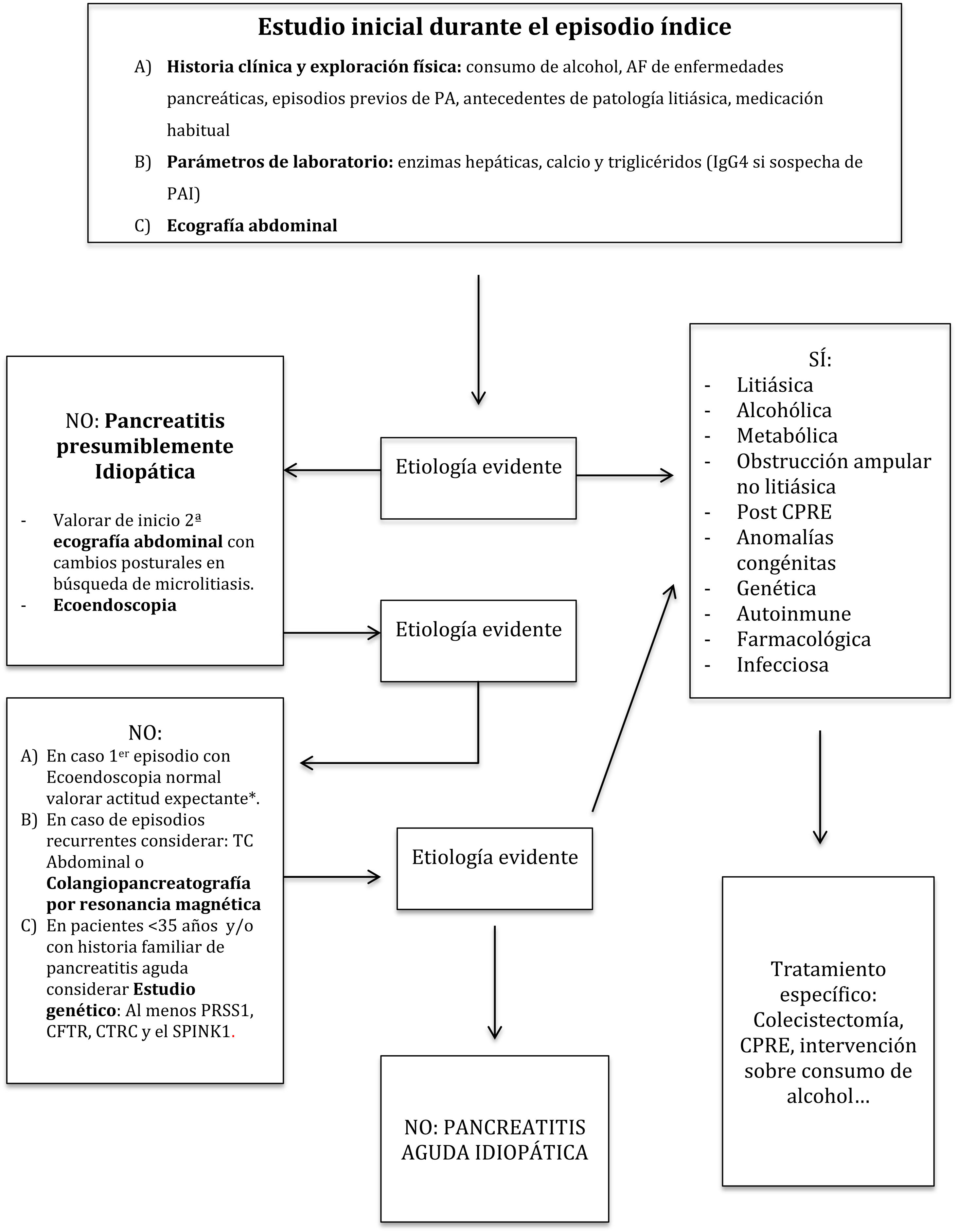
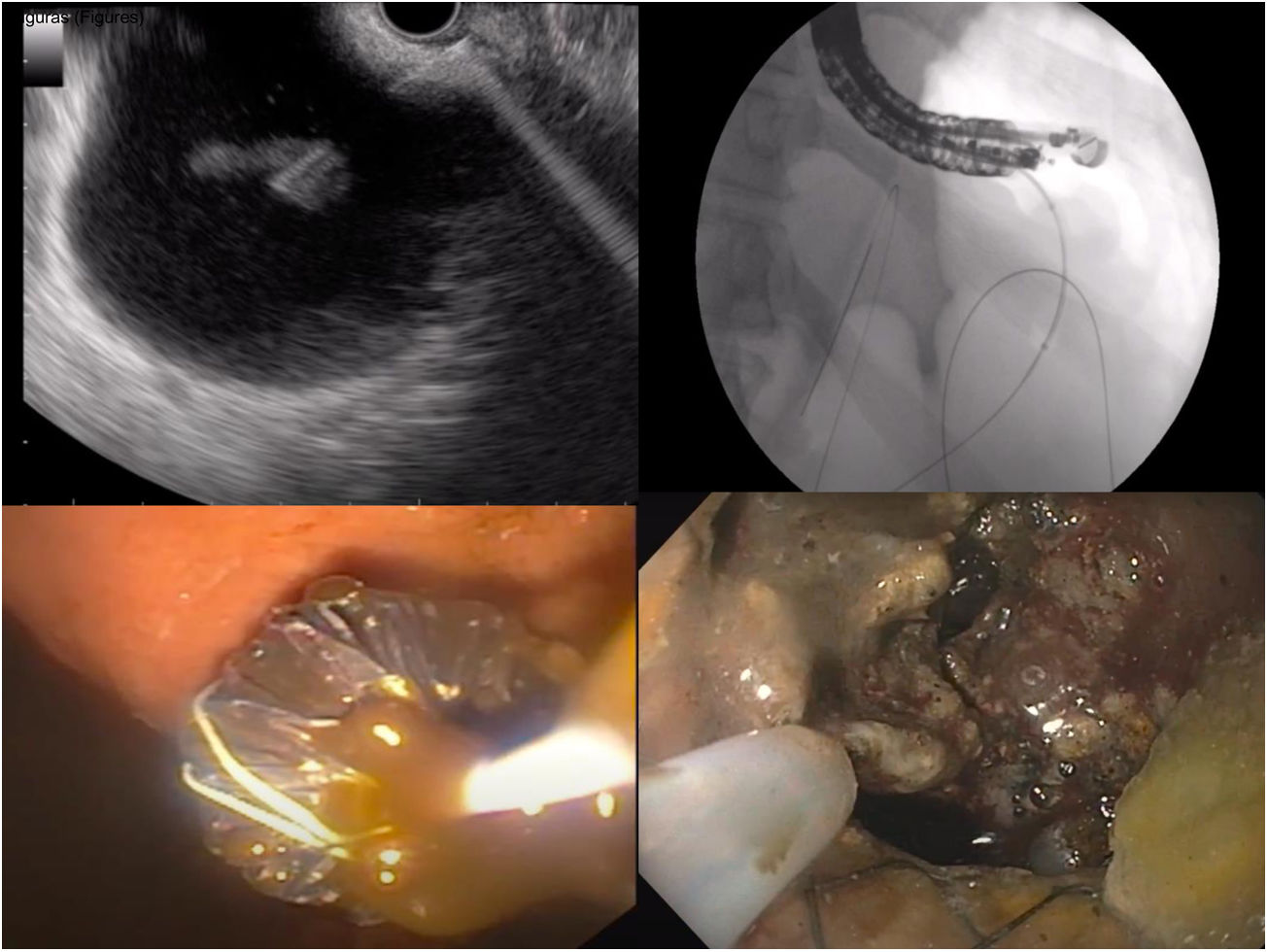
La pancreatitis aguda continúa siendo una de las patologías más relevantes en los servicios de aparato digestivo, destacando la litiasis y el alcohol como las causas principales. Presenta unos criterios diagnósticos bien establecidos y unas indicaciones específicas para la realización de pruebas de imagen, considerando de gran utilidad la ecografía abdominal en el estudio etiológico y la tomografía computarizada abdominal para la estratificación del riesgo y estudio de complicaciones locales. Una fluidoterapia basada en metas, el uso precoz de la nutrición por vía oral y una adecuada analgesia constituyen los pilares básicos del manejo inicial. La antibioterapia está indicada en casos de necrosis infectada o infecciones extrapancreáticas pero no ha demostrado beneficio como profilaxis en pancreatitis aguda necrotizante. En la última década se han desarrollado abordajes mínimamente invasivos que han cambiado radicalmente el tratamiento de las necrosis encapsuladas mejorando la tasa de complicaciones, estancia hospitalaria y calidad de vida de los pacientes.
Acute pancreatitis is nowadays one of the most common diseases among gastroenterology disorders, being gallstones and alcohol the main etiologies. Diagnostic criteria and indications of different imaging techniques are well defined, so that abdominal ultrasound is useful for etiological diagnosis whereas computarized tomography is better for risk stratification and local complications assessment. Goal directed fludtherapy, early starting of oral feeding and pain management are the mainstay of early treatment in acute pancreatitis. Antibiotics are useful when infected necrosis or extra pancreatic infections are documented or suspected but no as prophylaxis in sterile necrotizing pancreatitis. Minimally invasive approaches have emerged in the last decade for walled off necrosis management, improving complication rates, quality of life and length of hospital stay when compared with open surgery.