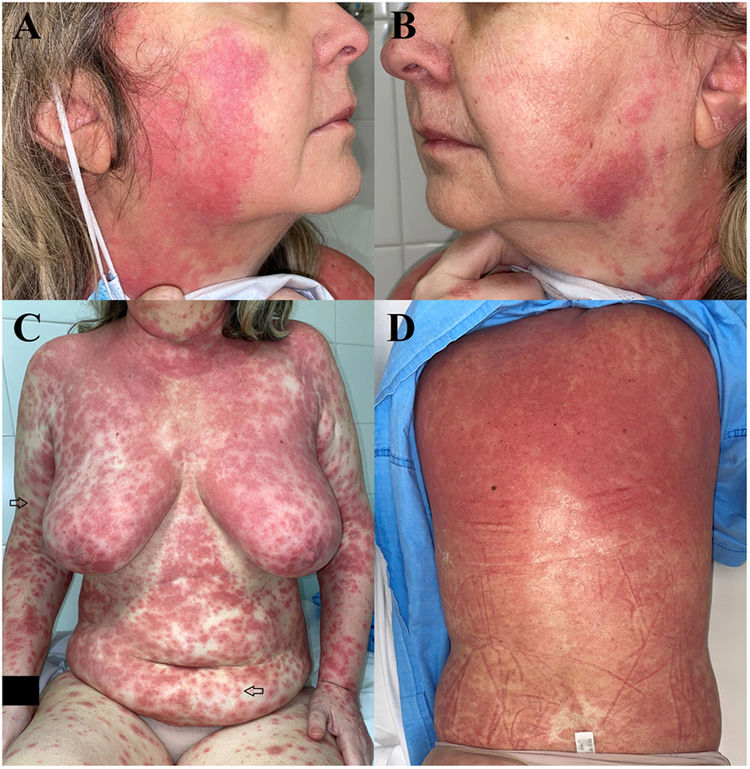
A 55-year-old woman who presented with a 6-day history of pruritic skin rash consisting of erythematous targetoid macules with a tendency to converge in trunk and upper limbs, without mucosal involvement (Fig. 1). She had previously started treatment with hydroxychloroquine, 12 days before the appearance of skin lesions, secondary to bilateral interstitial pneumonia with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR.
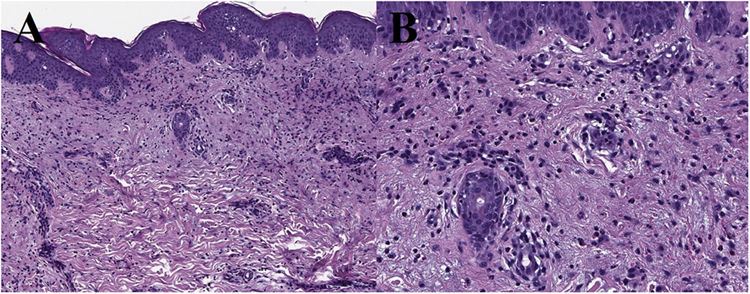
Titres for other common causes of erythema multiforme, including herpes simplex virus (HSV) and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, were negative. Skin biopsy showed interface dermatitis and eosinophil infiltration, findings consistent with an allergic drug reaction (Fig. 2).
Coinciding with the improvement in lab results and respiratory symptoms, it was decided to discontinue treatment with hydroxychloroquine.
Erythema multiforme is an immune-mediated reaction that affects the skin and, occasionally, the mucosa. Infections, especially from HSV or Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and some drugs constitute the main etiological agents. When the suspicion is drug-related, the withdrawal of the drug is essential, maintaining it only when its use is vital for the patient and in the absence of therapeutic alternatives.
Severe skin reactions to hydroxychloroquine are rare, however, because of its widespread use as a treatment for COVID-19, early detection is important to avoid future complications.
FundingNo assistance or financial funding has been received from public or private entities for the preparation of this article.
Please cite this article as: Monte-Serrano J, Cruañes-Monferrer J, García-García M, García-Gil MF. Eritema multiforme inducido por hidroxicloroquina en paciente con COVID-19. Med Clin (Barc). 2020;155:231.