Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome is the most common glomerular disease in children, but there are still some difficulties in treating childhood steroid-dependent or steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SDNS/SRNS). Rituximab (RTX) might be an effective and safe choice.
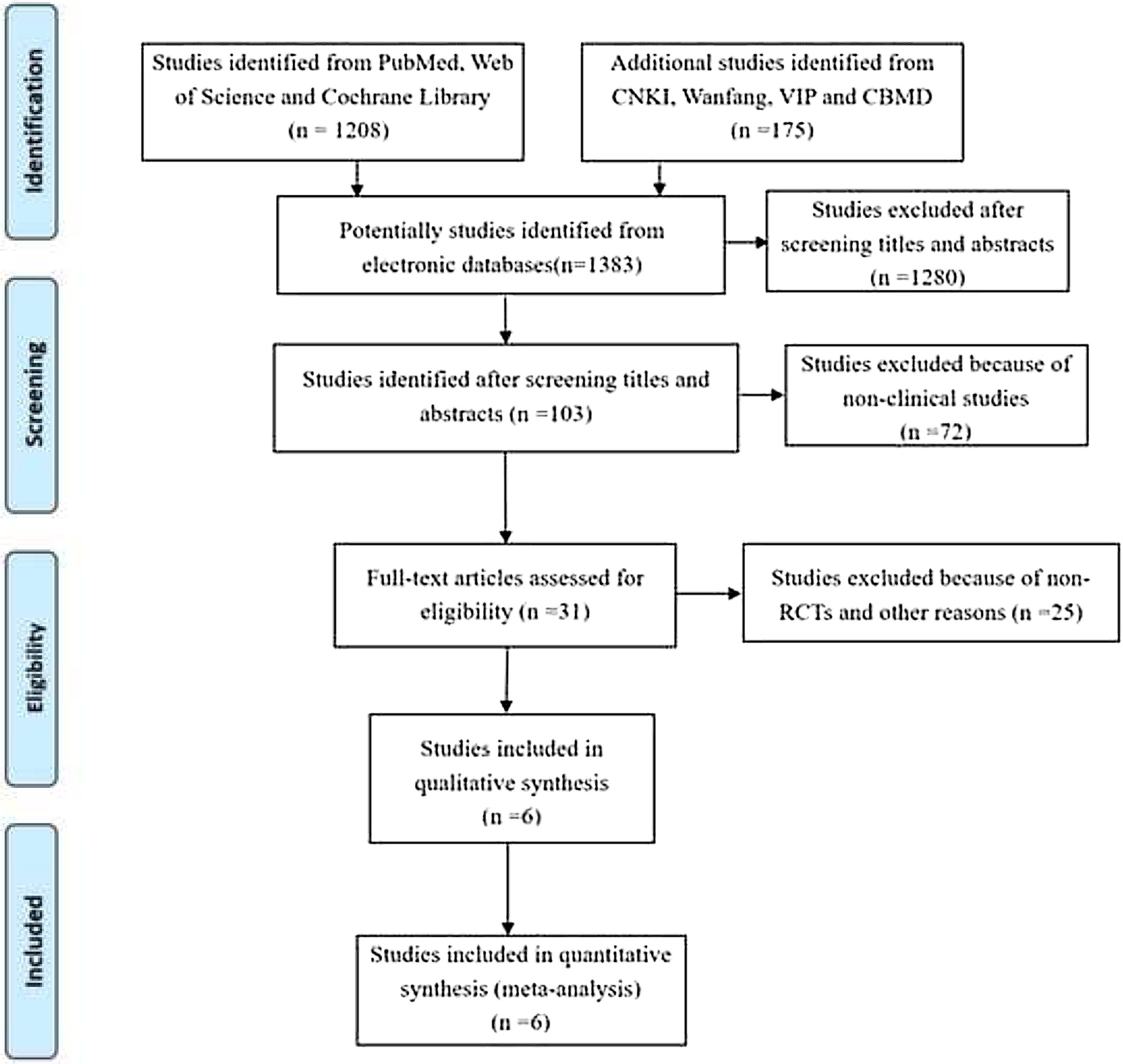
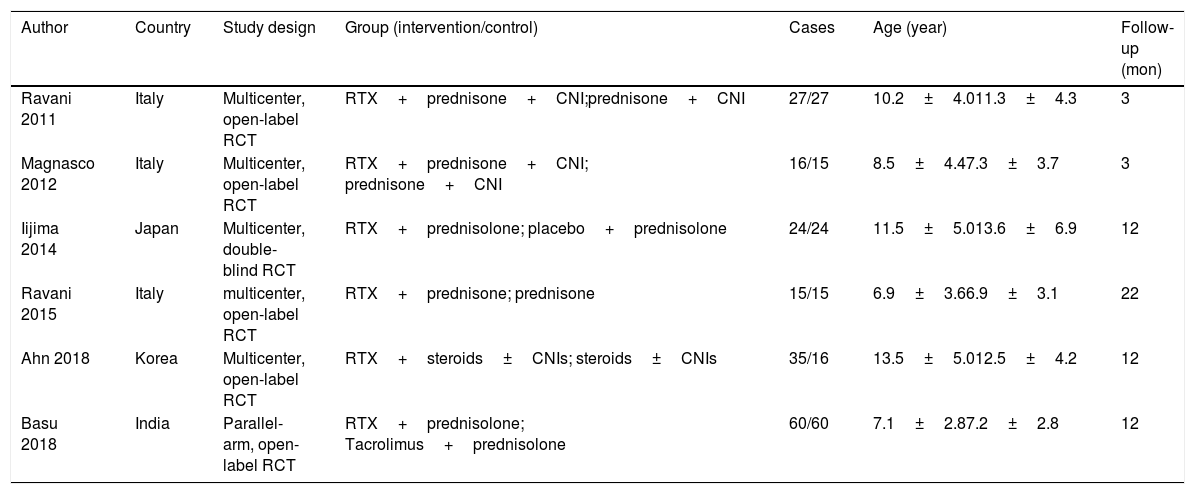
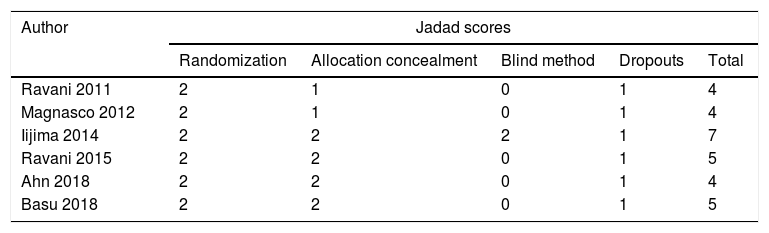
MethodsStudies were searched from PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane library and some Chinese databases up to April 2020. Only randomized controlled trials (RCT) were included.
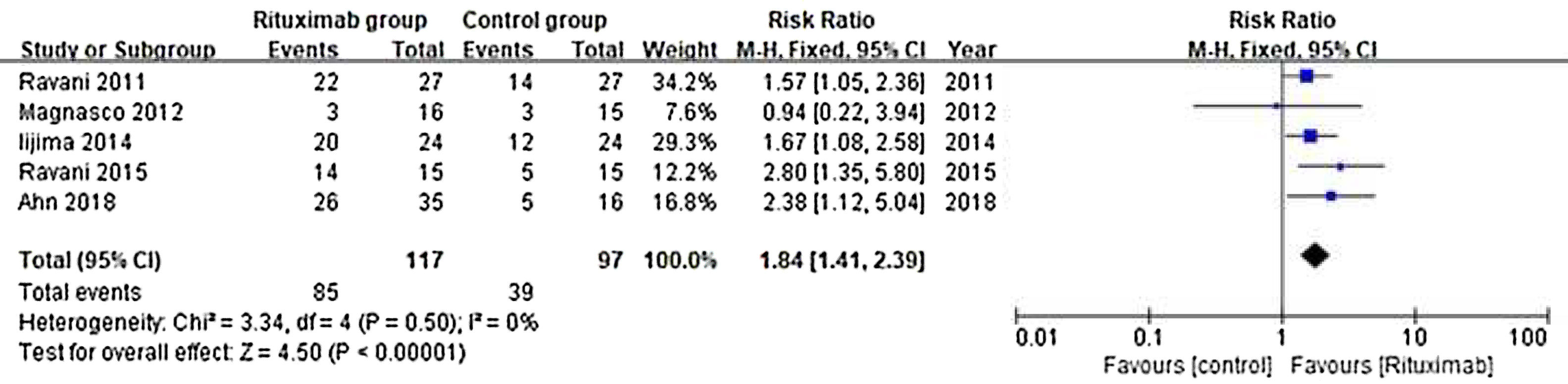
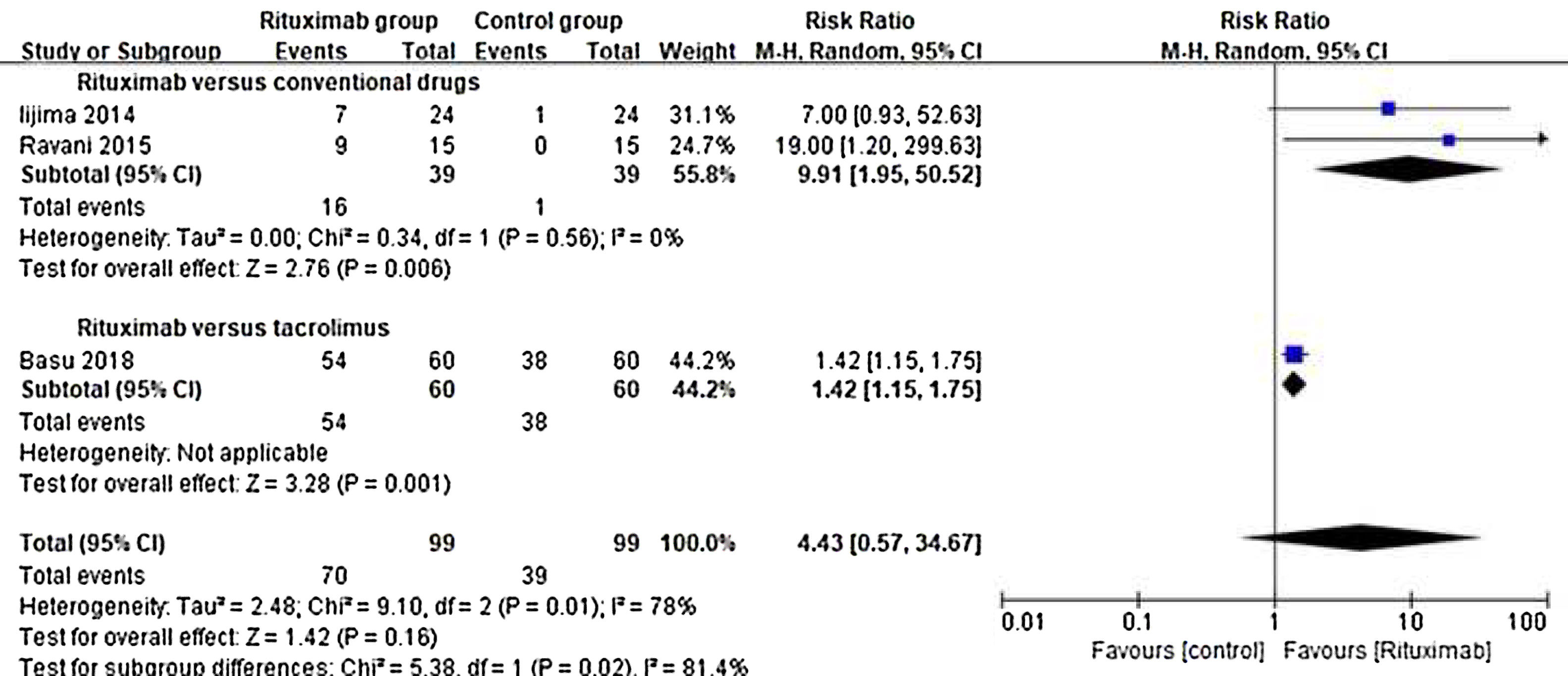
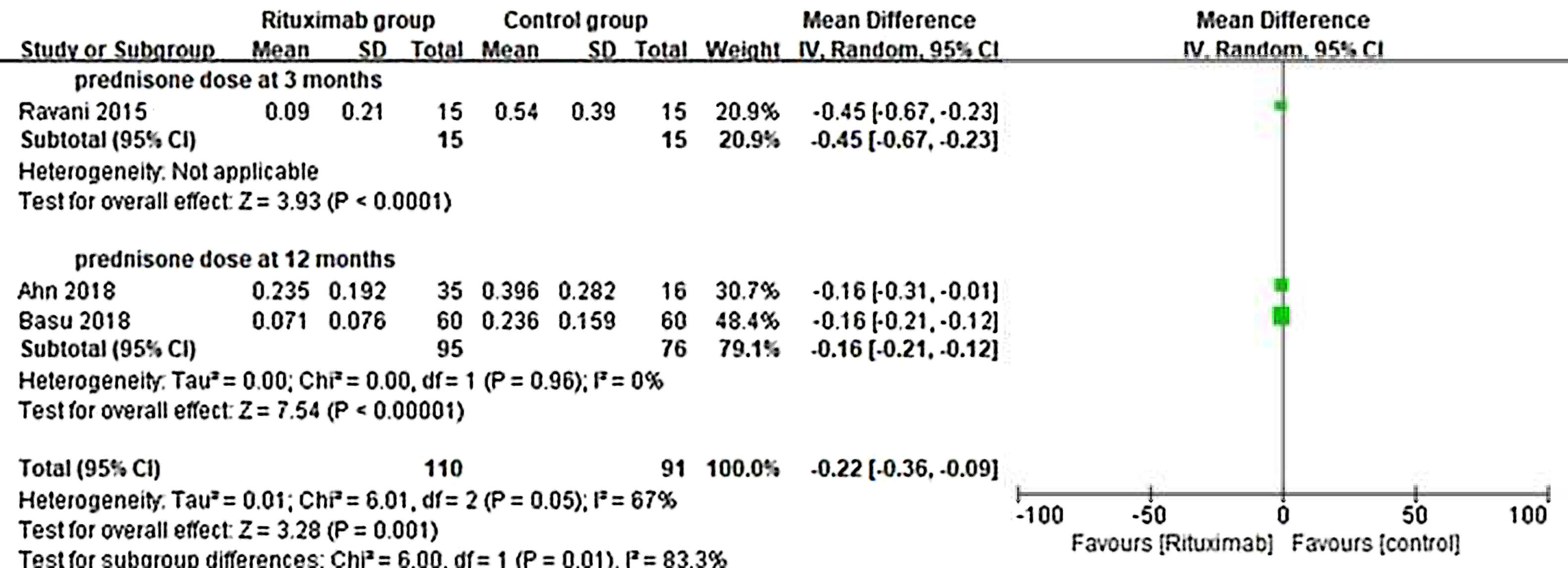
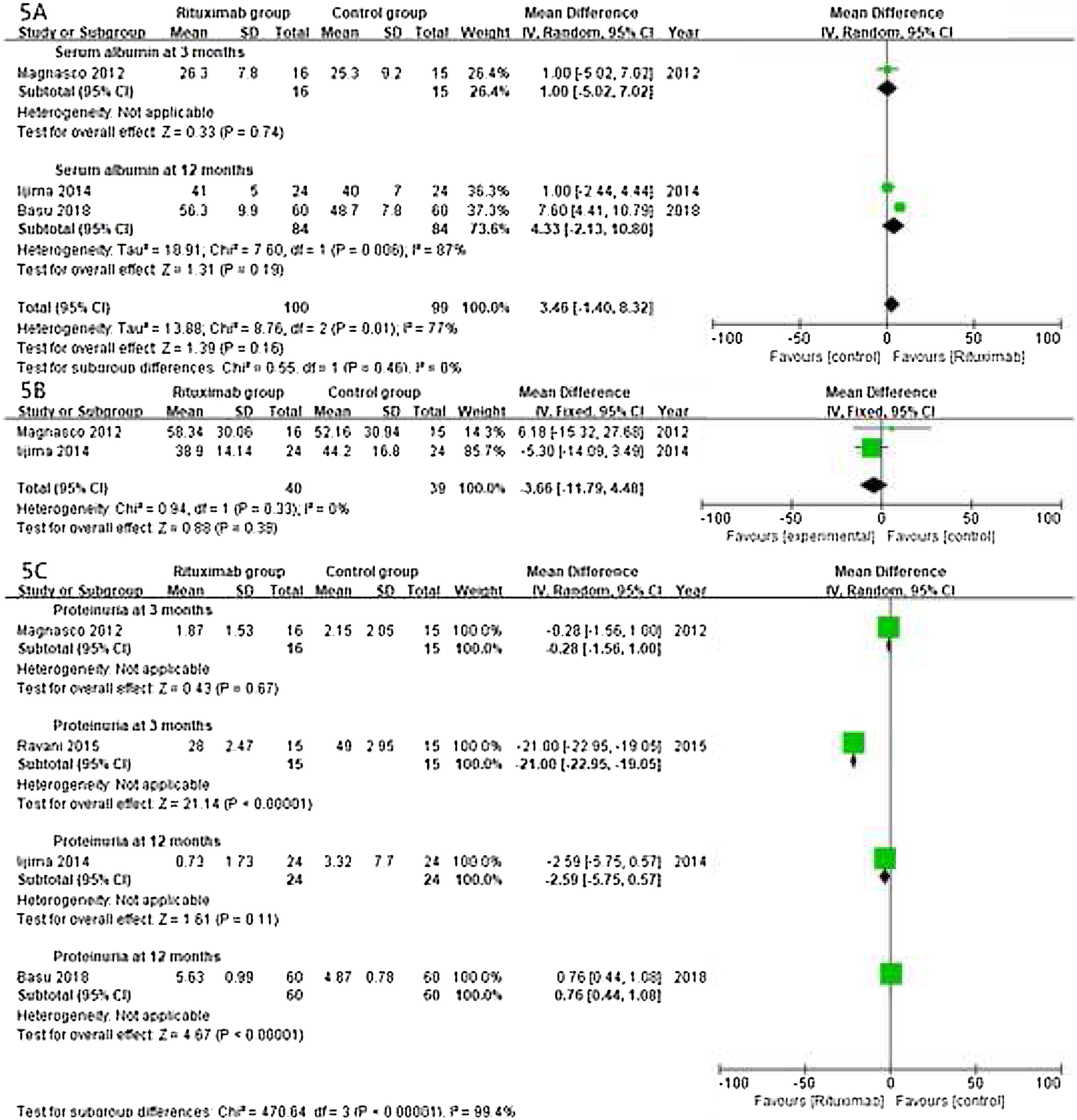
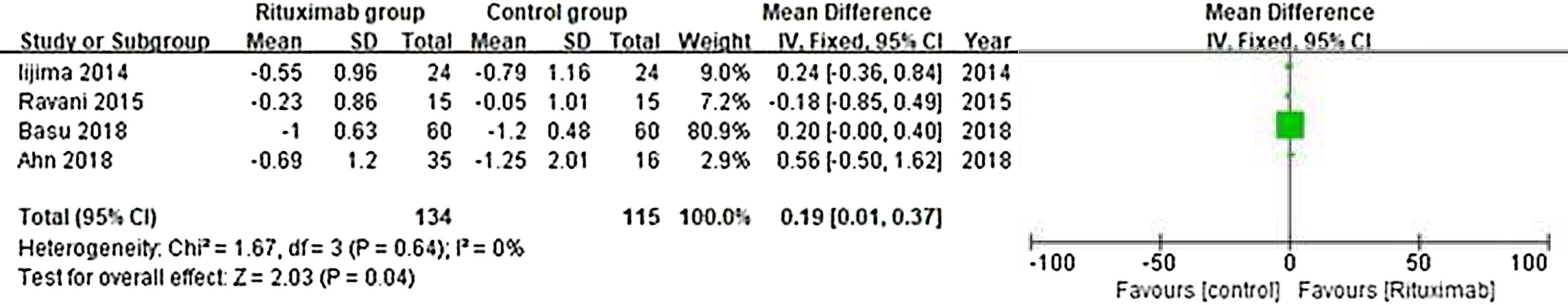
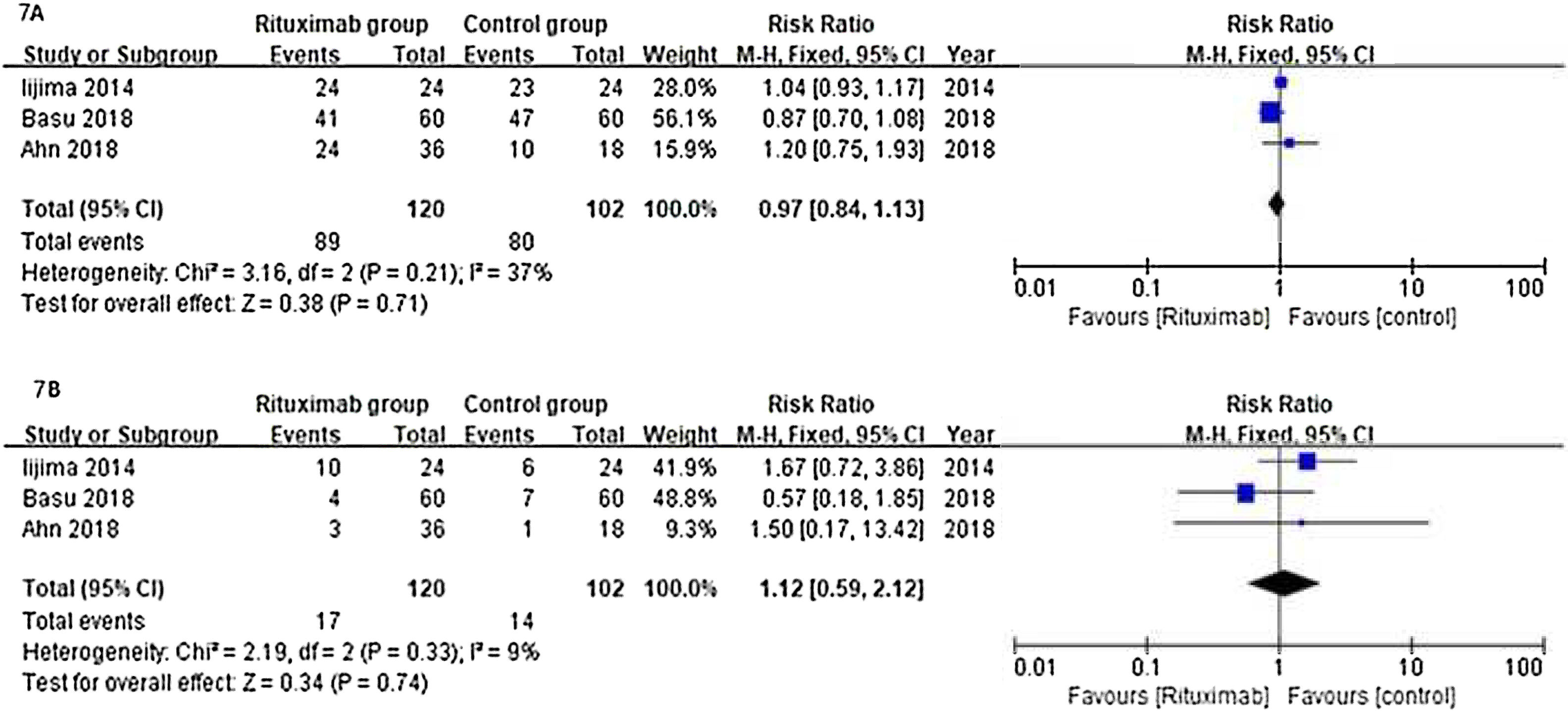
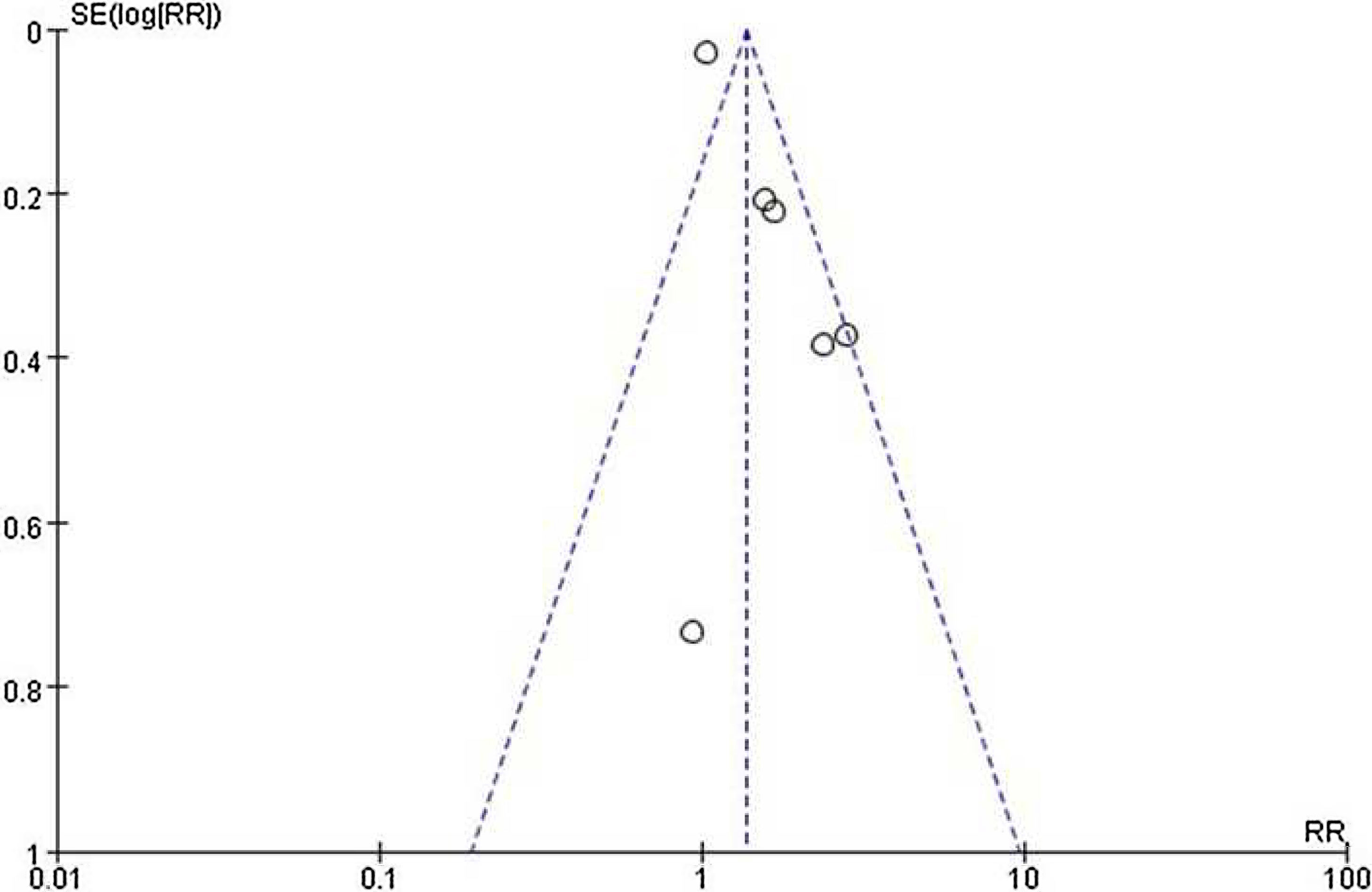
ResultsOf 1383 screened articles, 6 RCTs with 334 participants were included. RTX was better than the control group at improving relapse-free rate in the short term [RR (risk ratio) (95% CI (confidence interval)), 1.84(1.41, 2.39)]. As for long-term, RTX did not show significant improvement [RR (95% CI), 4.43(.57, 34.67)]; but in subgroup analysis, RTX was still better than conventional drugs and tacrolimus [RR (95% CI), 9.91(1.95, 50.52) and 1.42(1.15, 1.75), respectively]. And there was a difference between the two groups of prednisolone dose after treatment [MD (mean difference) (95% CI), −.22(−.36, −.09) mg/kg/d)]. However, RTX did not significantly improve serum albumin and creatinine [MD (95% CI), 3.46(−1.40, 8.32)g/L and −3.66(−11.79, 4.48)μmol/L, respectively]. No significant differences between the RTX and the control group were found in total adverse events (AEs) or serious AEs.
ConclusionChildhood SDNS/SRNS patients appear to benefit from RTX in relapse-free rate and dose of prednisolone use. Also, RTX did not significantly increase the incidence of AEs. But RTX did not show improvements in biological indicators, more studies are required to explain the effect of RTX.
El síndrome nefrótico idiopático es la enfermedad glomerular más común en niños, pero aún existen algunas dificultades para tratar el síndrome nefrótico infantil dependiente de esteroides o resistente a esteroides. El rituximab (RTX) podría ser una opción efectiva y segura.
MétodosSe realizaron búsquedas en los estudios de PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library y algunas bases de datos chinas hasta abril de 2020. Sólo se incluyó ensayo controlado aleatorio (ECA).
ResultadosDe 1.383 artículos seleccionados, se incluyeron 6 ECA con 334 participantes. RTX fue mejor que el grupo control para mejorar la tasa libre de recaídas a corto plazo [Relación de riesgo (IC95%), 1,84 (1,41, 2,39)]. En cuanto a largo plazo, RTX no mostró una mejora significativa [4,43 (0,57, 34,67)]; pero en el análisis de subgrupos, RTX fue aún mejor que los fármacos convencionales y el tacrolimus [9,91 (1,95, 50,52) y 1,42 (1,15, 1,75), respectivamente]. Se encontró una diferencia entre los dos grupos de dosis de prednisolona después del tratamiento [Diferencia media (IC95%), -0,22 (-0,36, -0,09) mg/kg/d)]. Sin embargo, RTX no mejoró significativamente la albúmina sérica y la creatinina [3,46 (-1,40, 8,32) g/L y -3,66 (-11,79, 4,48) μmol/L, respectivamente]. No se encontraron diferencias significativas entre RTX y el grupo de control en los eventos adversos totales (EA) o los EA graves.
ConclusiónLos niños con síndrome nefrótico refractario parecen beneficiarse de RTX en la tasa libre de recaídas y la dosis de uso de prednisolona. Además, RTX no aumentó significativamente la incidencia de EA. Pero RTX no mostró mejoras en los indicadores biológicos, se requieren más estudios para explicar el efecto de RTX.