues to be studied due to the controversy in its pathophysiology and neuroimaging.
Materials and methodsThe patients had confirmed mild COVID-19 infection with olfactory dysfunction of more than one month of evolution and they were compared to controls with normal olfaction, assessed using the Sniffin’ Sticks Olfactory Test and underwent brain, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the olfactory bulb and olfactory function.
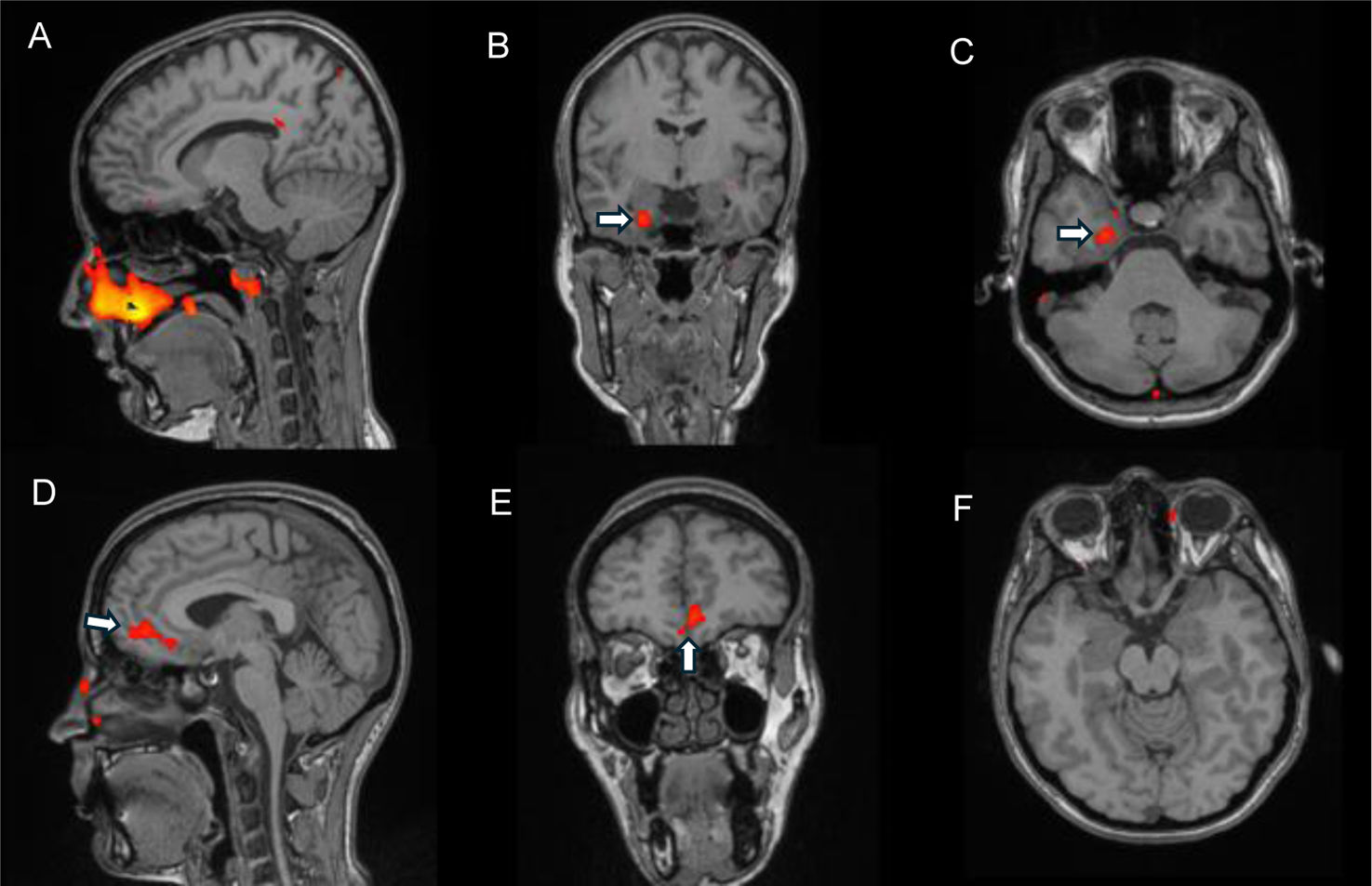
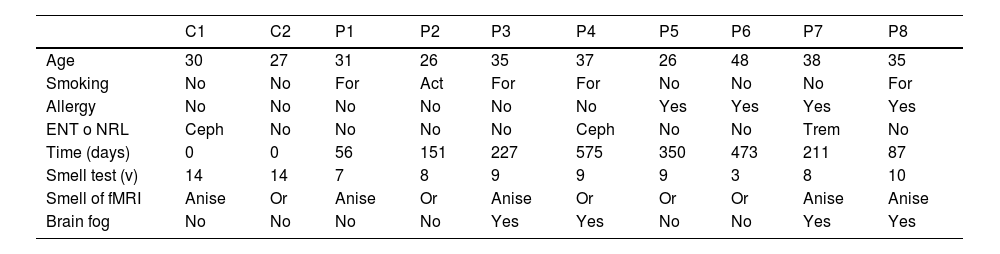
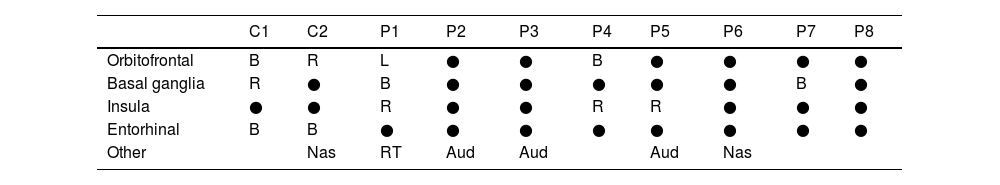
ResultsA total of 8 patients and 2 controls participated. The average age of the patients was 34.5 years (SD 8.5), and that of the controls was 28.5 (SD 2.1). The average score in the patients’ olfactory test was 7.9 points (SD 2.2). In brain and olfactory bulb MRI tests, no morphological differences were found. When evaluated by functional MRI, none of the patients activated the entorhinal area in comparison to the controls, who did show activation at this level. Activation of secondary olfactory areas in cases and controls were as follows: orbitofrontal (25% vs 100%), basal ganglia (25% vs 50%) and insula (38% vs 0%) respectively.
ConclusionsThere were no observed morphological changes in the brain MRI. Unlike the controls, none of the patients activated the entorhinal cortex in the olfactory functional MRI.
La alteración olfatoria persistente post-COVID continúa en estudio por la controversia en su fisiopatología y neuroimagen.
Materiales y métodosLas pacientes tuvieron COVID-19 leve confirmada con una disfunción olfatoria de más de un mes de evolución y se compararon con controles con olfacción normal, evaluados mediante el Sniffin’ Sticks Olfatory Test y sometidos a una resonancia magnética (RM) cerebral, del bulbo olfatorio y funcional olfatoria.
ResultadosParticiparon 8 pacientes y 2 controles. La edad media de las pacientes fue 34,5 años (DE 8,5) y la de los controles fue 28,5 (DE 2,1). La puntuación media de los pacientes en el test olfatorio fue de 7,9 puntos (DE 2,2). En las pruebas de RM cerebral y bulbo olfatorio no se encontraron diferencias morfológicas. En la RM funcional ninguna de las pacientes activó el área entorrinal, en contraposición a los controles que sí mostraron activación a este nivel. La activación de áreas olfatorias secundarias en casos y controles fue orbitofrontal (25% vs. 100%), ganglios basales (25% vs. 50%) e ínsula (38% vs. 0%) respectivamente.
ConclusionesNo se apreciaron cambios morfológicos en la RM cerebral ni en el bulbo olfatorio. A diferencia de los controles, ninguna de las pacientes activó la corteza entorrinal en la RM funcional olfatoria.