Polysomnography (PSG) is the gold standard technic for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). It is an expensive, complex and not always available technic, meaning that respiratory polygraphy (RP) has become usual. Although RP is not validated in low probability patients, Spanish guidelines recommend conservative treatment in patients with negative RP. We intended to study the prevalence and severity of OSAS through PSG in a sample of patients with low probability and negative RP.
Material and methodsRetrospective, observational, descriptive and analytic study of low probability OSAS patients with negative RP in whom a PSG was performed. Anthropometric, clinical and sleep data were collected.
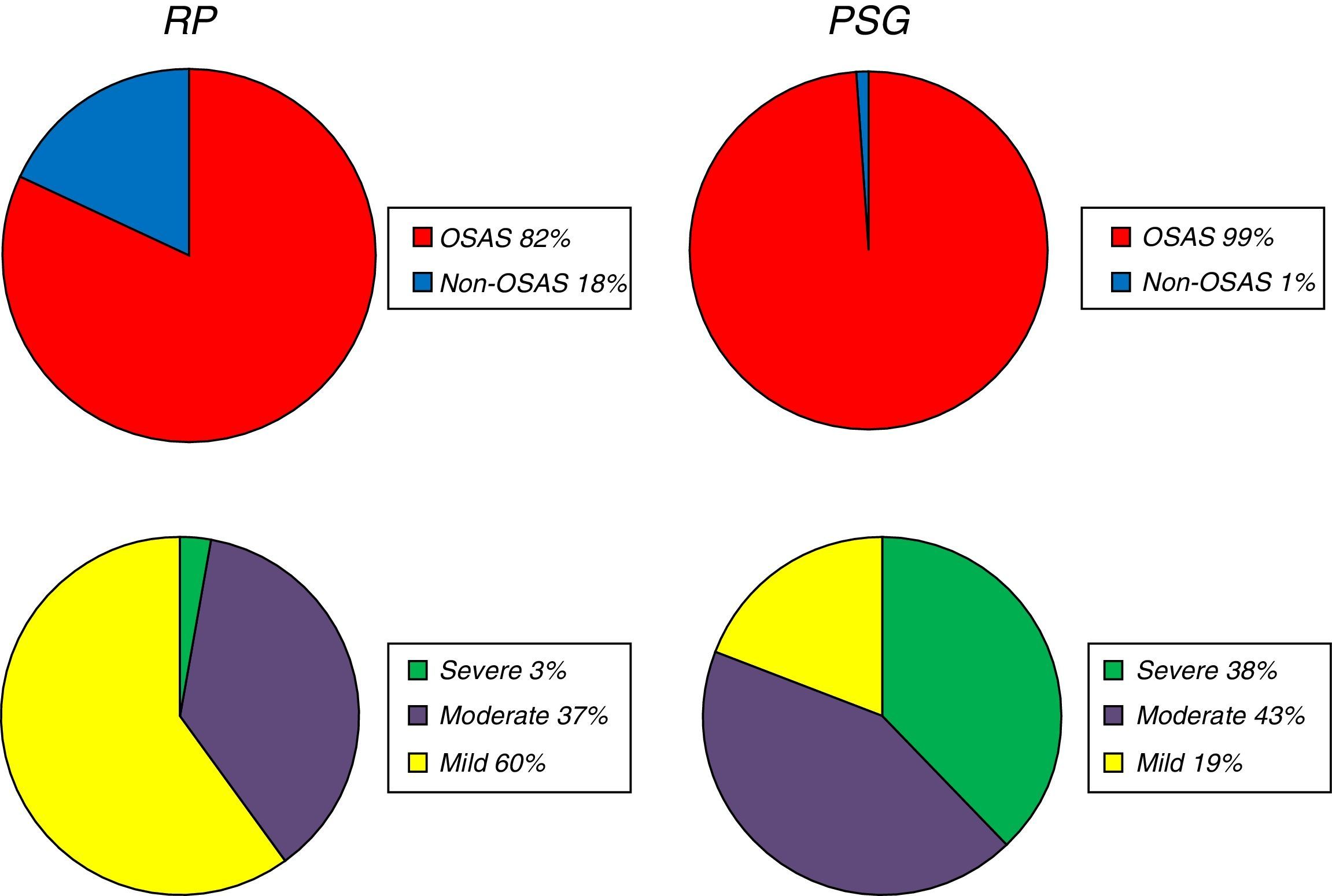
ResultsEighty-two patients were included. After PSG, a greater number of hypopneas (137.8±70.1 vs. 51.2±38.4 [p<0.05]) and apnea hypopnea index (27.8±15.6 vs. 11.7±7.1 [p<0.05]) was observed, as well as an increment in OSAS prevalence of 17%, which was 35% in severe OSAS. In mild OSAS, there was a decrement of 41%.
ConclusionAccording with the results of this study, RP significantly underestimates the prevalence and severity of OSAS in low probability patients. While it is necessary to adequately stratify the OSAS probability in order to correctly indicate diagnosis tests, we recommend performing a PSG in low probability patients with negative RP.
La polisomnografía (PSG) es el método estándar para el diagnóstico del síndrome de apneas e hipopneas del sueño (SAHS). Es una técnica cara, compleja y de poca disponibilidad, por lo que la poligrafía respiratoria (PR) es de uso habitual. La PR no está validada en casos de baja probabilidad; sin embargo, la normativa vigente contempla el tratamiento conservador en caso de PR negativa. Nos hemos propuesto estudiar la prevalencia y gravedad del SAHS mediante PSG, en una muestra de pacientes con baja probabilidad y PR negativa.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo, observacional, descriptivo y analítico de pacientes con baja probabilidad de SAHS y PR negativa a los que se les realizó posteriormente una PSG. Se registraron datos antropométricos, clínicos y características del sueño.
ResultadosOchenta y dos pacientes fueron incluidos. En el registro de la PSG se observó un incremento de hipopneas (137,8±70,1 frente a 51,2±38,4 [p<0.05]) y del índice de apneas e hipopneas (27,8±15,6 frente a 11,7±7,1 [p<0,05]), así como un aumento del 17% en la prevalencia de SAHS, de un 35% de casos graves y una disminución de un 41% de los casos leves.
ConclusiónDe acuerdo con los resultados de este estudio, la PR subestima de forma estadísticamente significativa la prevalencia y gravedad del SAHS en pacientes con baja probabilidad. Es necesario un adecuado proceso de estratificación de riesgo para la correcta indicación de pruebas diagnósticas, y recomendable realizar una PSG cuando se ha realizado una PR con resultado negativo en estos pacientes.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora