Los antidiabéticos orales inhibidores del cotransportador sodio-glucosa (iSGLT2) reducen la morbimortalidad cardiovascular en la DM2. El aumento de la rigidez arterial puede participar en esta morbimortalidad. El objetivo de este trabajo fue analizar el efecto de la administración de dapagliflozina en la rigidez arterial.
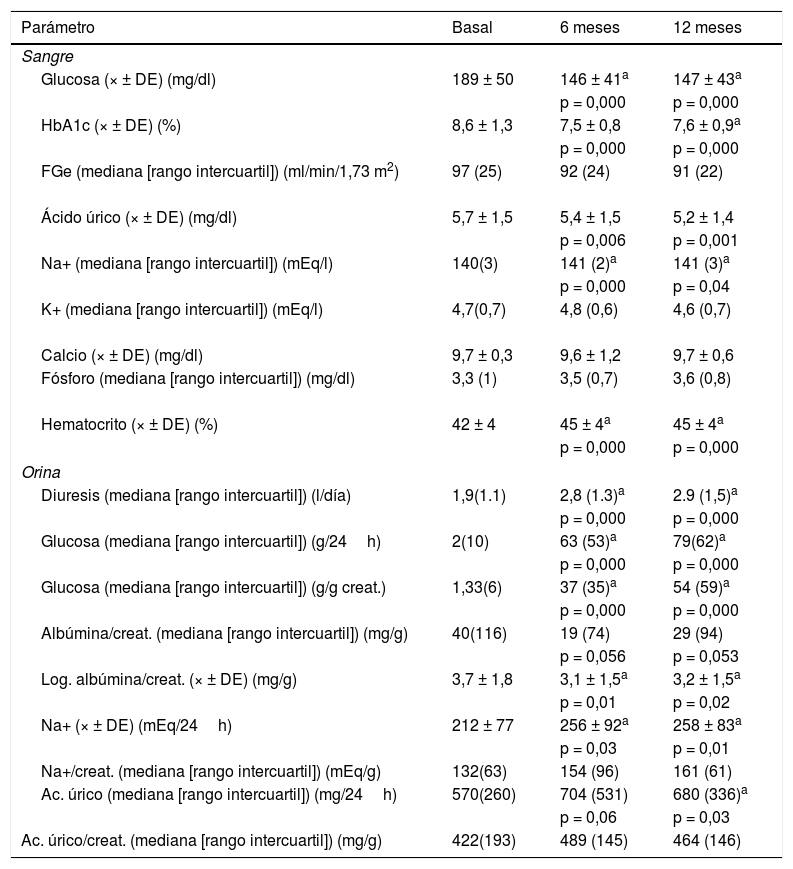
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, prospectivo que incluyó a 32 pacientes con DM2. Antes del inicio de dapagliflozina y a los 6 y 12 meses, se analizaron parámetros bioquímicos en sangre y orina. Basalmente y a los 12 meses se determinó la velocidad de pulso carótida-femoral (VPc-f) mediante tonometría. El análisis de los cambios en las variables y su interrelación se hizo mediante ANOVA de datos repetidos, test de Wilcoxon y regresión múltiple.
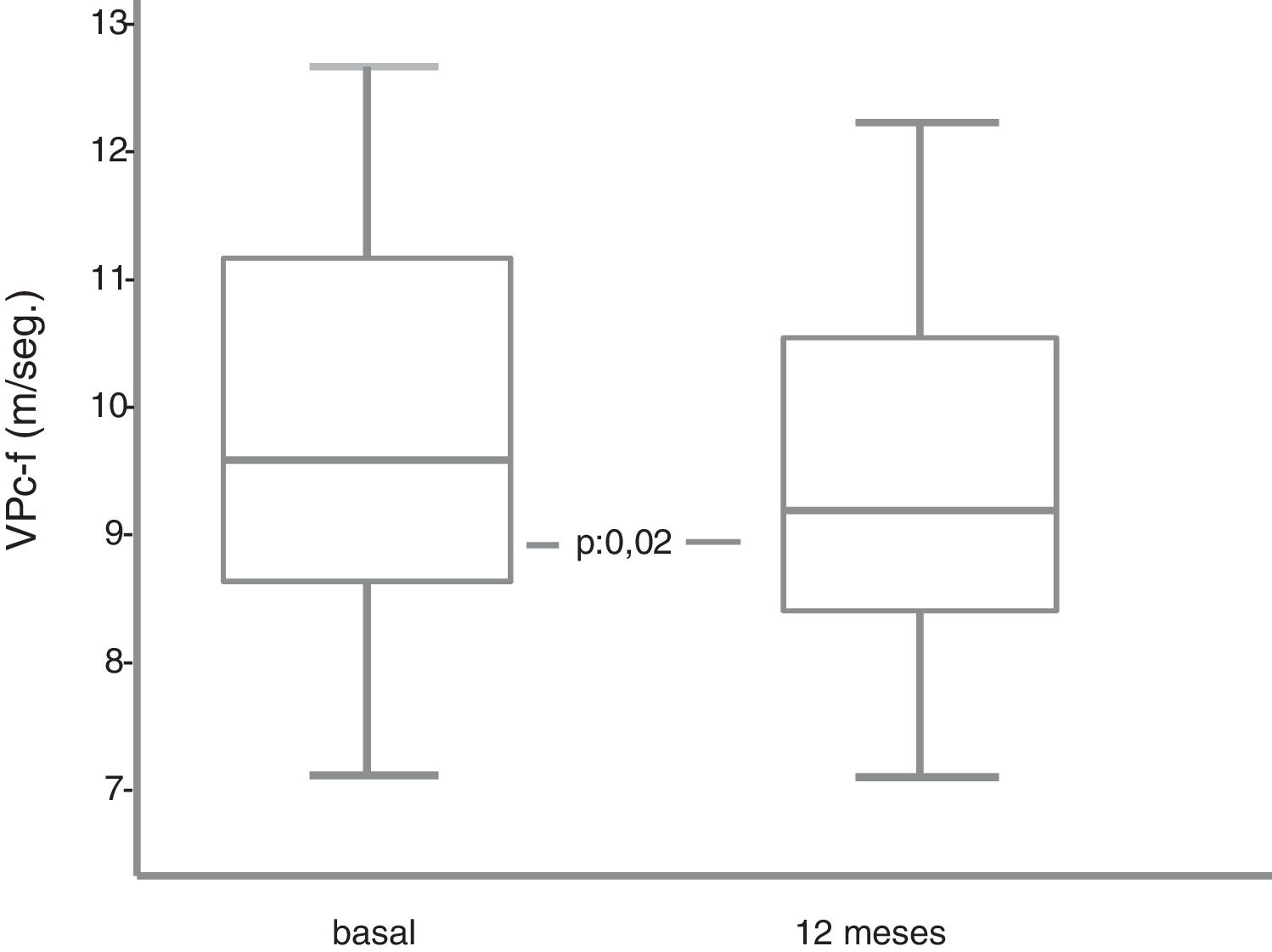
ResultadosSe objetivó un descenso significativo de la VPc-f. No se evidenció asociación entre descenso de VPc-f y cambios de la glucemia, la uricemia, la presión arterial ni del peso.
ConclusionesDapagliflozina, en sujetos con DM2, produce, a medio-largo plazo, una disminución de la rigidez arterial.
Oral antidiabetic inhibitors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT2i) reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in DM2. The increase in arterial stiffness can participate in this morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to analyse the effect of the administration of dapagliflozin on arterial stiffness.
Patients and methodsProspective observational study that included 32 patients with DM2. Before starting dapagliflozin, and at 6 and 12 months, biochemical parameters in blood and urine were analysed. Before starting dapagliflozin and at 12 months the velocity of the carotid-femoral pulse (VPc-f) was determined by tonometry. Changes in the variables and their interrelation was analysed by repeated data ANOVA, Wilcoxon's test and multiple regression.
ResultsA significant decrease in the VPc-f was observed. There was no association between decreased VPc-f and changes in blood glucose, uric acid, blood pressure or weight.
ConclusionsDapagliflozin, in subjects with DM2, produces a medium to long-term decrease in arterial stiffness.